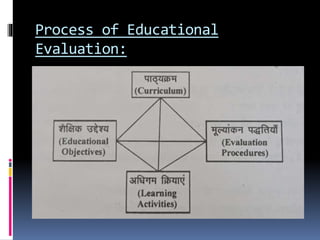
The document outlines the concept of evaluation in education as a comprehensive process that assesses both academic and non-academic behaviors for holistic student development. It describes various definitions, characteristics, and principles of evaluation while emphasizing its importance in enhancing educational objectives, planning, and curriculum development. Additionally, it details the objectives and steps involved in the educational evaluation process.