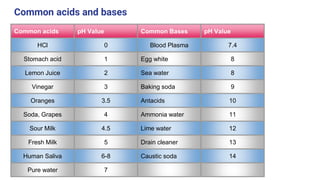
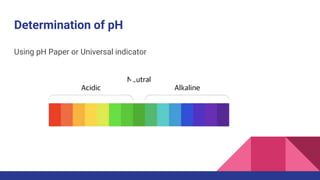
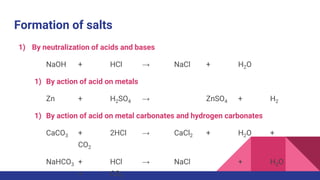
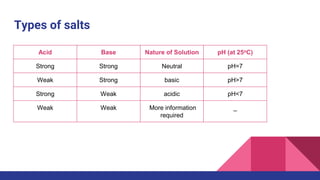
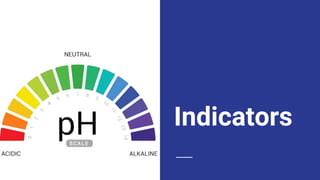
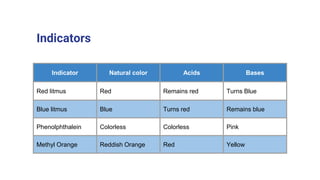
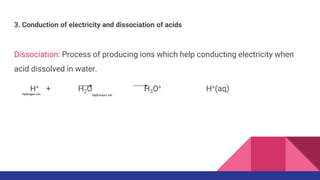
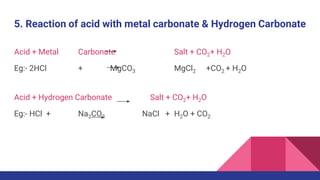
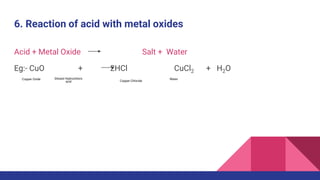
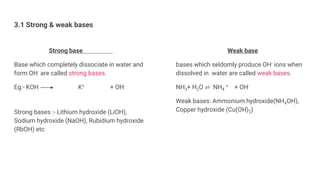
This document discusses acids, bases, and salts. It defines acids as substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) in water, and bases as substances that release hydroxide ions (OH-). Strong acids and bases fully dissociate in water, while weak ones only partially dissociate. Acids react with metals and bases to produce salts and either water or hydrogen gas. The pH scale is used to measure acidity, with acidic solutions having a pH below 7 and basic solutions above 7. Common examples of acids, bases, and salts are also provided.























![Self dissociation of water
➔ Dissociation of water itself is extremely small and only about 2 out of every billion water
molecules are dissociated in 25oC.
➔ H2O ⇌ H+ +OH-
➔ H+= OH- = 1.0 x 10-7
➔ Pure water or ionic product of water is H+= OH- It’s symbolized as Kw (Ionic Constant
product of water). So we conclude that:
Kw = [H+] [OH-] ie: Kw = (1.0 x 10-7) x (1.0 x 10-7)
Kw = 1.0 x 10-14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scienceplusone-230523052641-66ddf471/85/Acid-Base-and-Salt-Science-Plus-one-NIOS-30-320.jpg)
![Solutions
❏ Neutral Solution: H+= OH- = 1.0 x10-7 mol L-1
❏ Acidic Solution: H+> OH- Or [H+] > 1.0 x10-7 mol L-1
❏ Basic Solution: H+< OH- or [H+] < 1.0 x10-7 mol L-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scienceplusone-230523052641-66ddf471/85/Acid-Base-and-Salt-Science-Plus-one-NIOS-31-320.jpg)

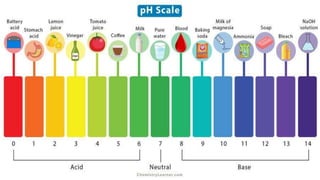
![pH and its importance
➔ pH means the power of hydrogen
➔ It was denoted by Danish biochemist Soren Sorensen in 1909.
pH= log 1/[H+]
➔ Acid rain is 5.6 pH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scienceplusone-230523052641-66ddf471/85/Acid-Base-and-Salt-Science-Plus-one-NIOS-34-320.jpg)

![pH and its importance
➔ pH= -log [H+]
➔ pOH= -log [OH-]
➔ pKa= -log Ka
➔ pKb= -log Kb
➔ pKw= -log Kw](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scienceplusone-230523052641-66ddf471/85/Acid-Base-and-Salt-Science-Plus-one-NIOS-36-320.jpg)

![Examples
Question: [H+] = 5x 10-3 , then what is pH?
Answer: pH= -log [H+]
-log a x 10-x = x- log a
= -log 5x 10-3
= 3- log 5
3-0.7= 2.3
Question: [H+] = 0.0002, then what is pH?
Answer: = 2x 10-4
Then,
pH= -log [H+]
pH = -log 2x 10-4
= 4- log 2
= 4 - 0.3
= 3.7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scienceplusone-230523052641-66ddf471/85/Acid-Base-and-Salt-Science-Plus-one-NIOS-38-320.jpg)
![Comprehensive checking
Question: 0.02 HCl
[H+] = 0.02x 1
[H+] = 2 x 10-2
pH= -log 2 x 10-2
= 2- log 2
=1.7
Question: 0.02 H2SO4
[H+] = 0.02x 2
[H+]= 4 x 10-2
pH= -log 4 x 10-2
2- log 4 = 2- 0.6
= 1.4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scienceplusone-230523052641-66ddf471/85/Acid-Base-and-Salt-Science-Plus-one-NIOS-39-320.jpg)