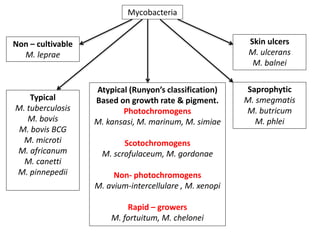
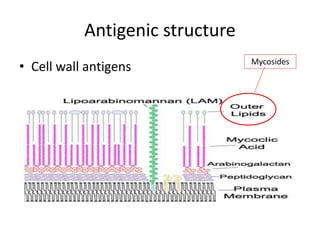
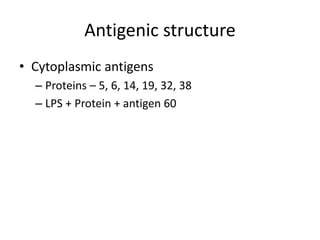
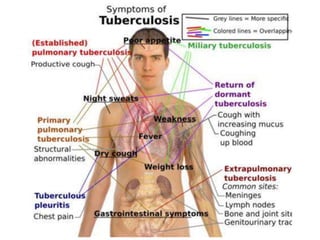
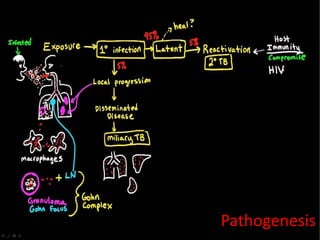
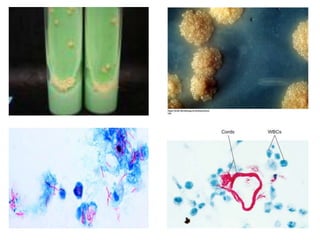
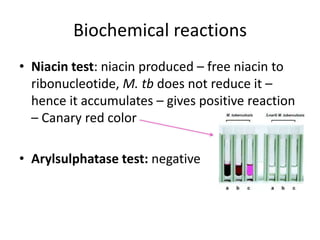
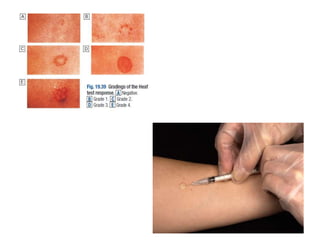
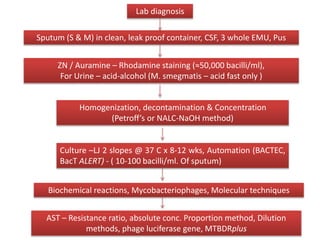
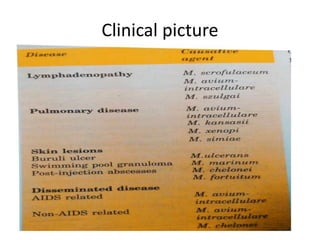
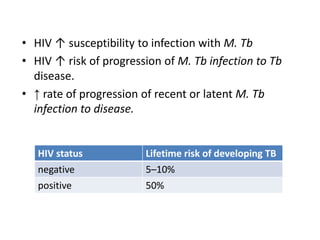
This document discusses Mycobacteria, which are slender bacilli that are slow growing and acid-fast. It covers the classification of mycobacteria including typical pathogens like M. tuberculosis and M. leprae, as well as atypical or environmental mycobacteria. Key details about morphology, culture techniques, biochemical reactions, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis are provided. The relationship between tuberculosis and HIV is also summarized.