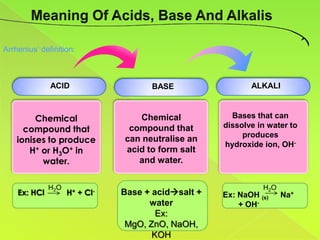
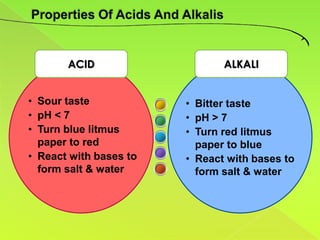
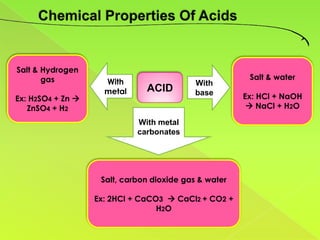
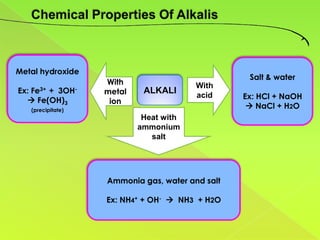
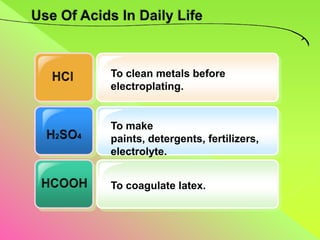
The document discusses acids, bases, and alkalis. It defines them, provides examples, and explains their properties and uses. Acids donate H+ ions in water, bases accept H+ ions and alkalis dissolve in water to form hydroxide ions. Properties of acids include sour taste and turning litmus red, while alkalis have a bitter taste and turn litmus blue. Common acids and bases are used in products like cleaners, soaps, batteries, and more.