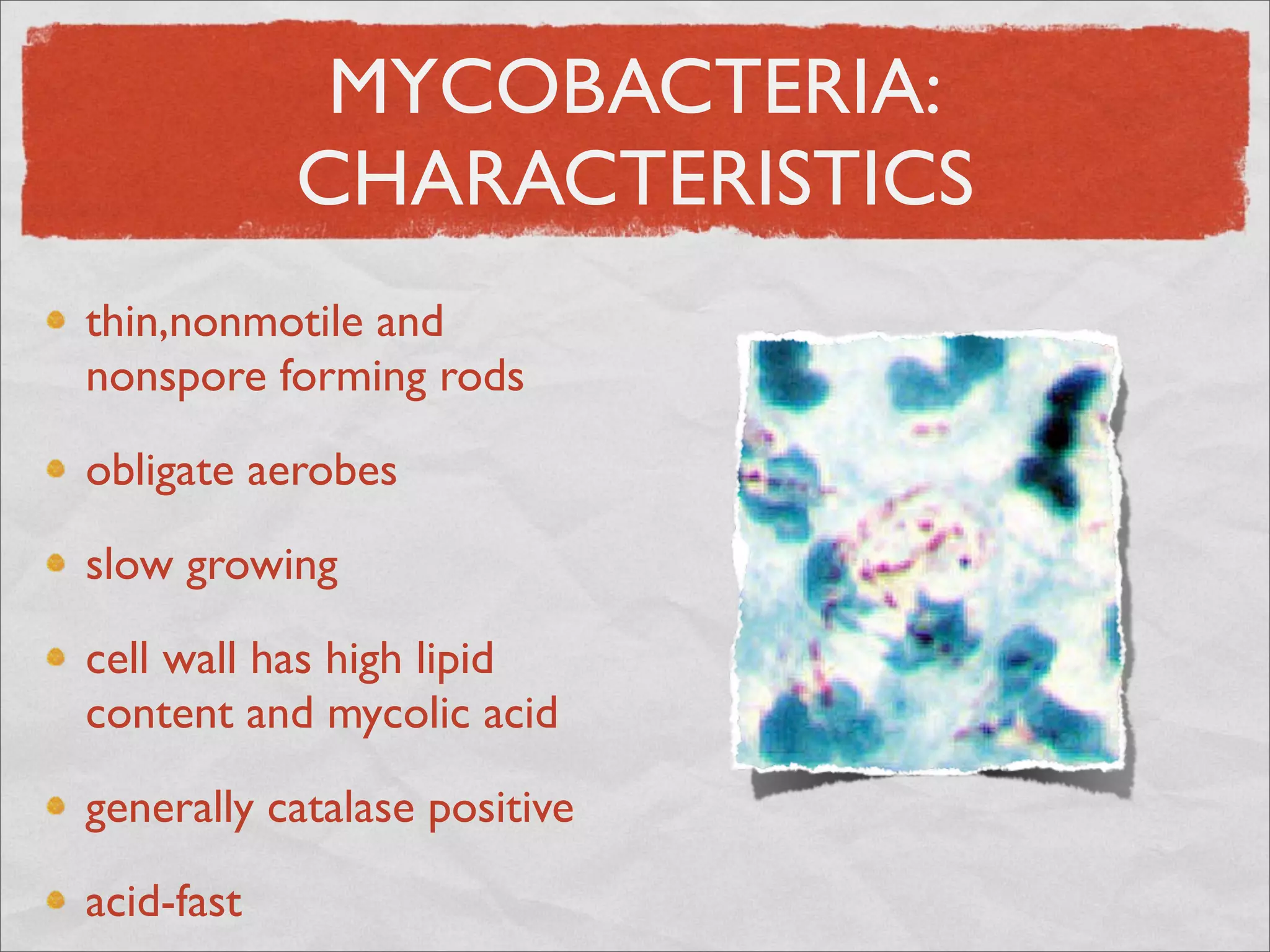
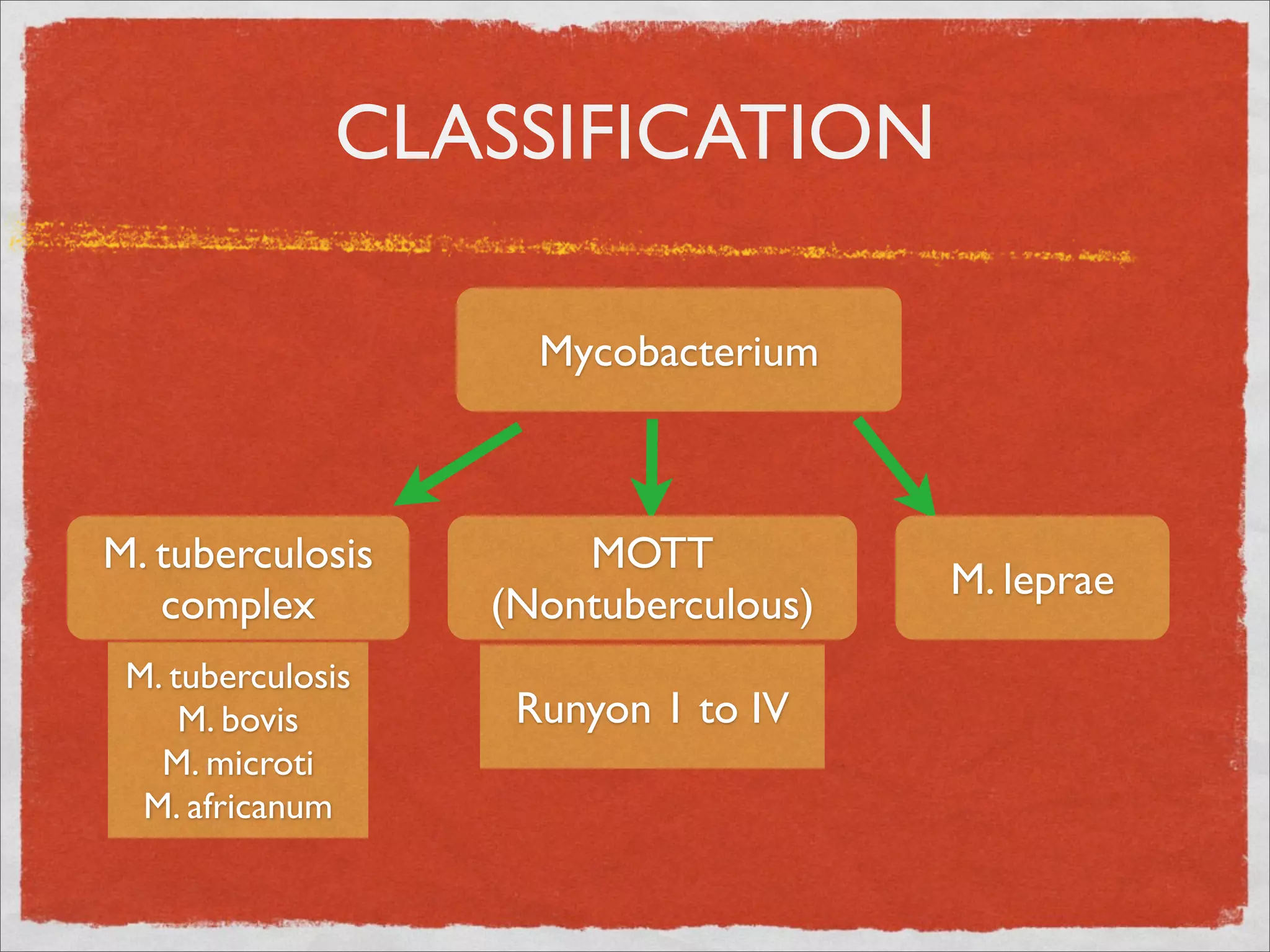
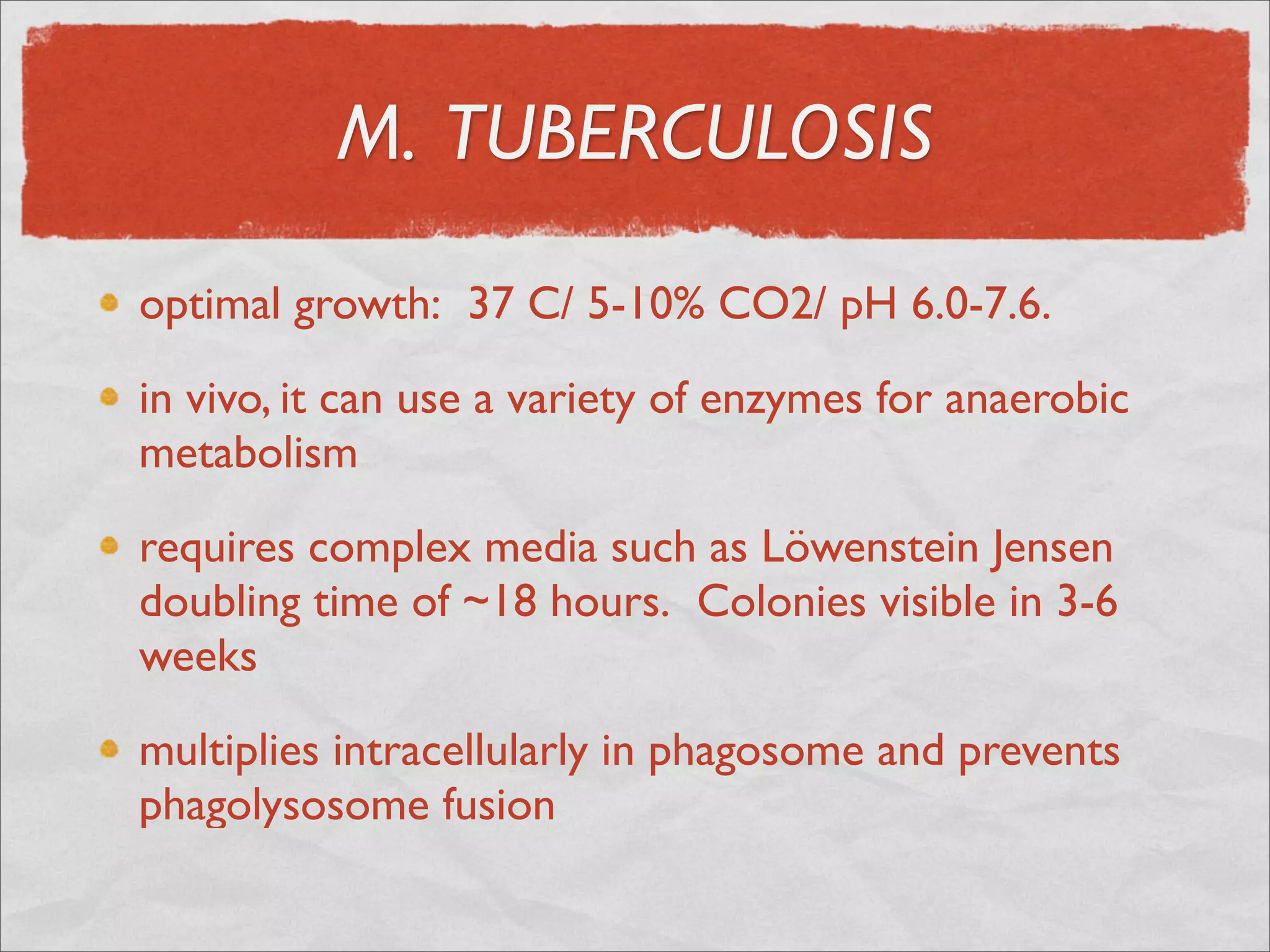
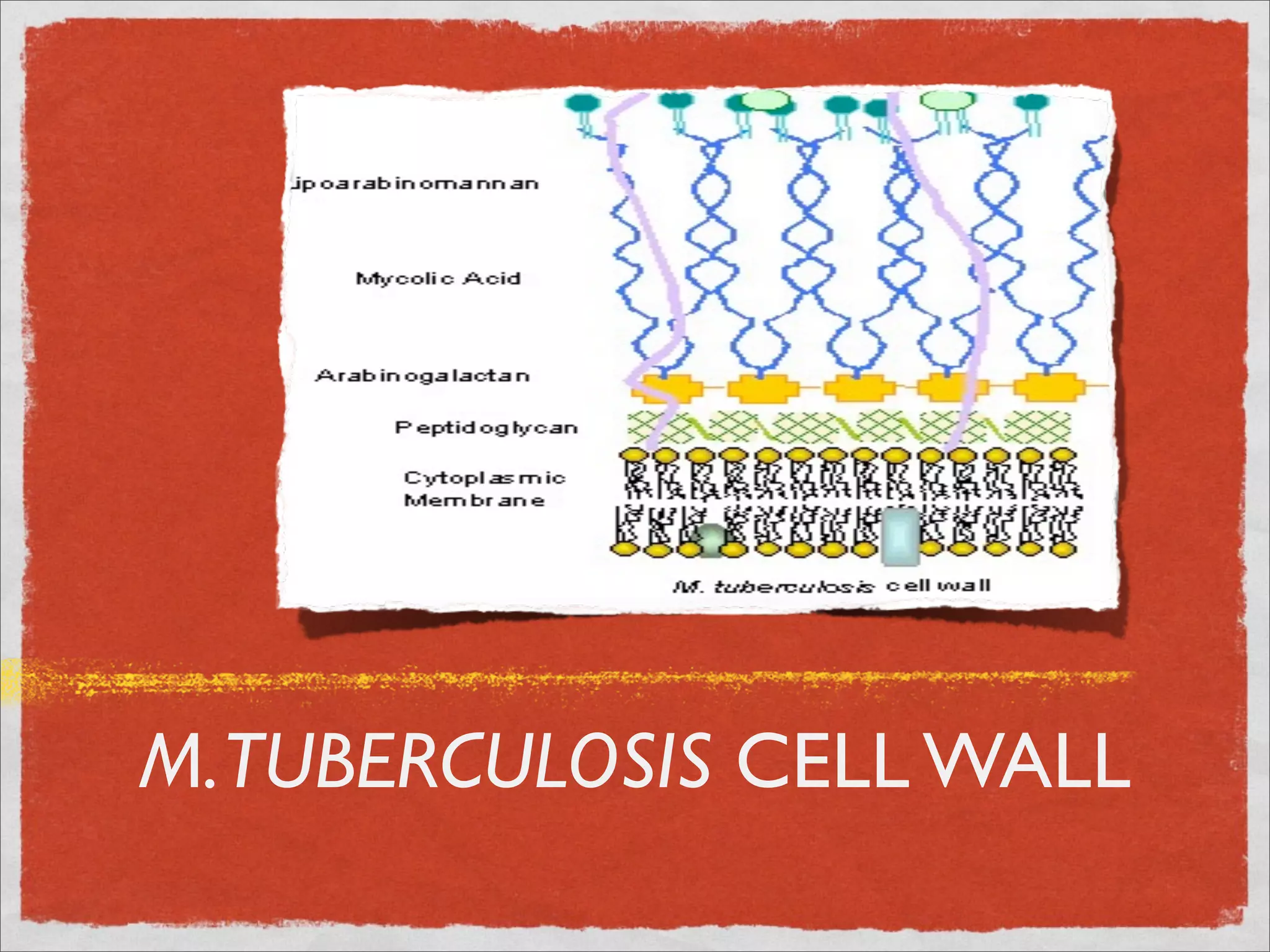
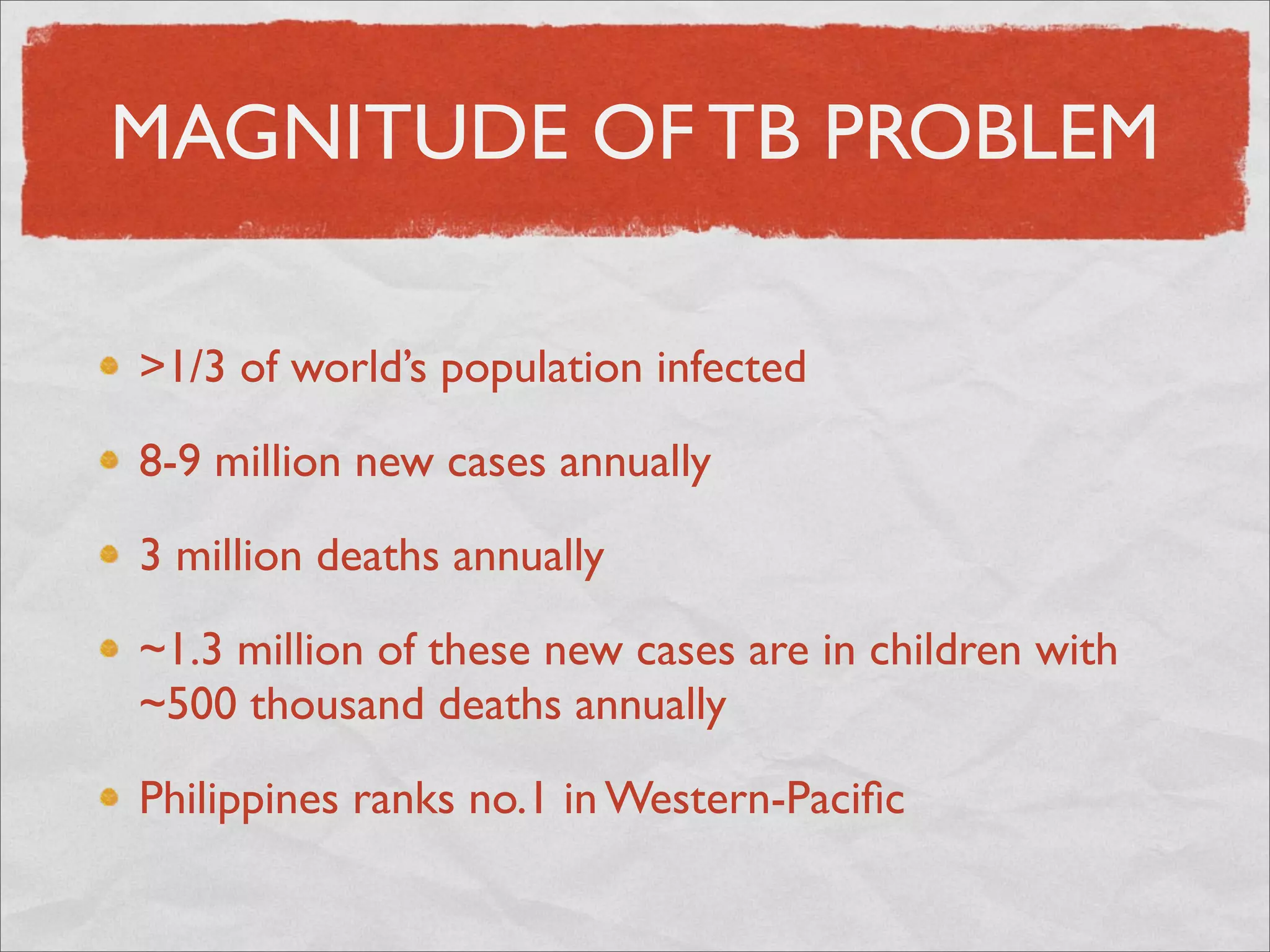
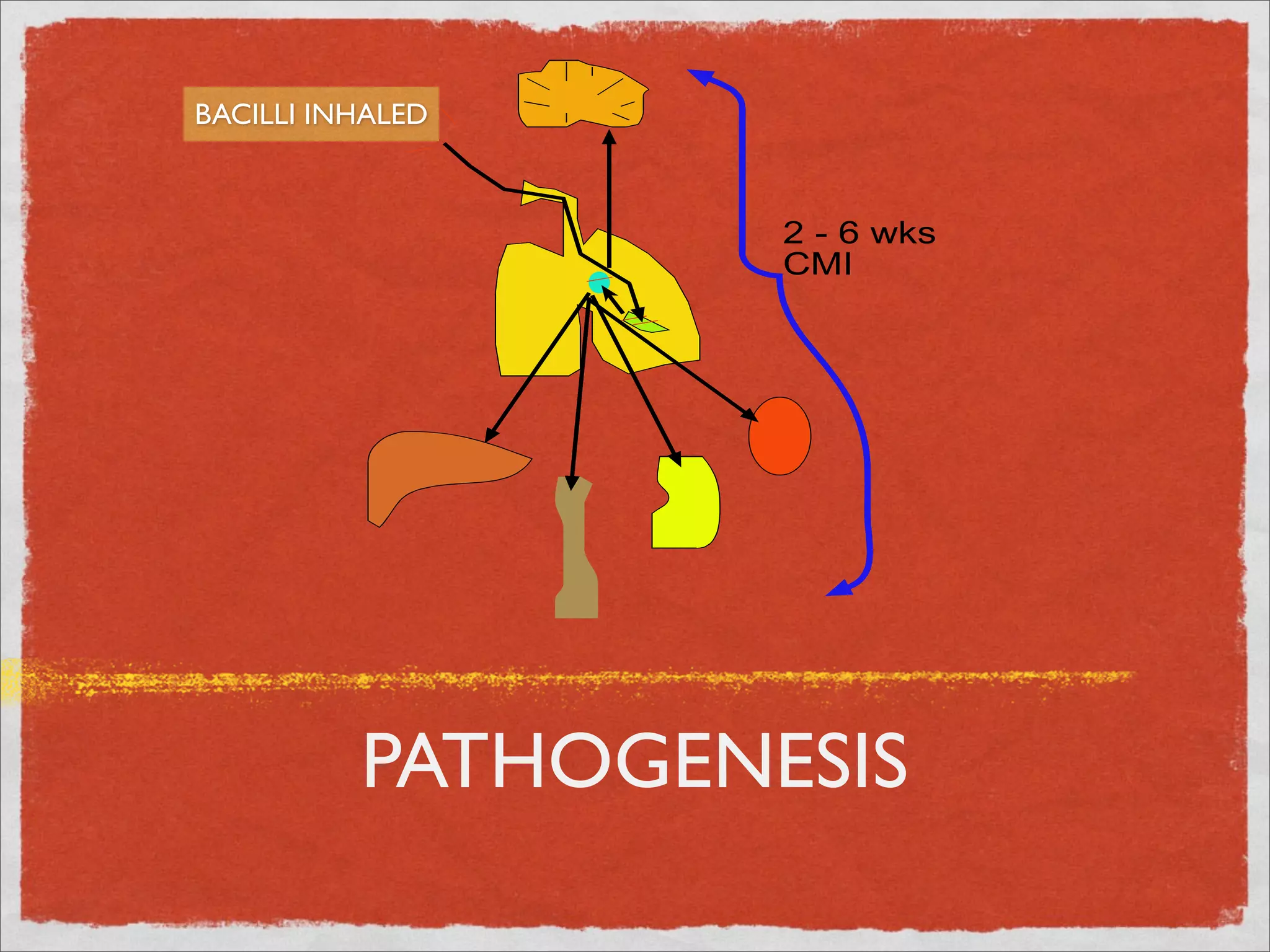
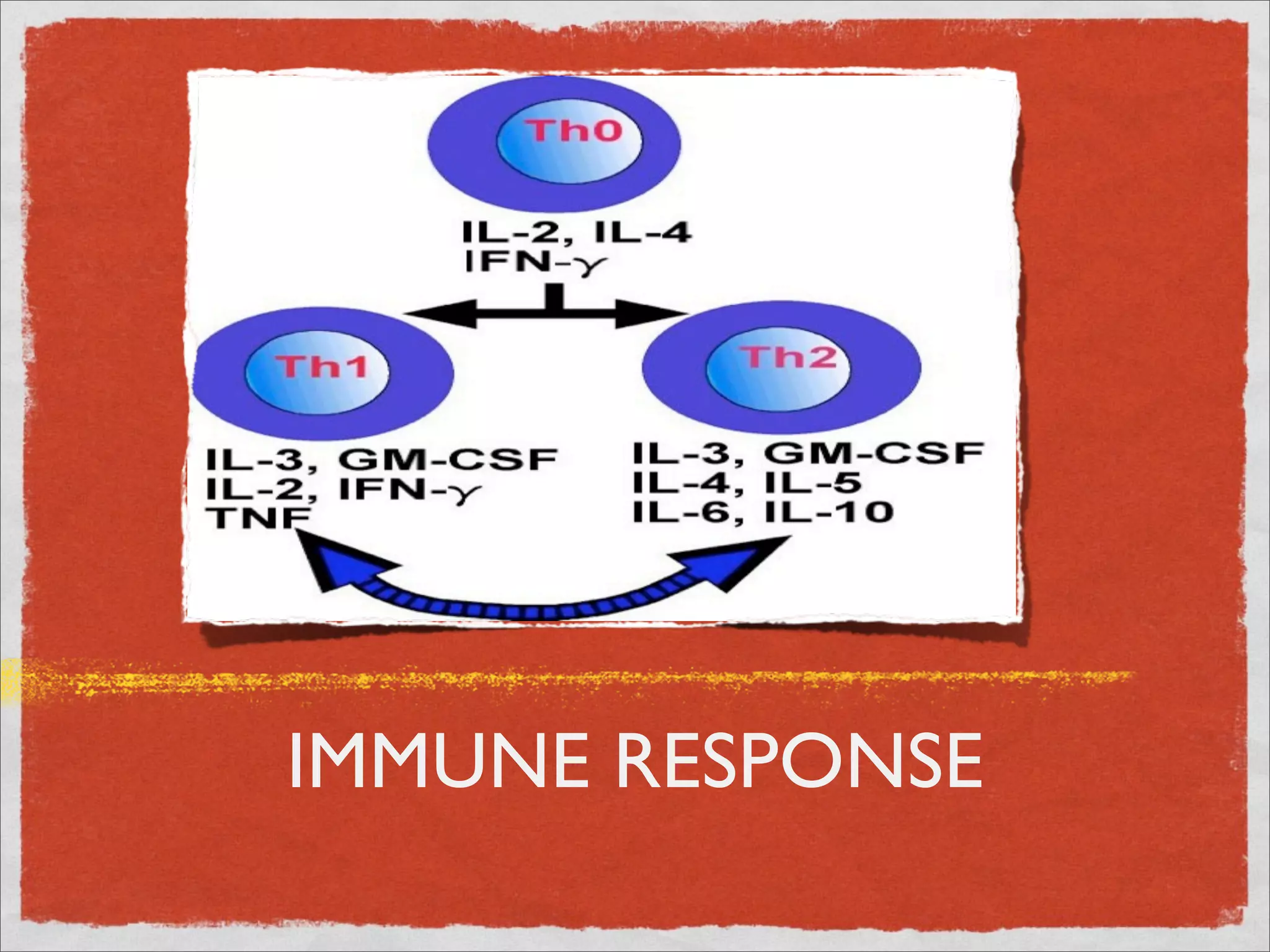
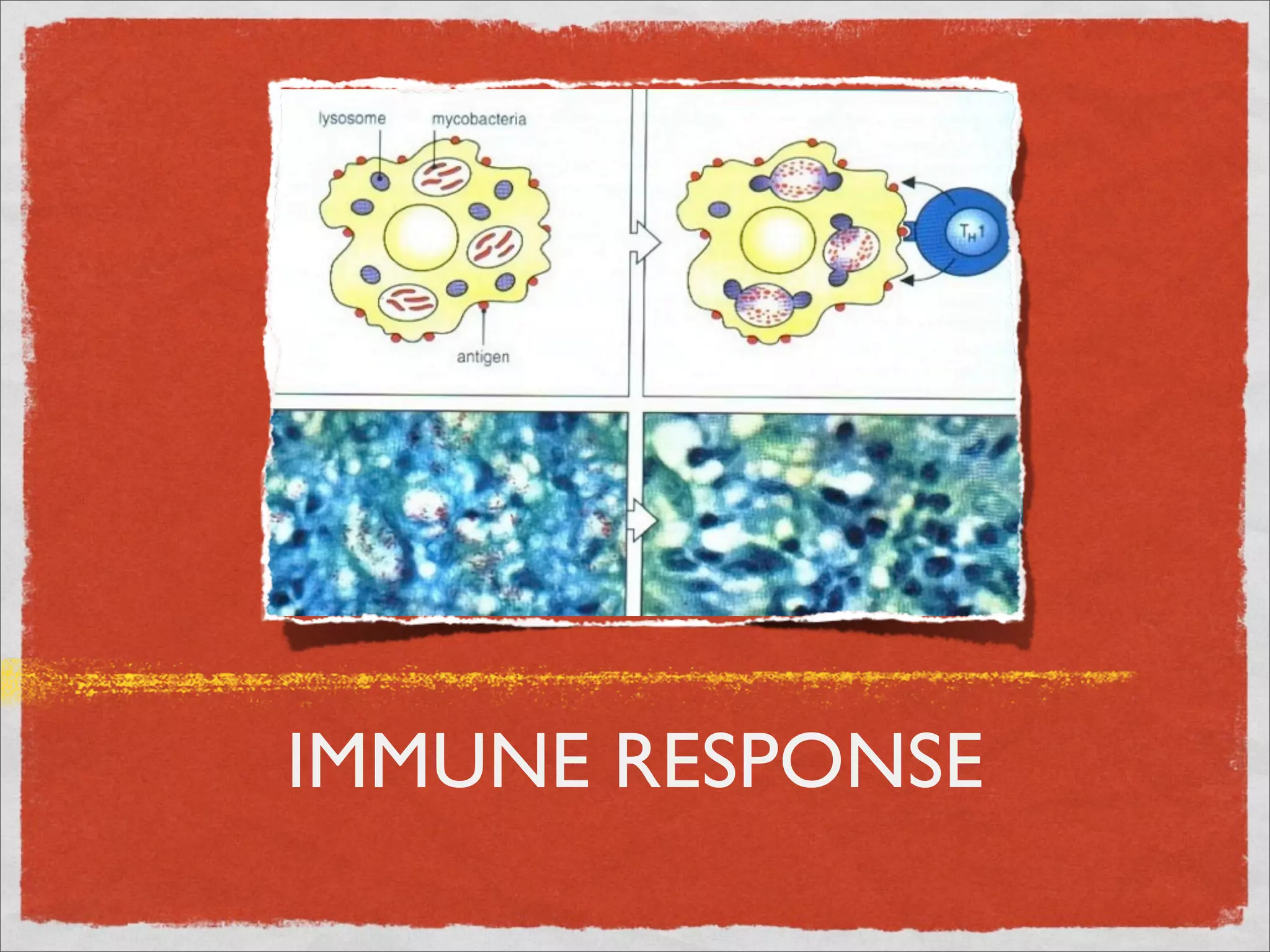
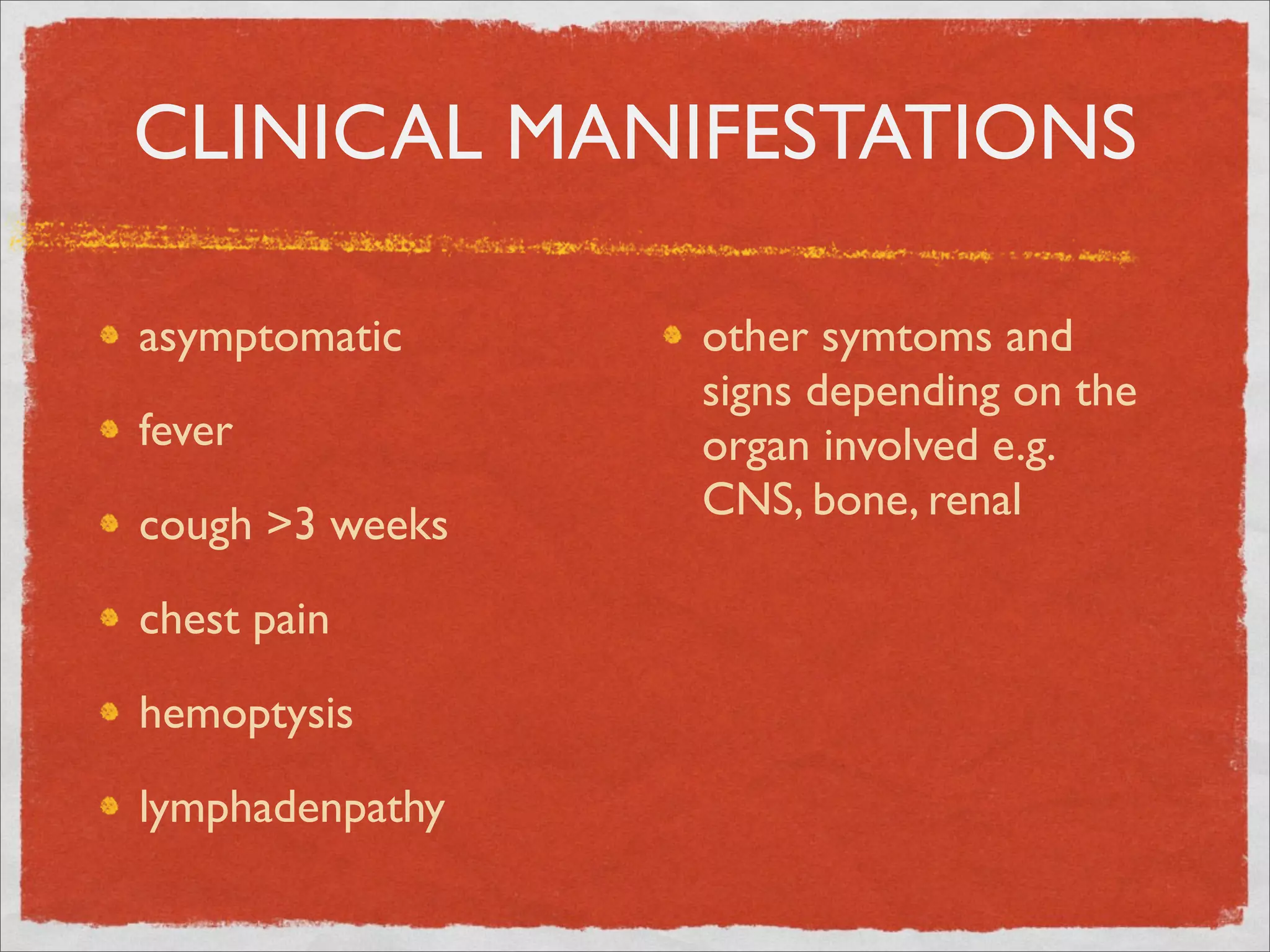
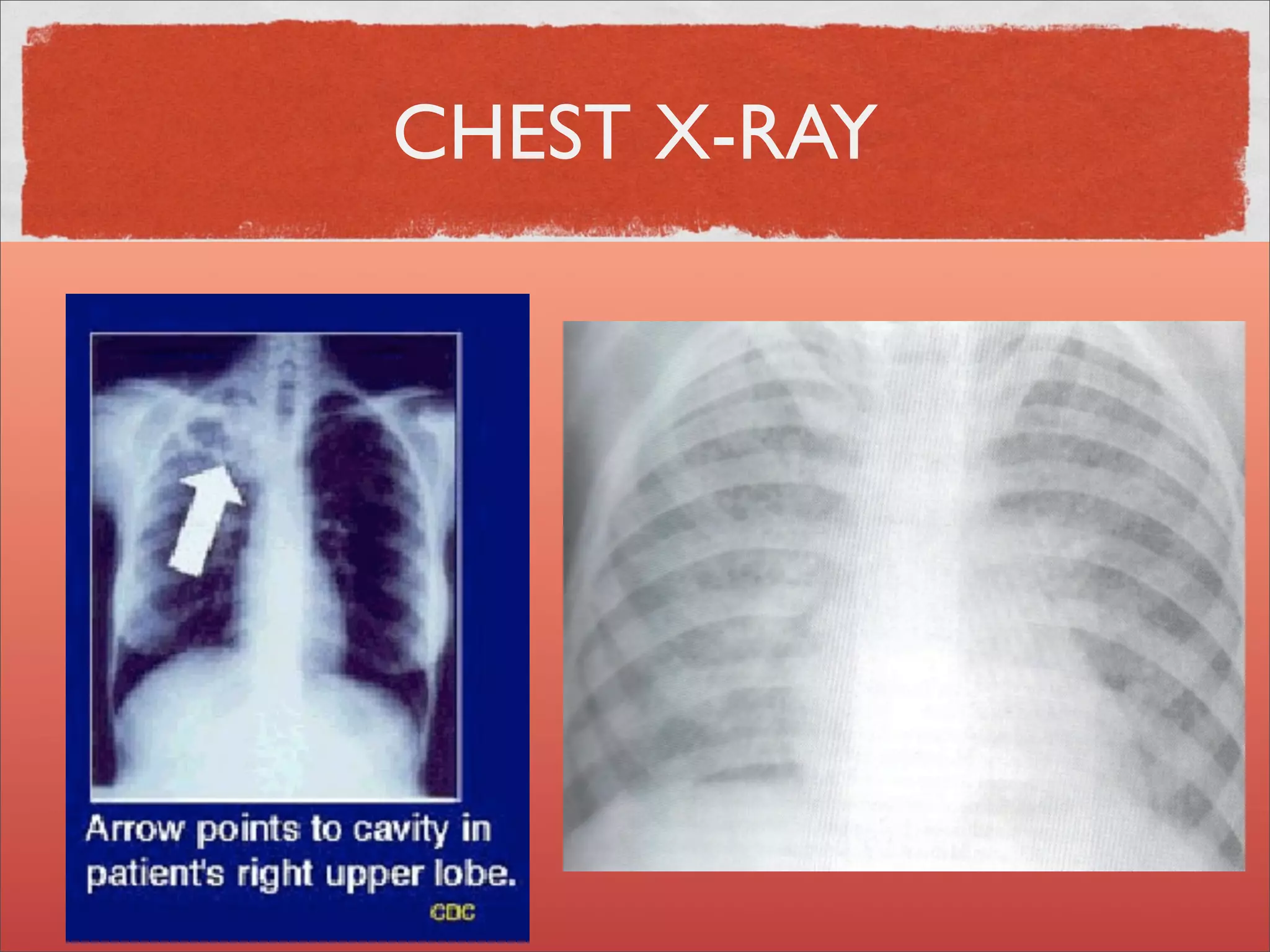
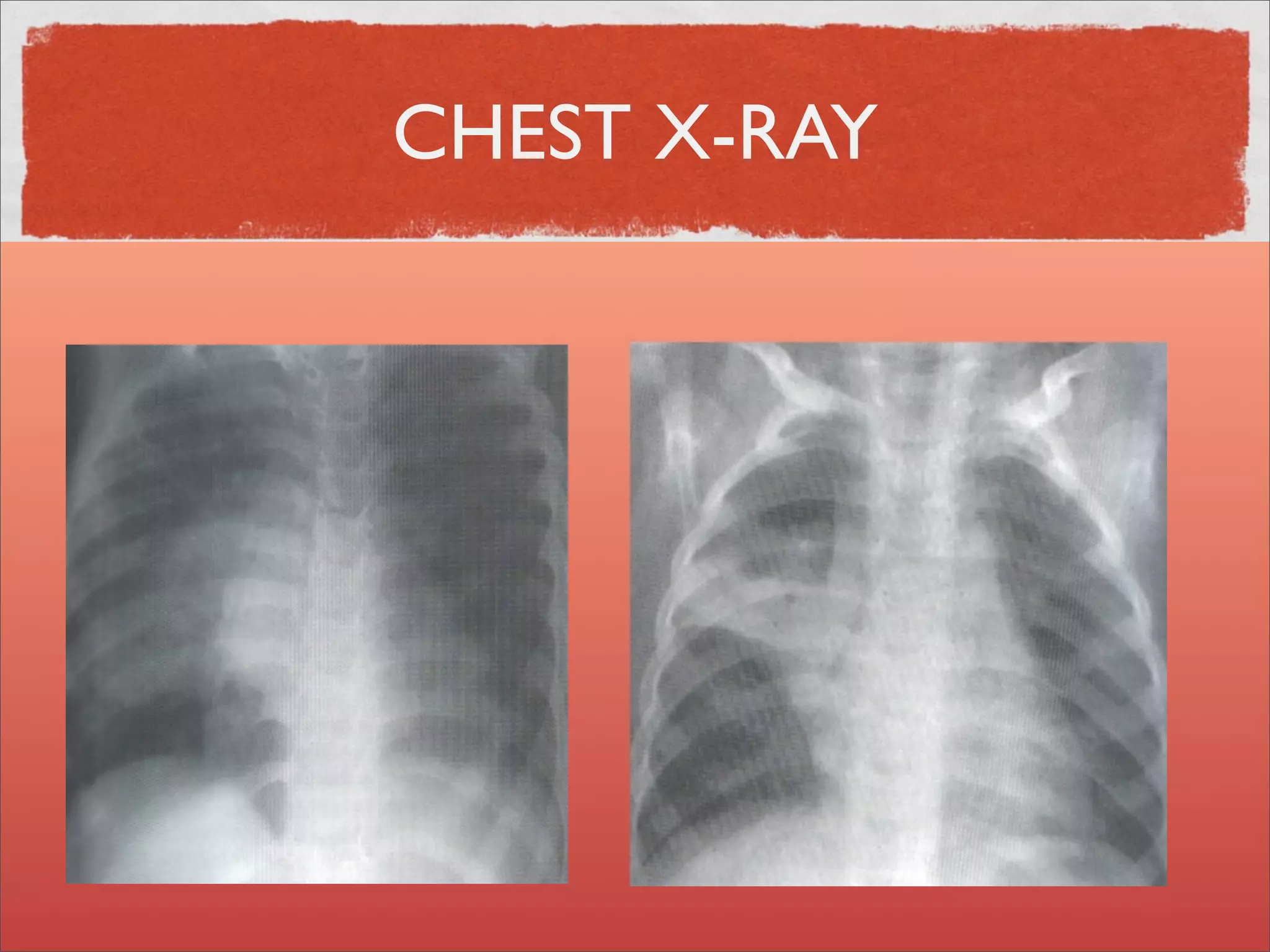
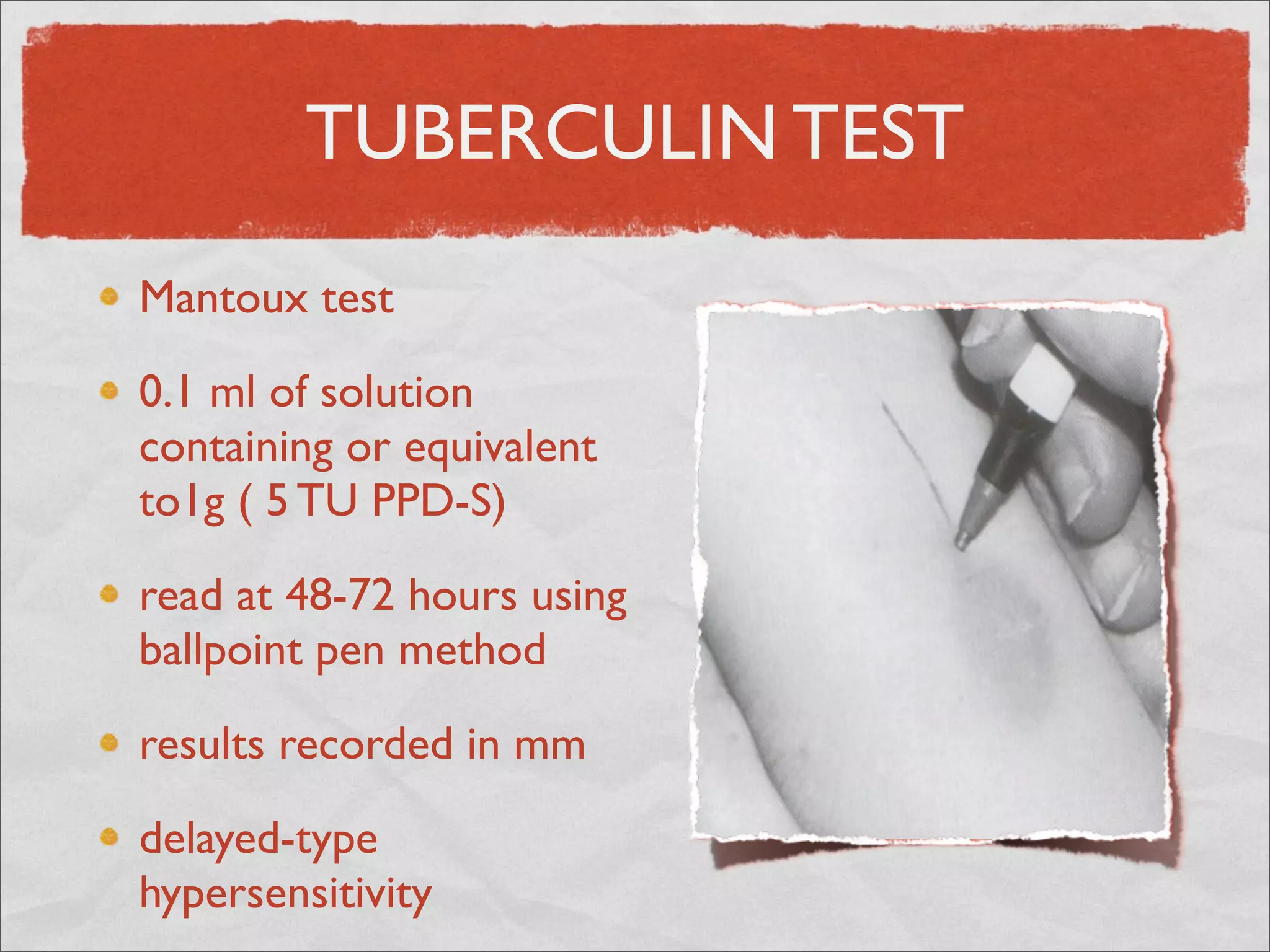
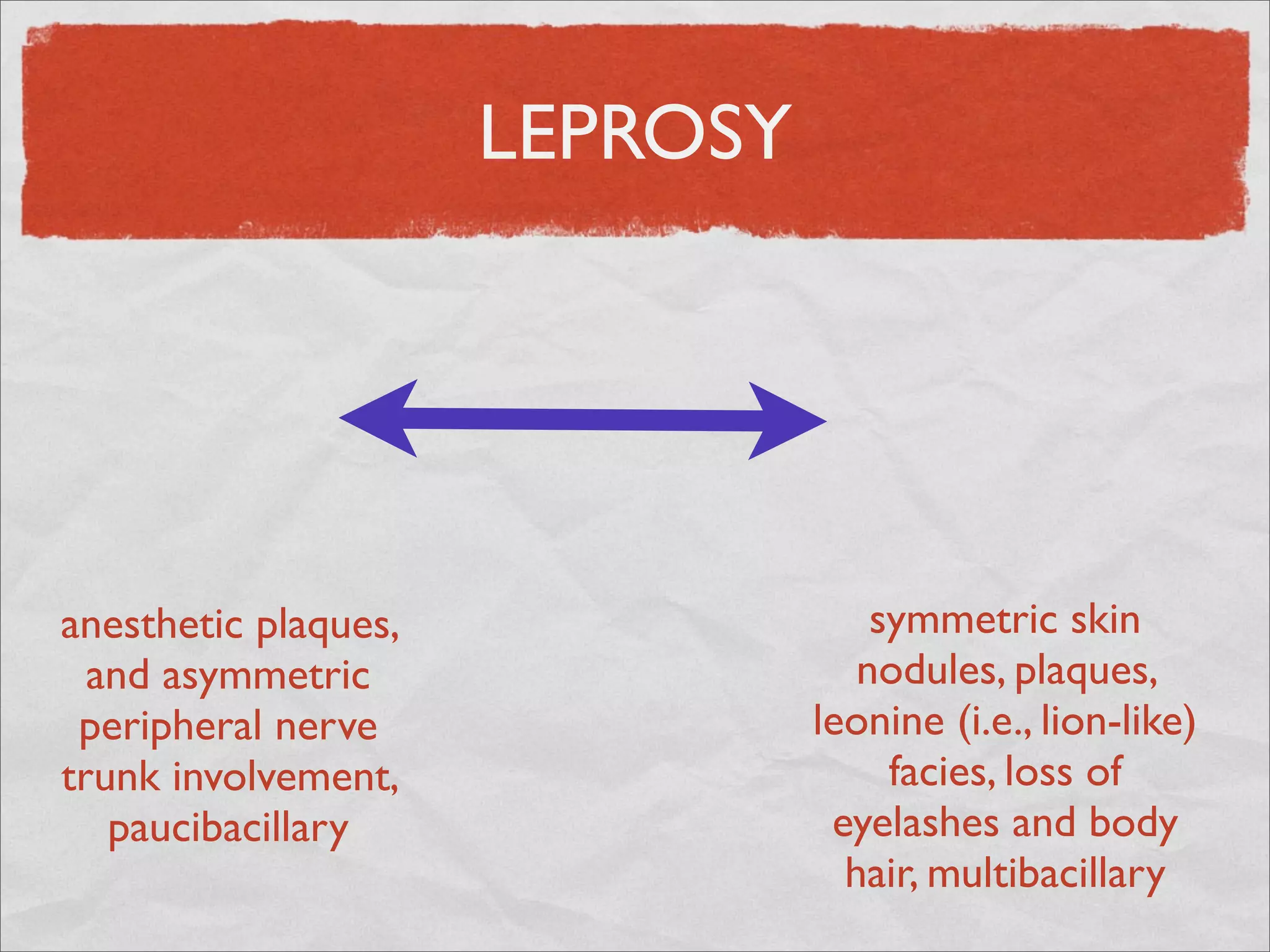
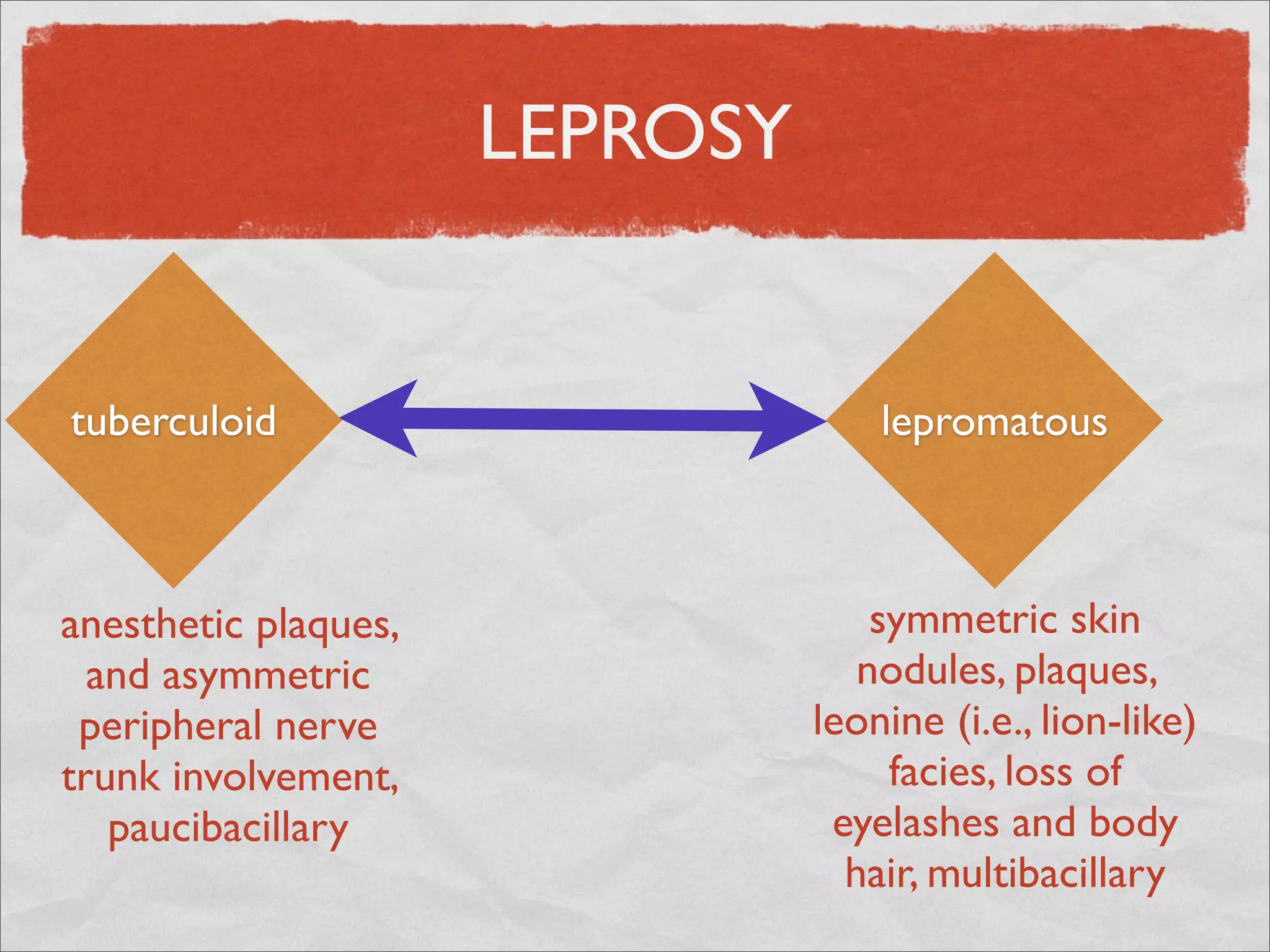
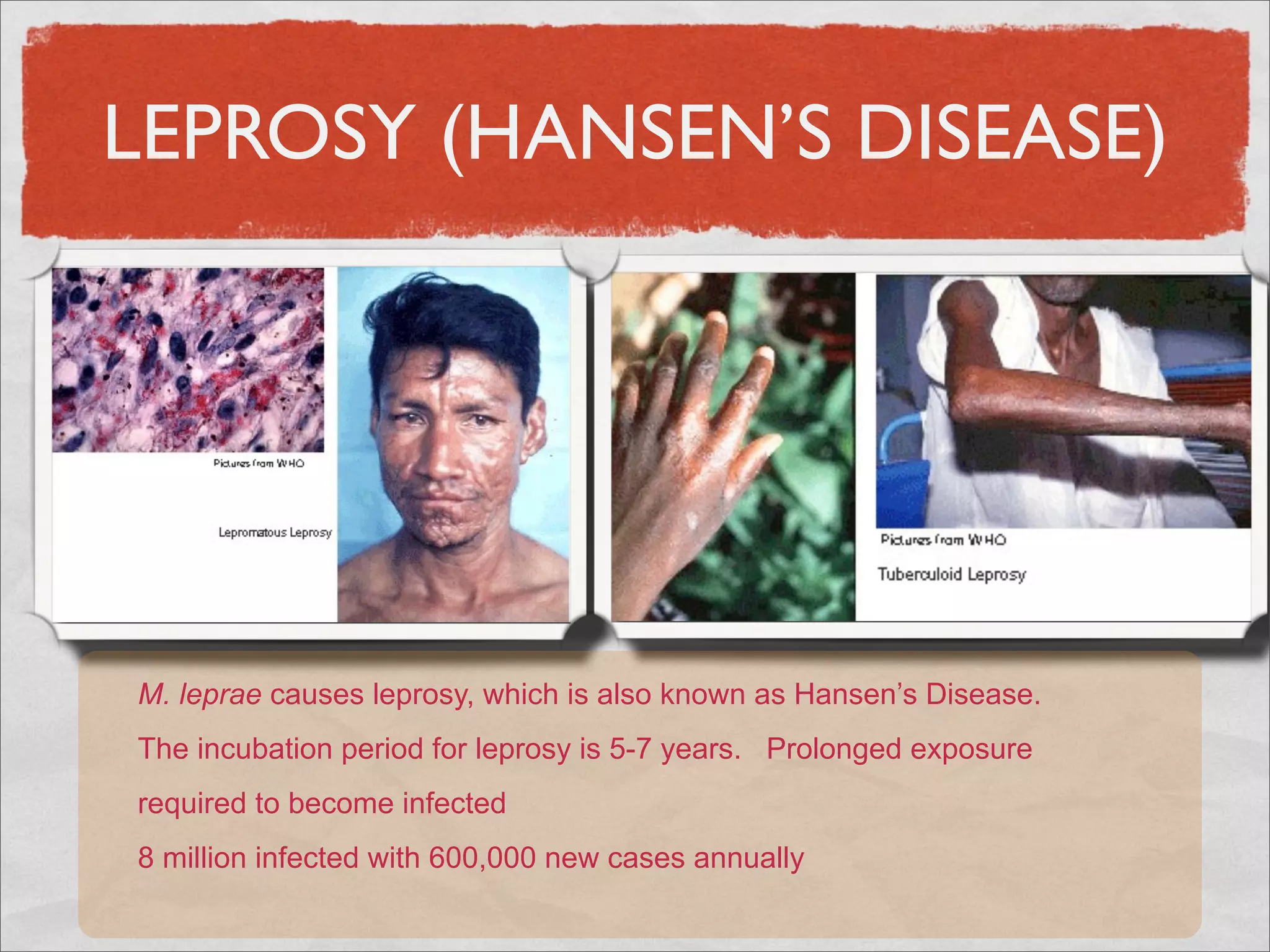
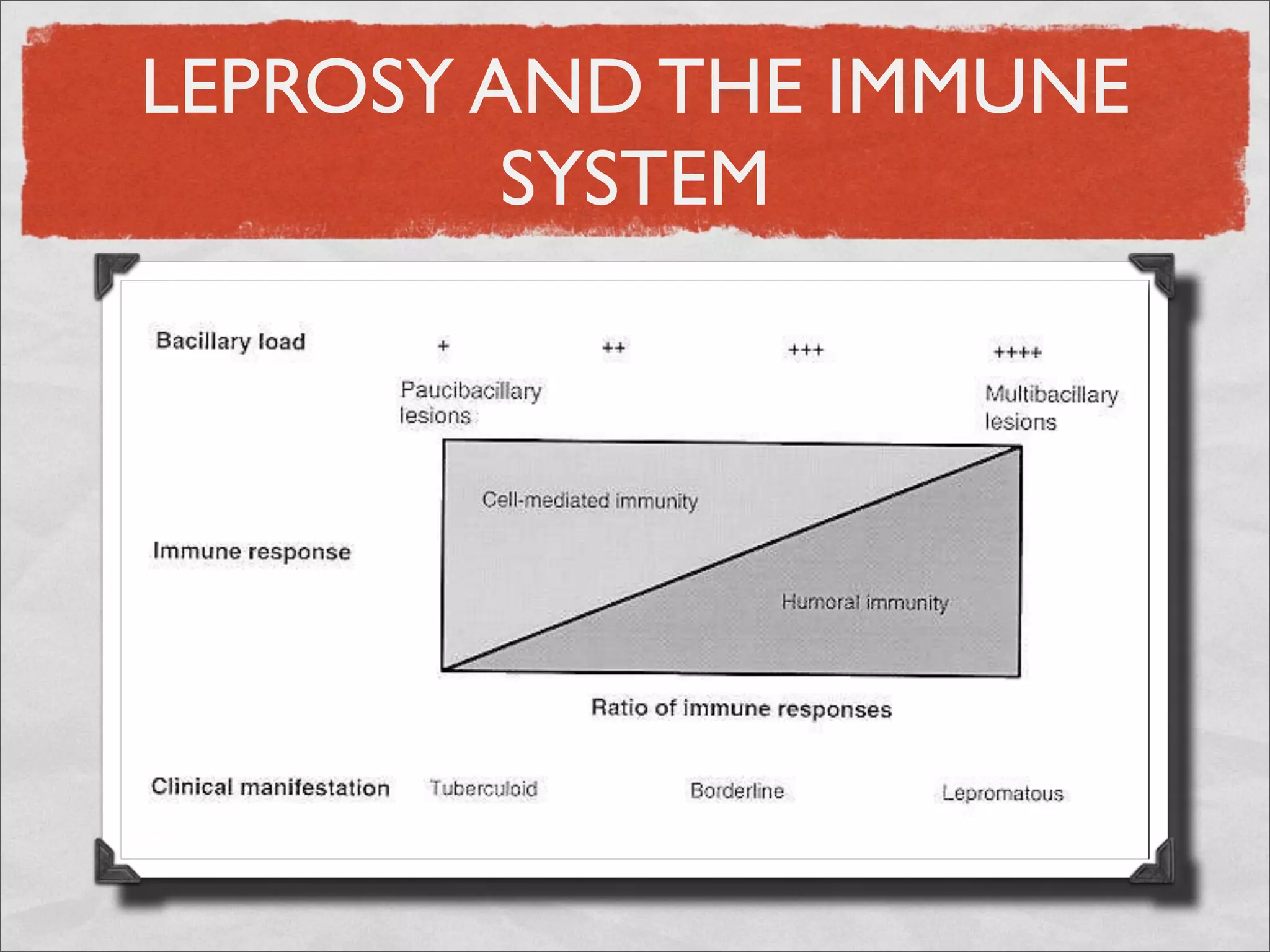
Mycobacteria are thin, nonmotile, nonspore forming rods that are obligate aerobes and slow growing. They have a cell wall with high lipid content and mycolic acid. Mycobacteria include M. tuberculosis, M. leprae, and several non-tuberculosis mycobacteria (NTM). M. tuberculosis causes tuberculosis and has several virulence factors that allow it to survive inside host cells. TB remains a major global health problem, infecting over 1/3 of the world's population. M. leprae causes leprosy (Hansen's disease), which has an incubation period of 5-7 years.