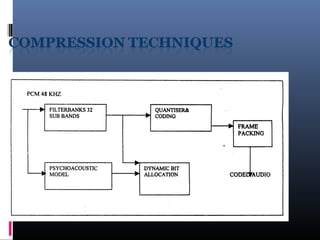
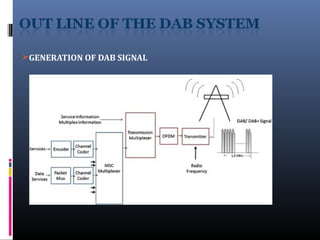
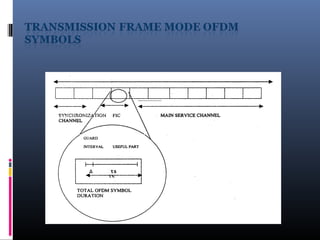
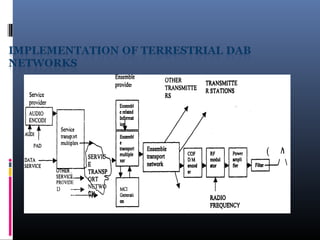
Digital audio broadcasting (DAB) provides CD-quality sound, many station choices, and interference-free reception. It offers advantages over analog FM like high quality audio, error correction, and reduced multipath interference. DAB uses MPEG audio compression and OFDM modulation to transmit multiple signals over a single frequency band. While DAB coverage is still limited compared to FM in many areas, it provides better sound quality and has the potential to become the future of radio broadcasting worldwide as more countries adopt the technology.