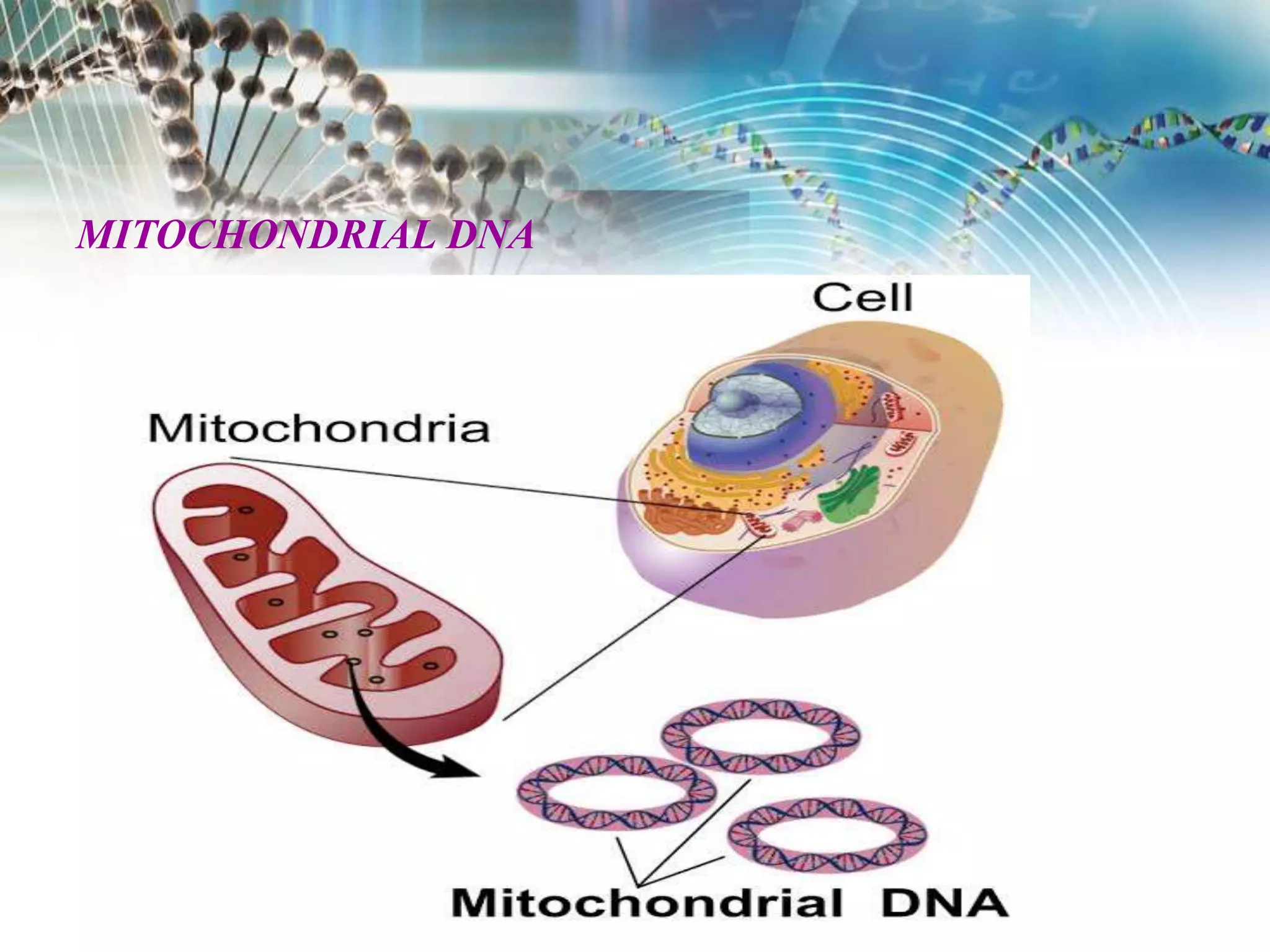
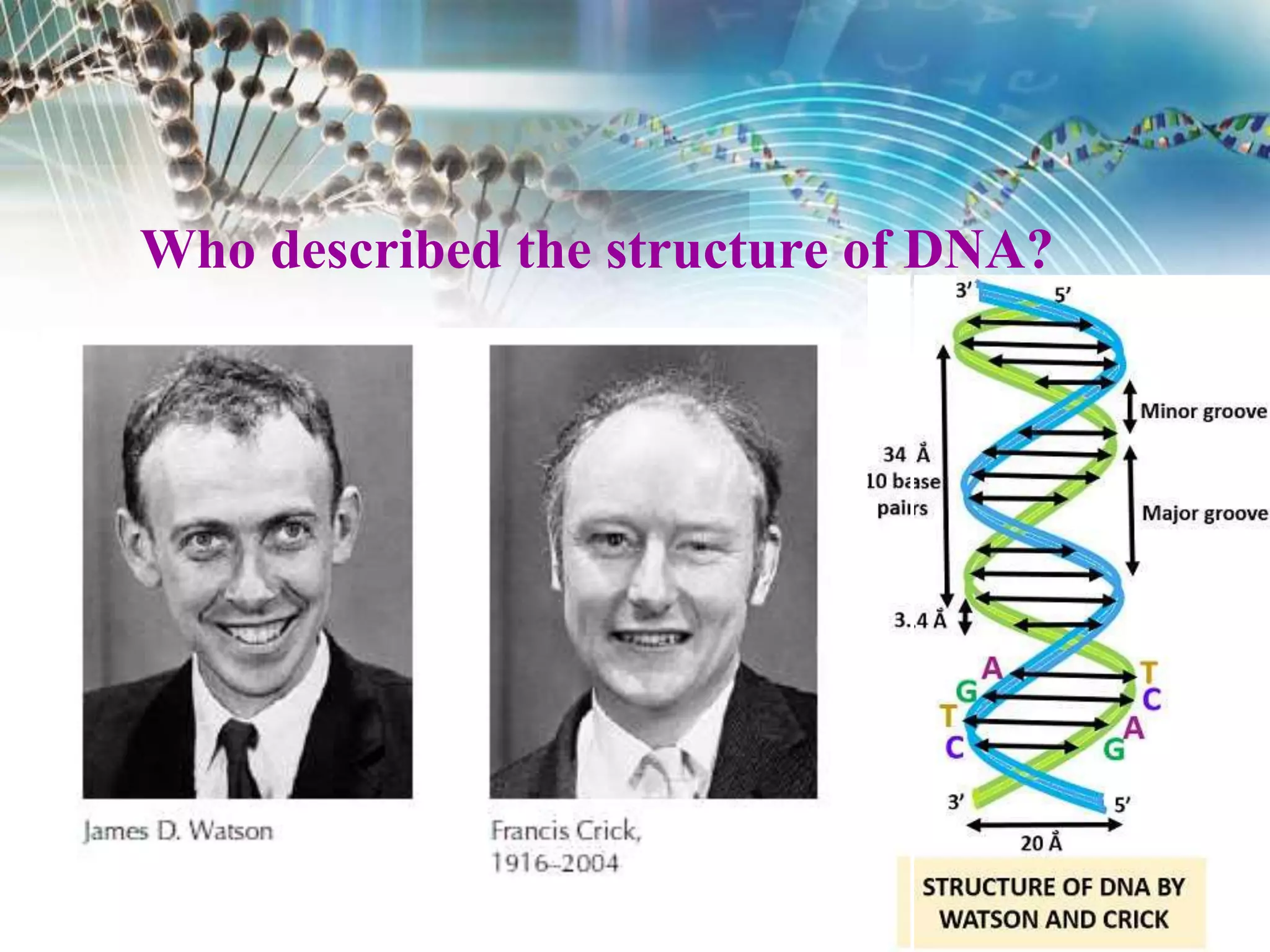
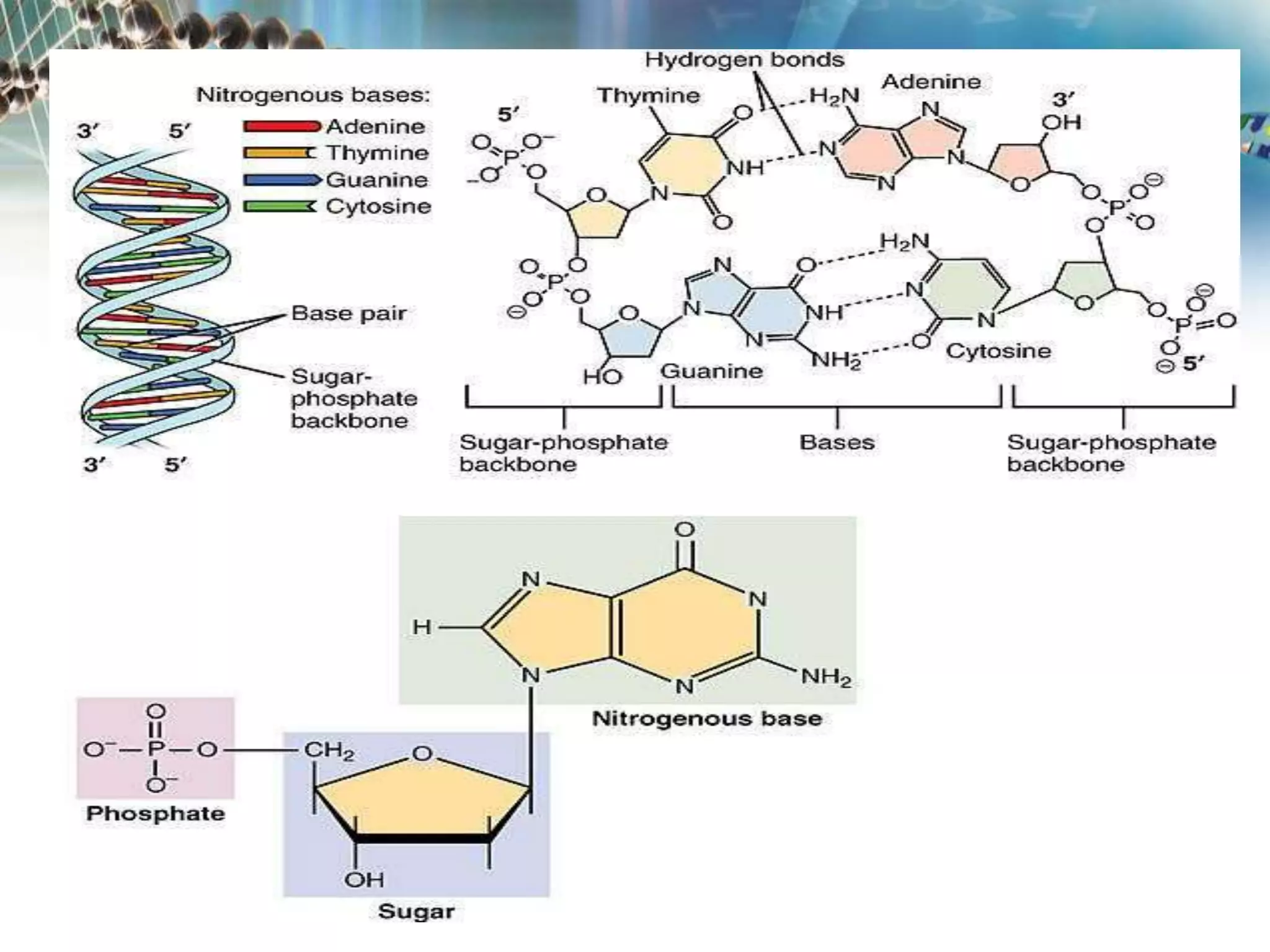
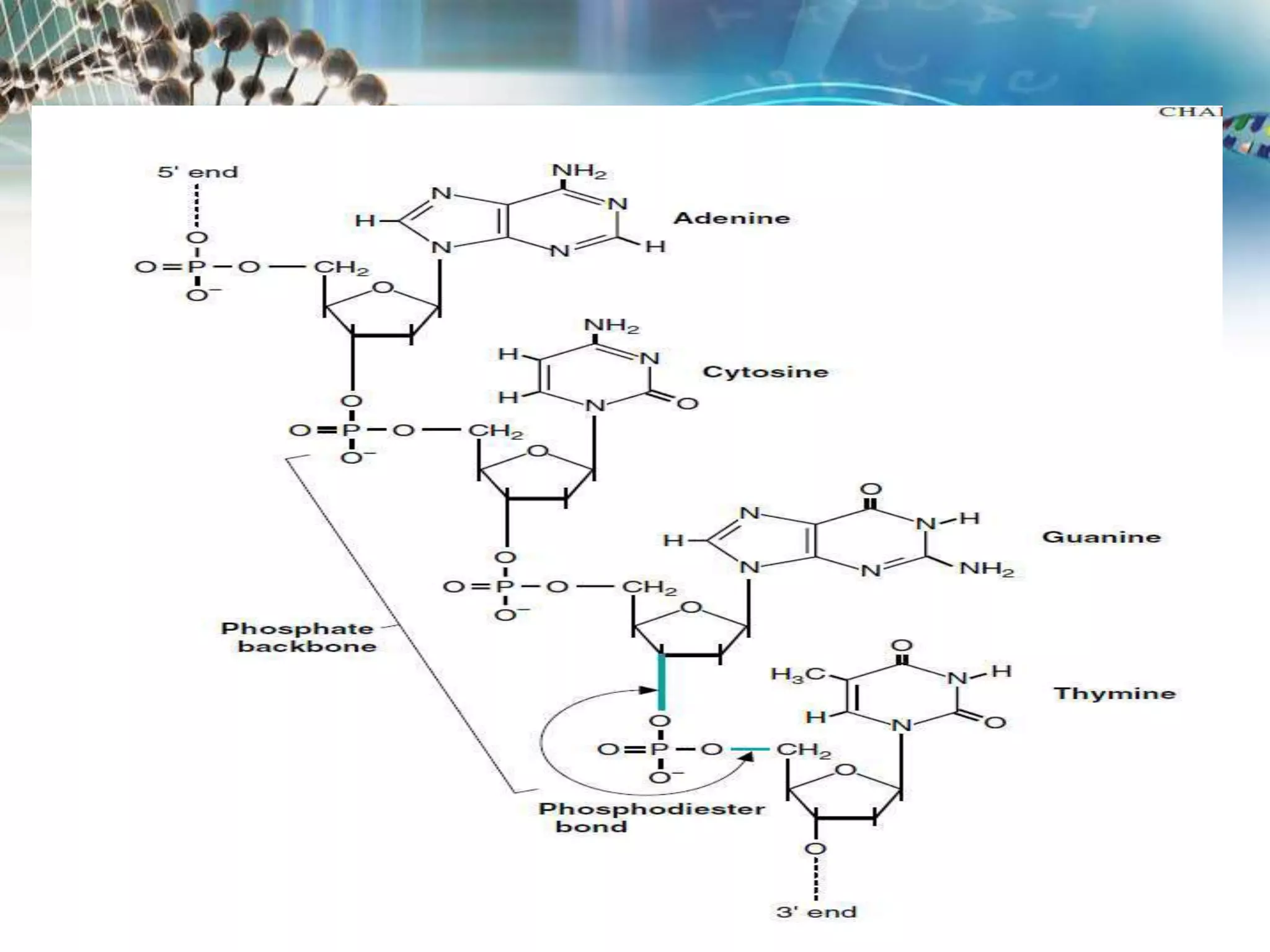
Watson and Crick discovered that DNA has a double helix structure, with two polynucleotide chains coiled around each other. They described DNA as a twisted ladder, with the bases on the inside of the helix and the sugar-phosphate backbones on the outside. The four bases - adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine - form hydrogen bonds between the chains in a specific pairing: adenine binds to thymine, and cytosine binds to guanine. This double helix structure allows DNA to efficiently store and replicate genetic information in cells.