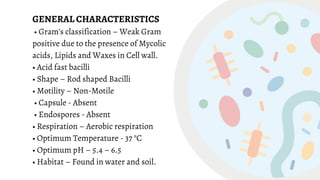
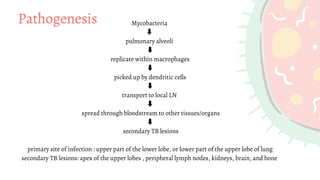
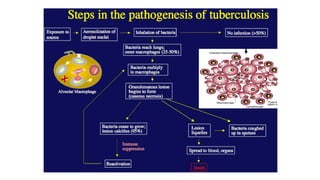
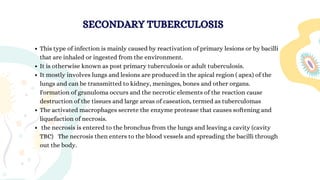
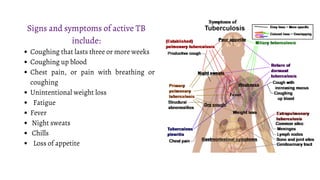
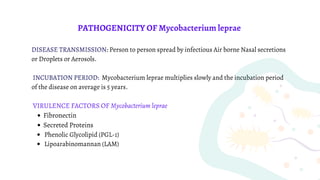
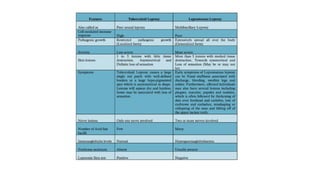
Mycobacterium is a genus of bacteria classified based on being acid-fast, having mycolic acids in their cell wall, and high G+C content in their DNA. M. tuberculosis is an aerobic, non-motile, acid-fast bacillus that causes tuberculosis. It has virulence factors like cord factor and catalase peroxidase that allow it to survive inside macrophages. M. leprae is an intracellular pathogen that causes leprosy. It enters Schwann cells and macrophages, where it multiplies slowly. The immune response determines the clinical manifestation as tuberculoid or lepromatous leprosy. Both diseases spread through airborne droplets and have variable incubation periods.