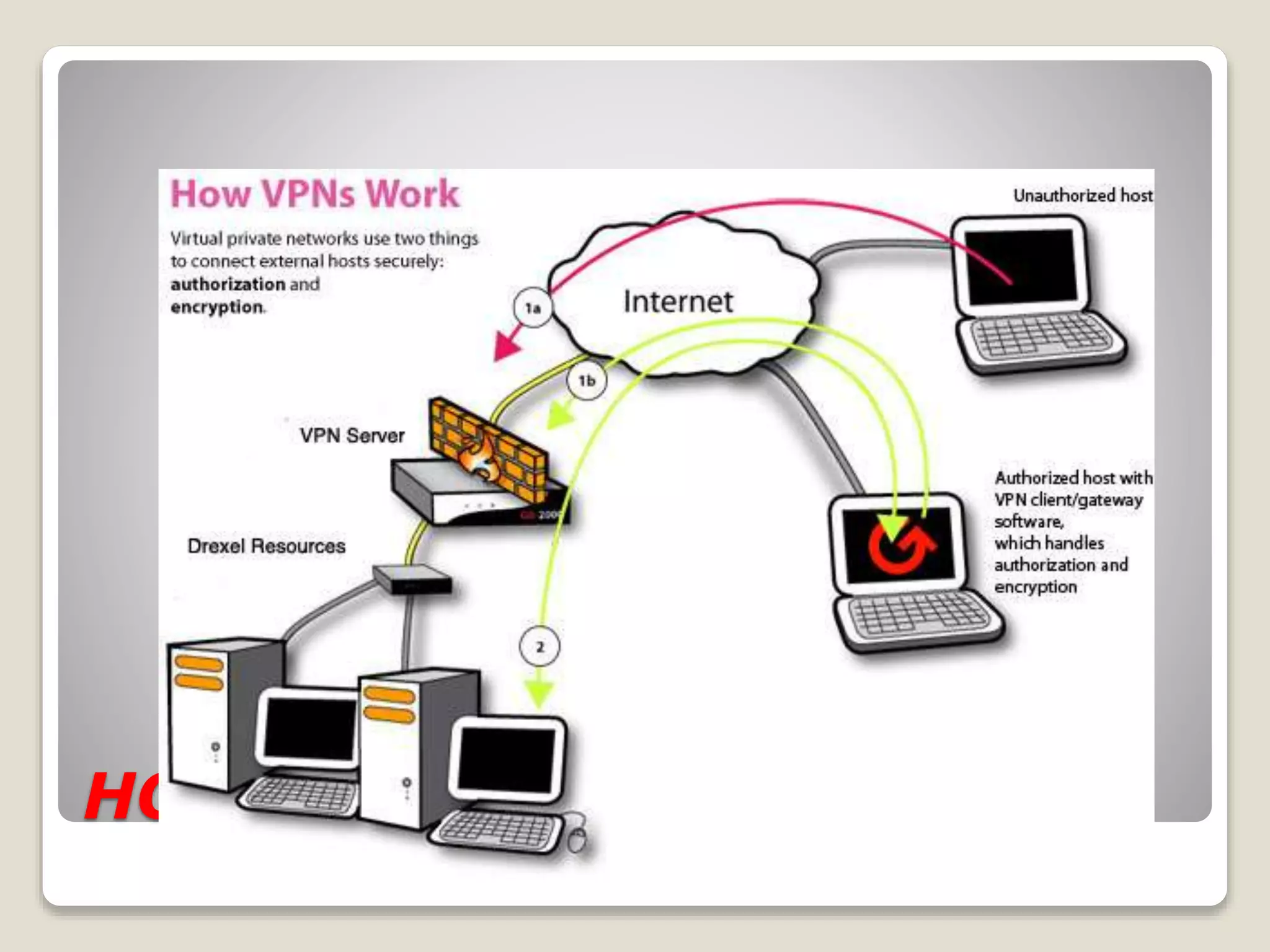
Virtual private networks (VPNs) allow for secure data transmission over public networks like the Internet. VPNs create virtual tunnels between devices to securely transmit encrypted data. There are three main types of VPNs: remote-access VPNs for remote users, intranet-based site-to-site VPNs to connect locations within a company, and extranet-based site-to-site VPNs to connect companies. VPNs use protocols like IPsec and SSL to encrypt data and tunneling protocols to transmit data securely between devices.