1. The document discusses acid-base reactions and how salts can affect pH.
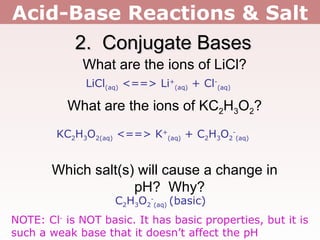
2. Salts containing conjugate acids of weak bases or conjugate bases of weak acids can change the pH, making solutions acidic or basic respectively.
3. Group 1 and 2 metal ions like Li+ and Mg2+ do not affect pH, except for Be2+ which makes solutions acidic. Metals with 3+ charges or higher often hydrolyze to form acidic solutions.