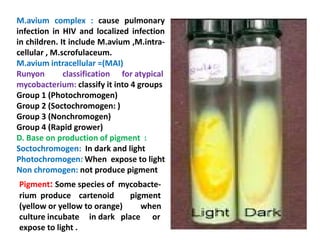
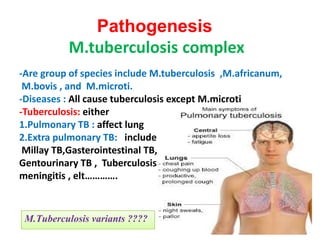
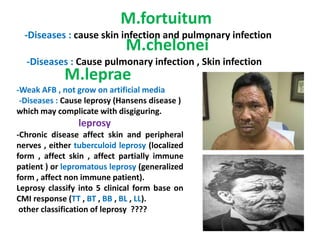
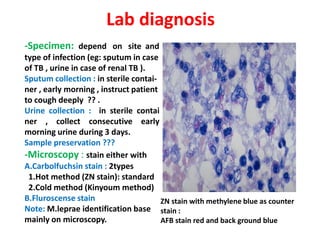
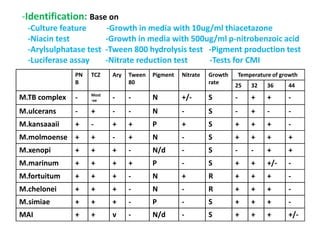
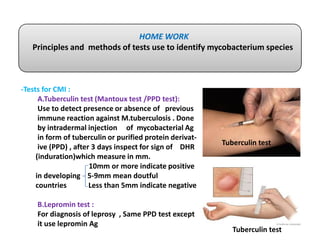
This document discusses the genus Mycobacterium, detailing its classification, important species, and pathogenic characteristics, as well as lab diagnosis and treatment options for infections such as tuberculosis and leprosy. It covers the properties of mycobacteria, including their acid-fastness, slow growth, and the need for enriched media for culturing. The document also describes the various species of mycobacteria, their associated diseases, and the methods used for laboratory identification and treatment protocols.