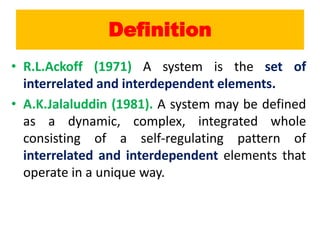
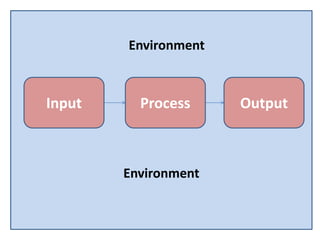
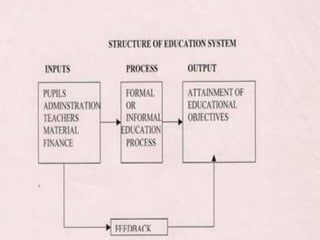
The document discusses the system approach in education. It defines a system as interrelated and interdependent elements that work together as a whole. An educational system has inputs (students, teachers, curriculum), processes (teaching and learning), outputs (achievement of educational goals), and an environmental context. The systems approach involves analyzing a system, designing and developing it, and operating and evaluating it. Applying this approach can improve instruction, administration, resource use, planning, evaluation, and teacher training.