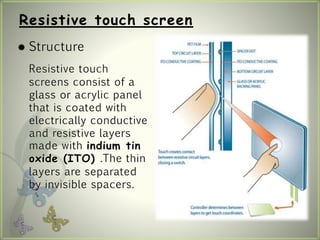
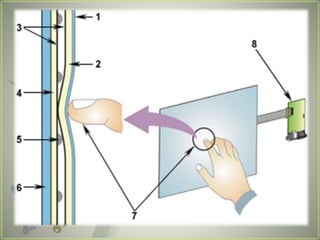
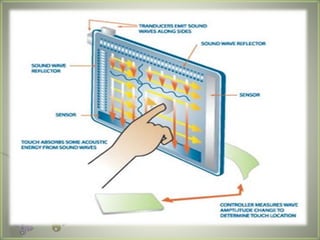
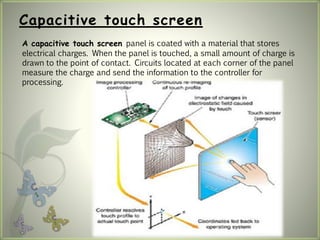
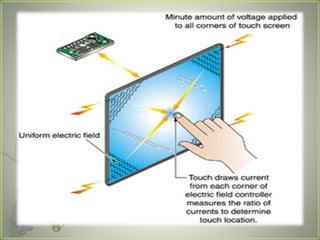
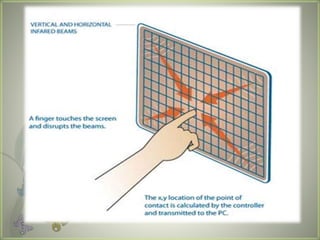
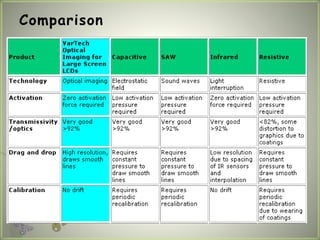
A touch screen is an electronic display that can detect touch input. It allows direct interaction with what is displayed without needing an intermediate pointing device. The first touch screen was developed in the 1960s for air traffic control. Touch screens work by using touch sensors and controllers to detect touch locations and relay that information to software. Common touch screen technologies include resistive, surface acoustic wave, capacitive, infrared, and optical imaging. Touch screens are now widely used in devices like phones, tablets, and public information kiosks.