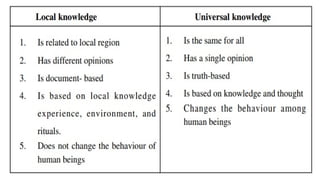
The document contrasts local knowledge, specific to communities and shaped over time through experiences, with universal knowledge, which is accepted globally and based on scientific understanding. Local knowledge includes practical skills and cultural practices, while universal knowledge encompasses broader truths and phenomena. Both types of knowledge evolve with time, reflecting the relationship between individuals and their environments.