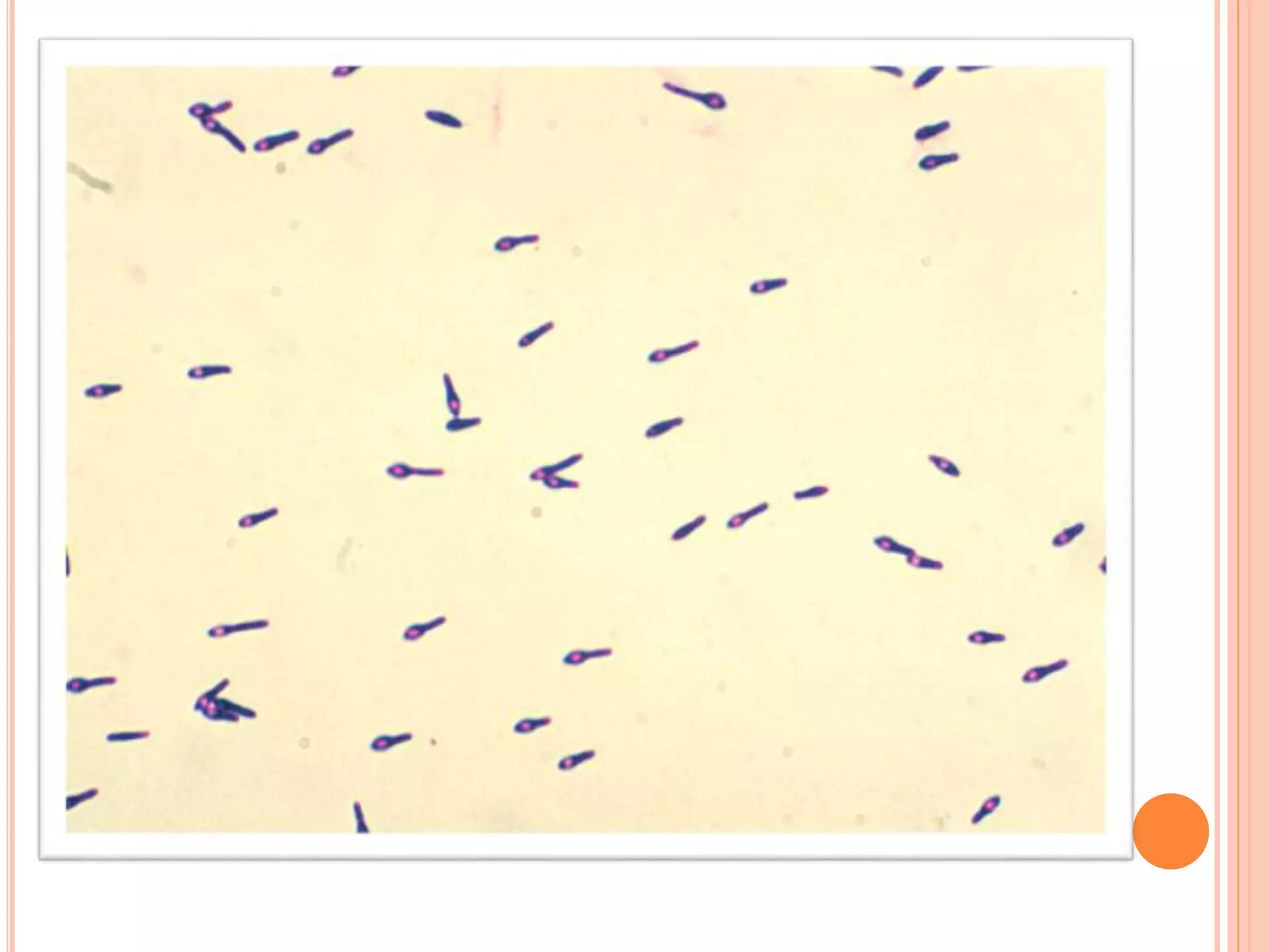
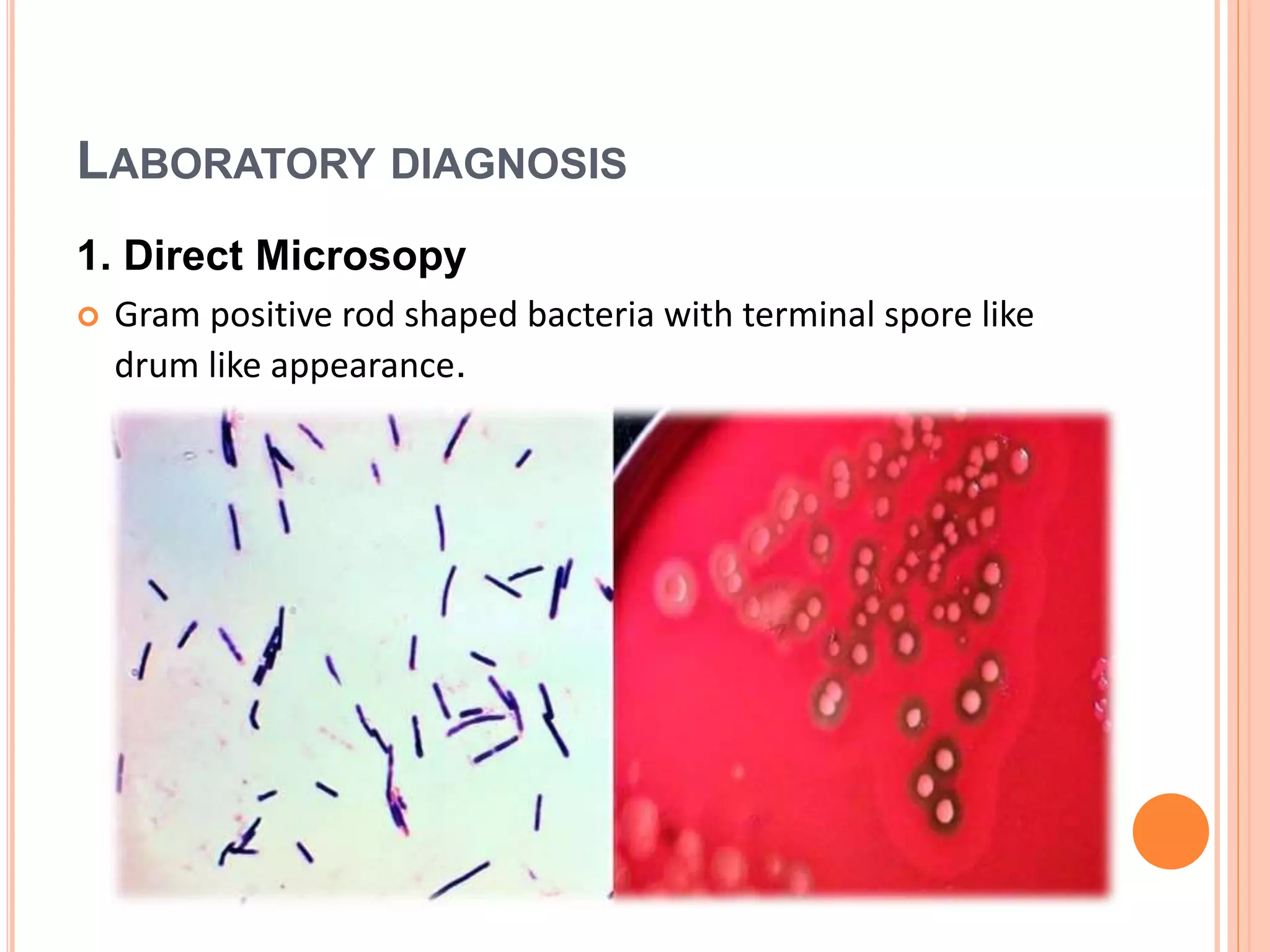
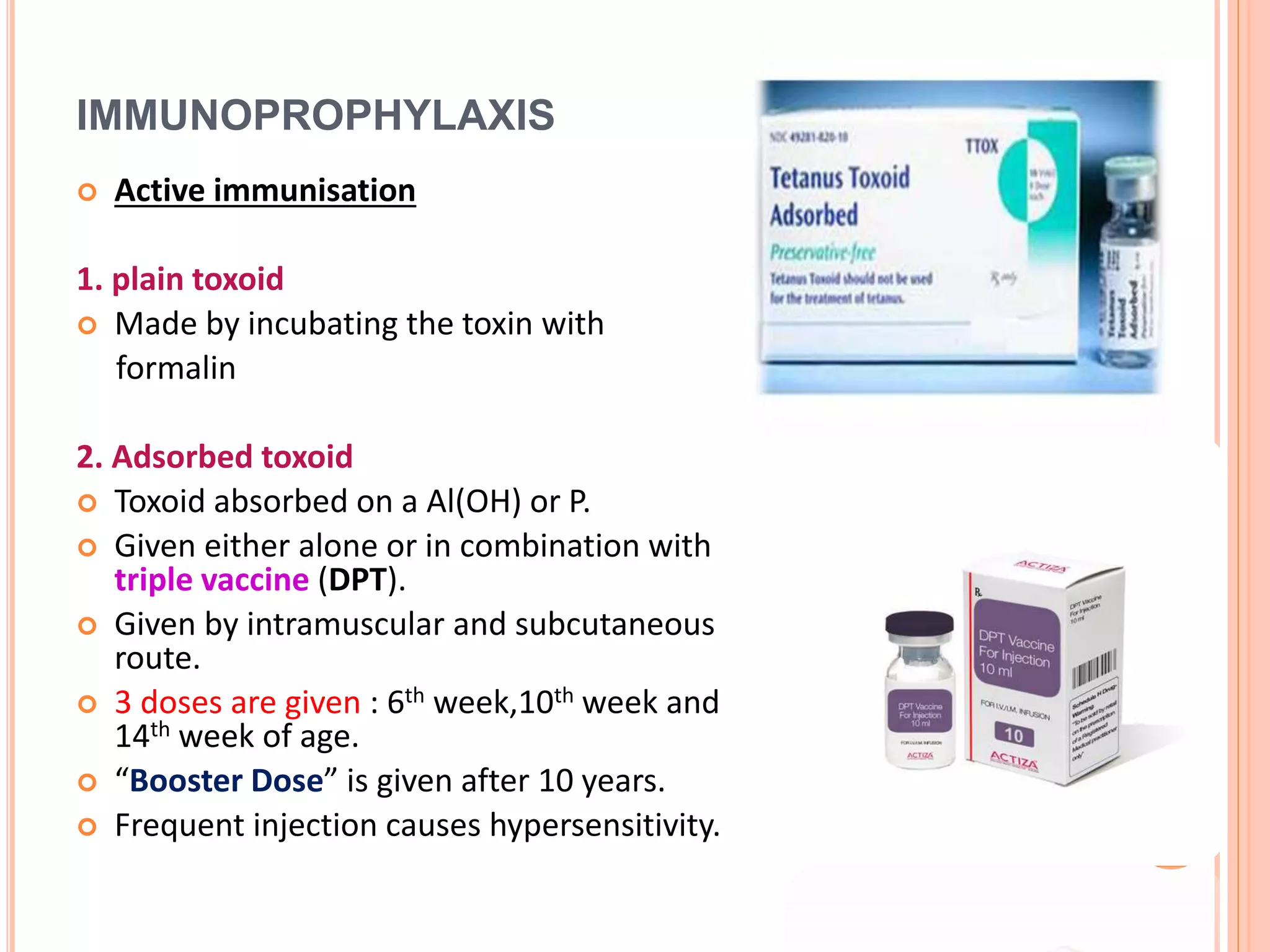
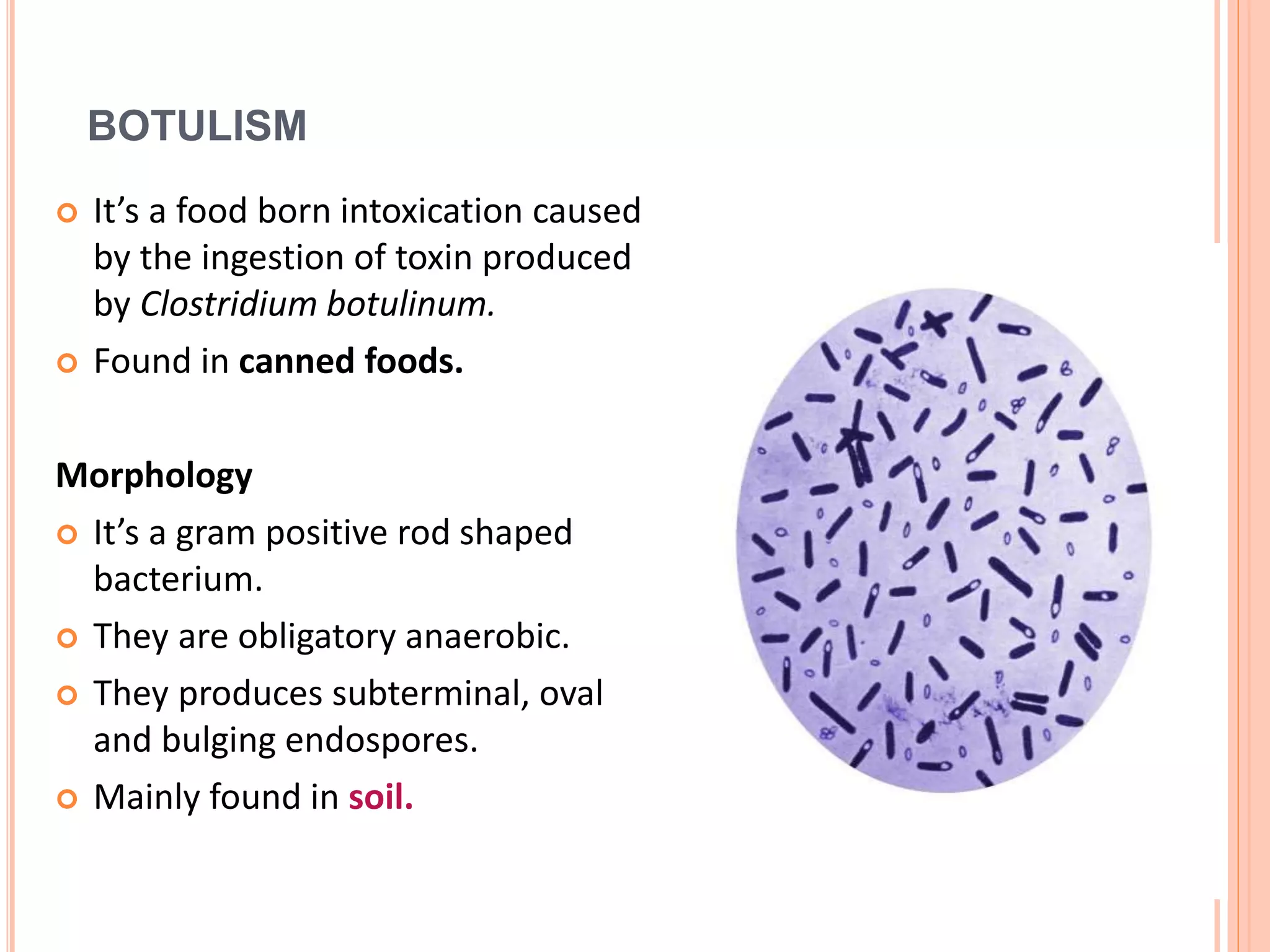
Tetanus and botulism are acute diseases caused by Clostridium tetani and Clostridium botulinum respectively. C. tetani produces a neurotoxin called tetanospasmin which causes muscle rigidity and spasms. It enters through wounds in the skin. C. botulinum produces a toxin that blocks acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis. The bacteria forms spores that allow it to survive in soils and foods. Proper wound care and vaccination can prevent tetanus, while safe food handling prevents botulism.