Embed presentation
Downloaded 58 times


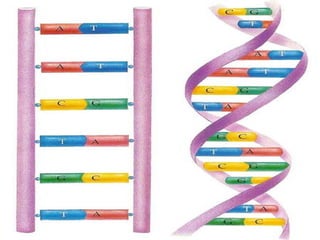

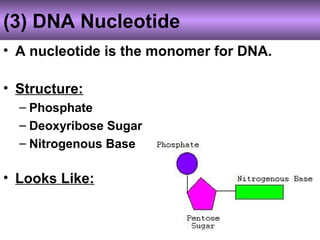

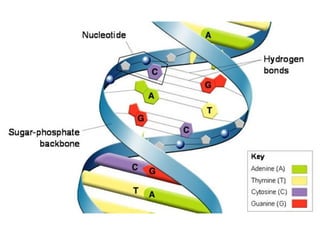
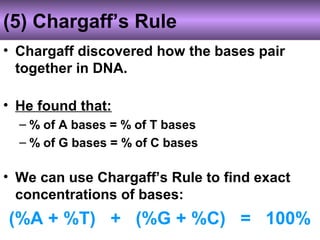
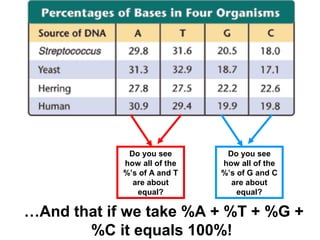


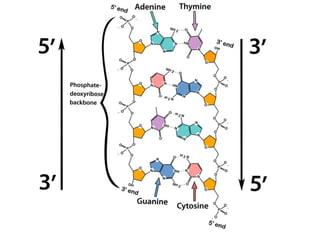
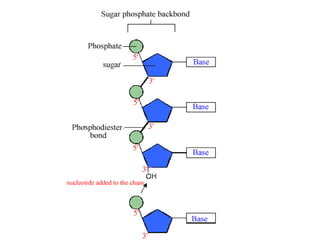
DNA stores genetic instructions in the form of a code made up of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). DNA has a double-stranded helical structure, with the strands bonded together via complementary base pairing between A and T and between G and C. According to Chargaff's rule, the percentage of A bases is always equal to the percentage of T bases, and the percentage of G bases is always equal to the percentage of C bases within a DNA sample. The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions of each other (anti-parallel) and form a double helix.















