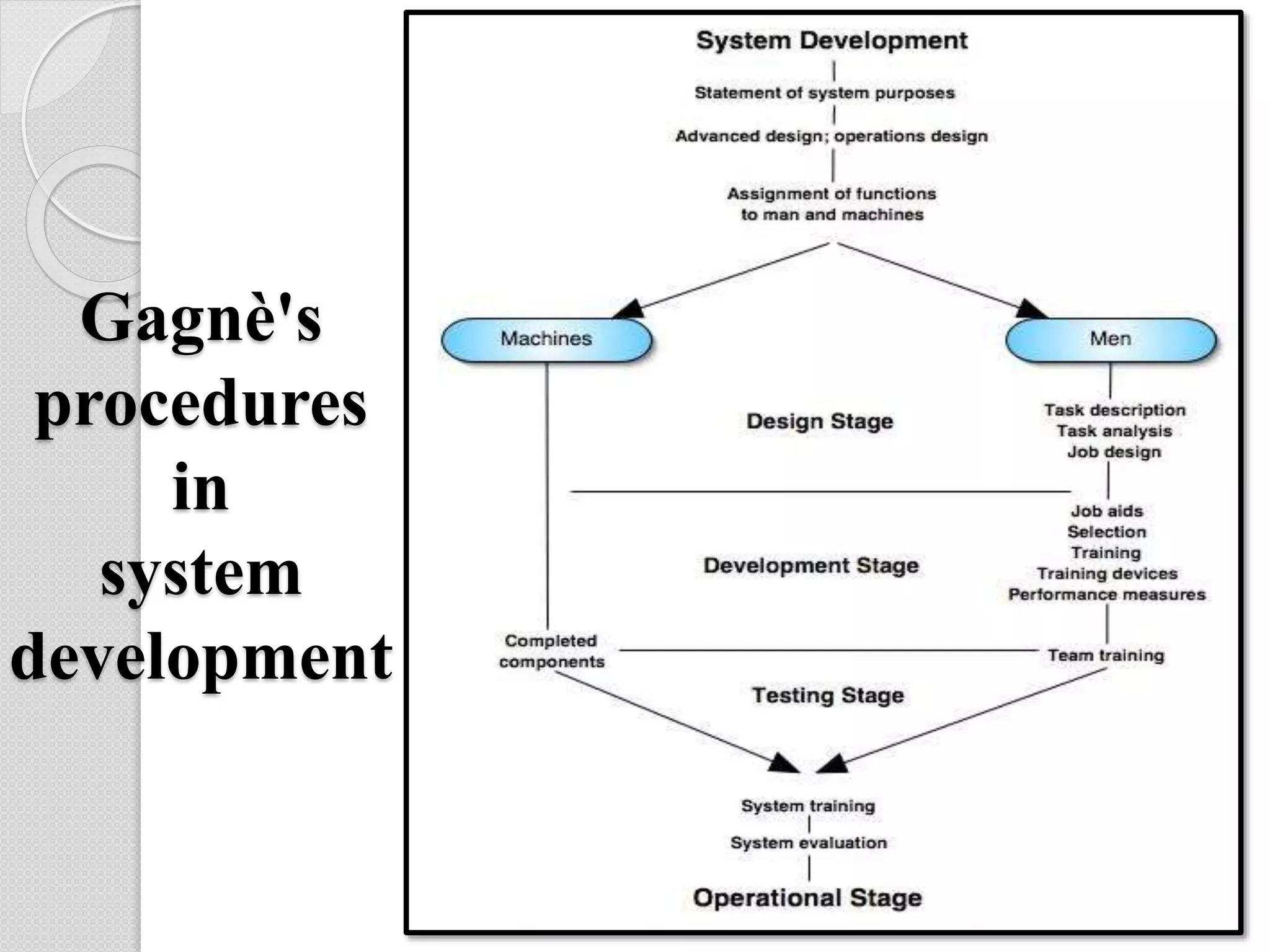
This document discusses systems and system approaches to instruction. It defines a system as a set of interconnected parts that work together to achieve objectives. An instruction system specifically refers to a set of events that affect students and lead to the learning process. The key components of an instruction system are identified as the student, objectives, conditions, learning resources, and learning outcomes. A systems approach to instruction involves systematically analyzing problems and reaching conclusions through a process of system analysis and system synthesis. Some benefits of a systems approach include effective planning, optimization of resources, feedback, and increased student learning and achievement.