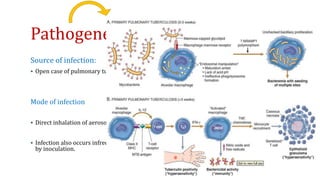
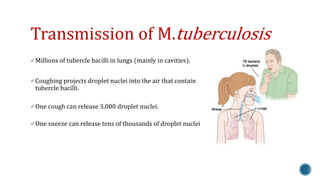
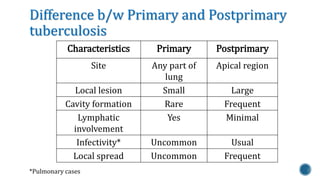
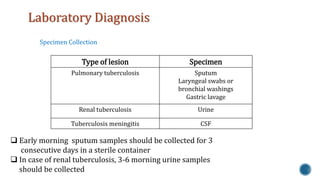
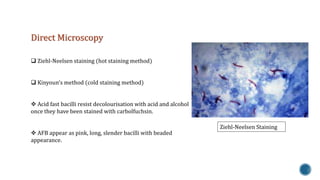
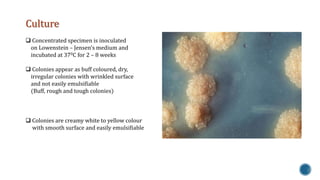
This document discusses Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that causes tuberculosis. It begins by describing the genus Mycobacterium and some of the important species that cause diseases like tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. It then classifies mycobacteria into three groups: obligate parasites like M. tuberculosis and M. leprae, opportunistic pathogens, and saprophytes. The document goes on to describe the pathogenesis and transmission of M. tuberculosis, the immune response it elicits, and various laboratory methods for diagnosing tuberculosis like microscopy, culture, and antibody detection.