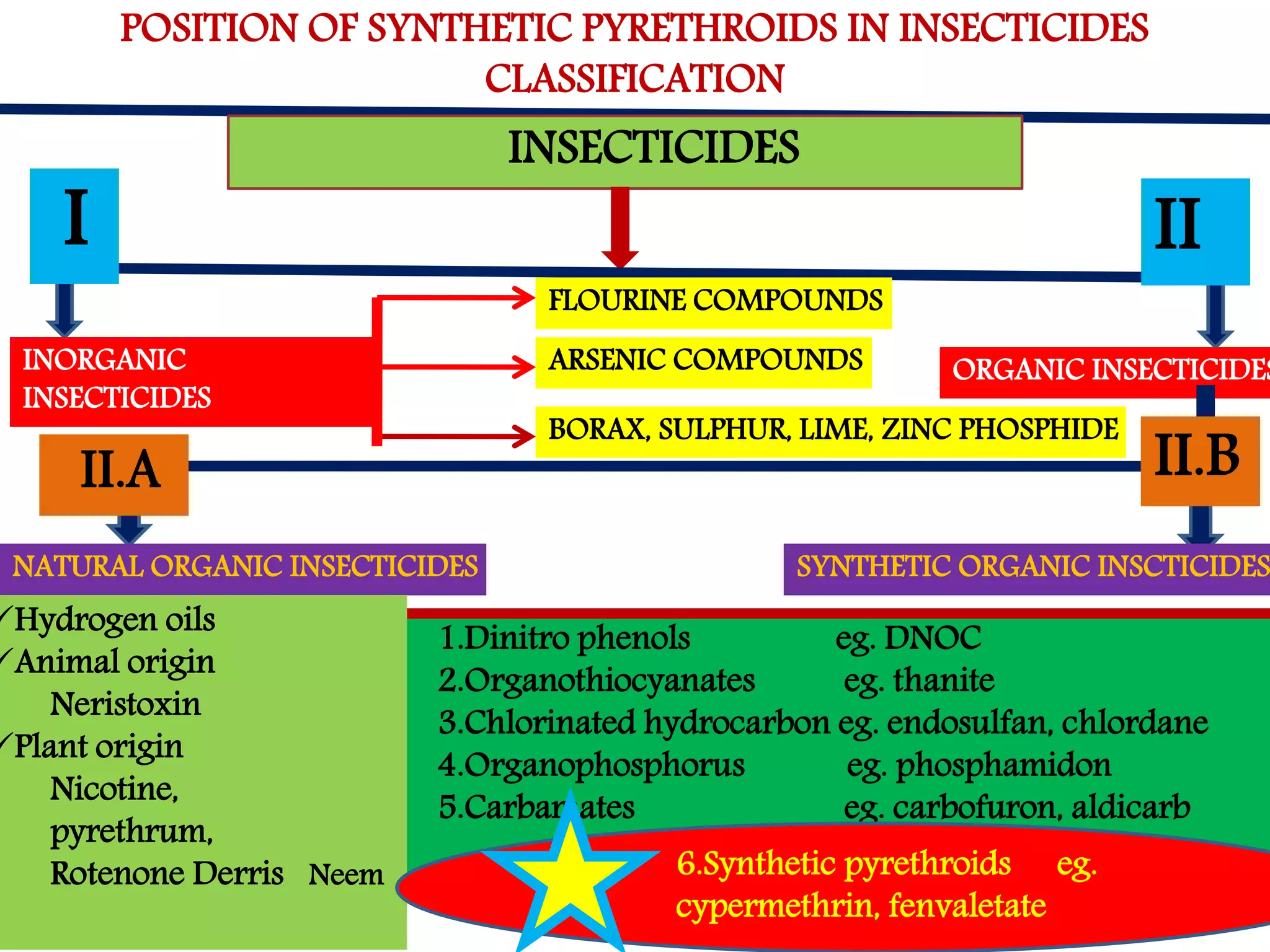
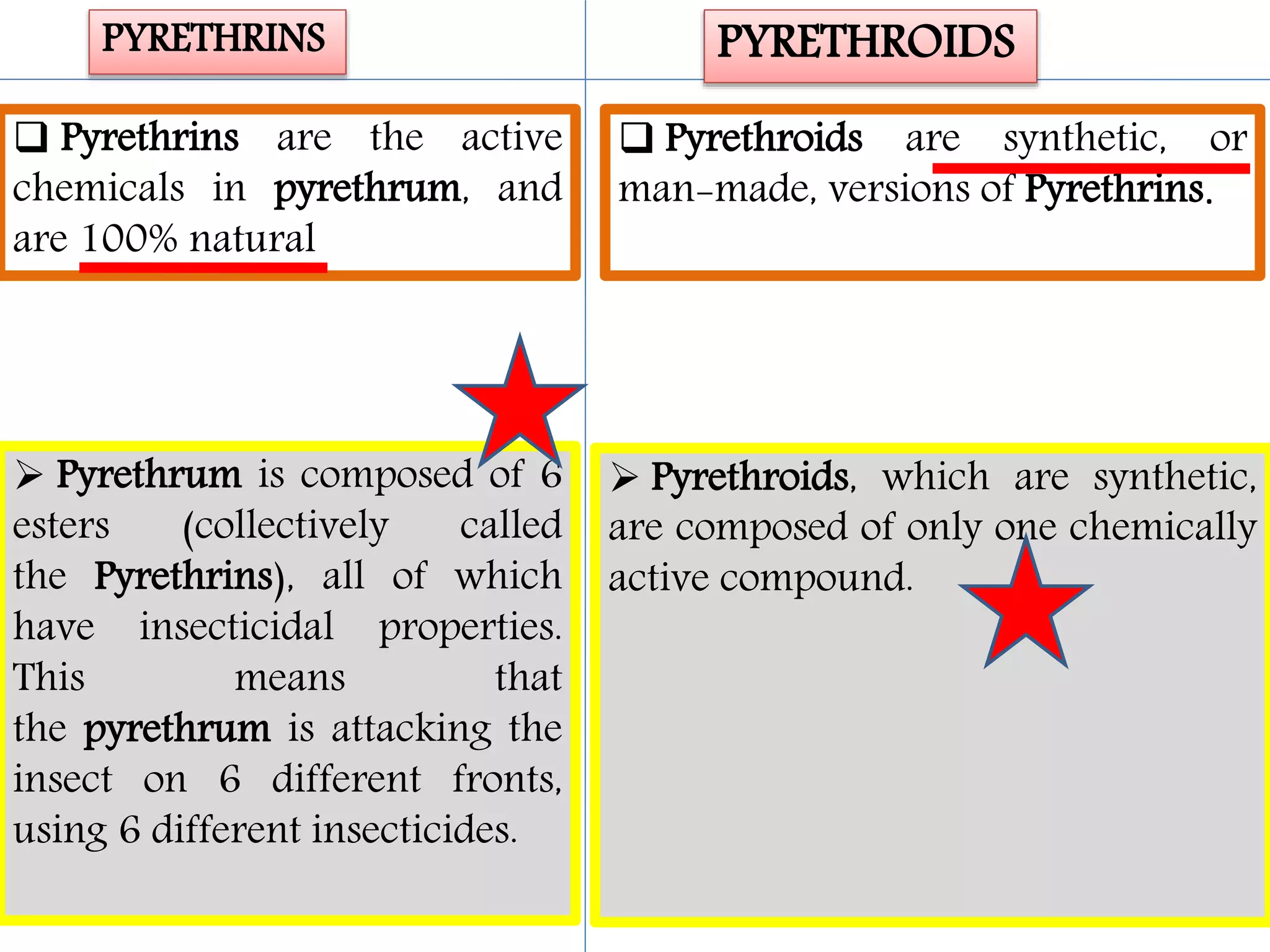
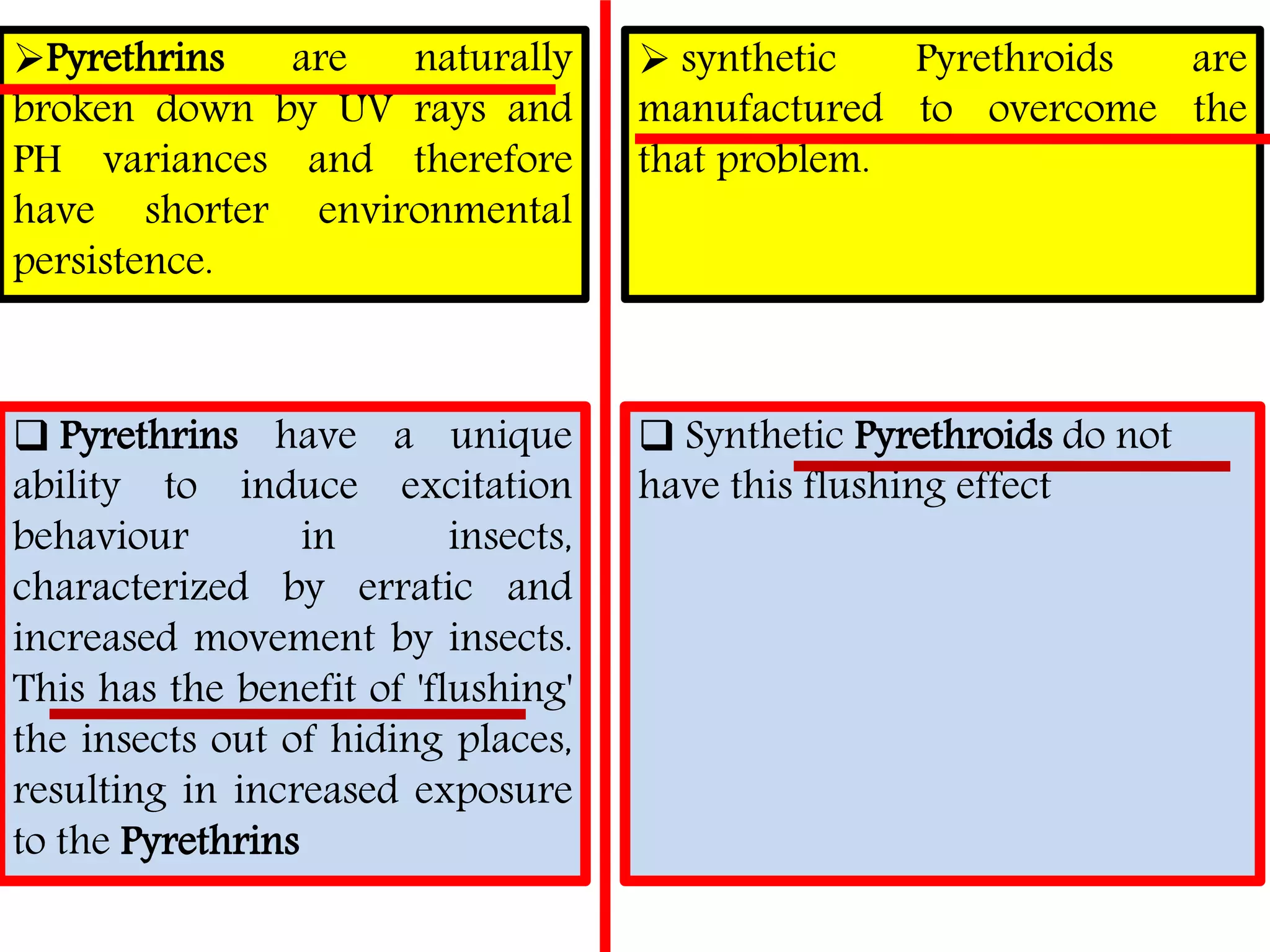
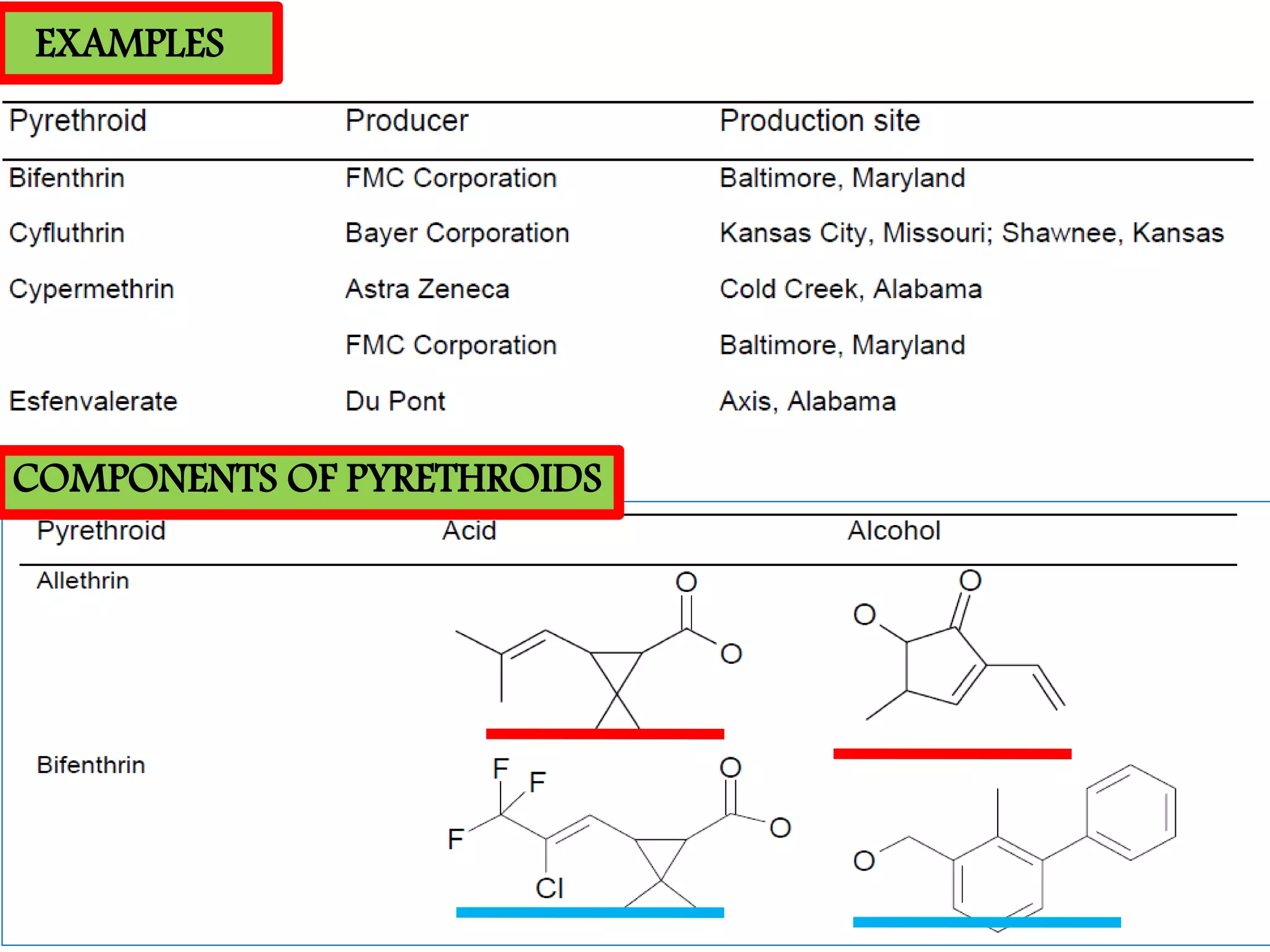
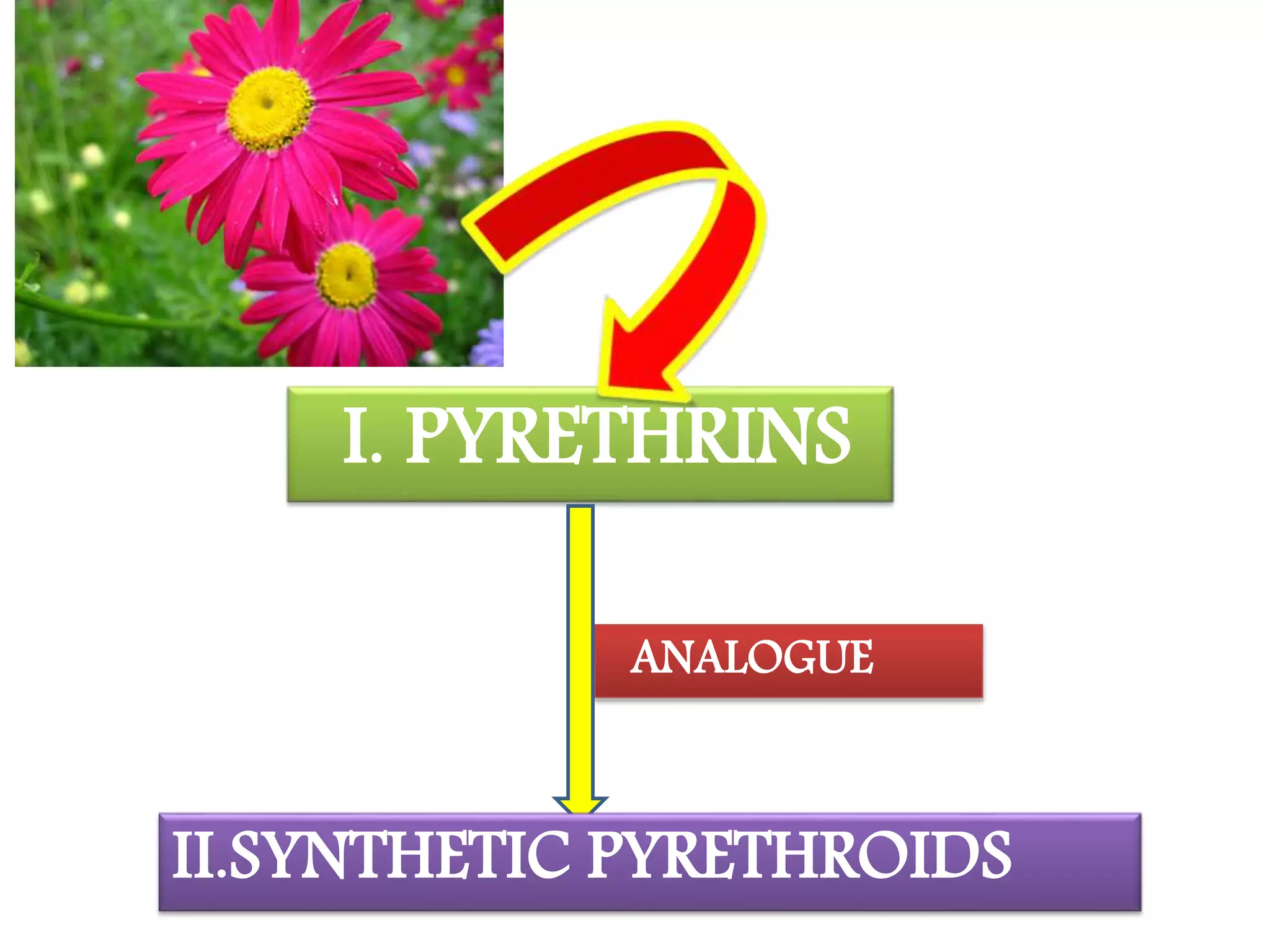
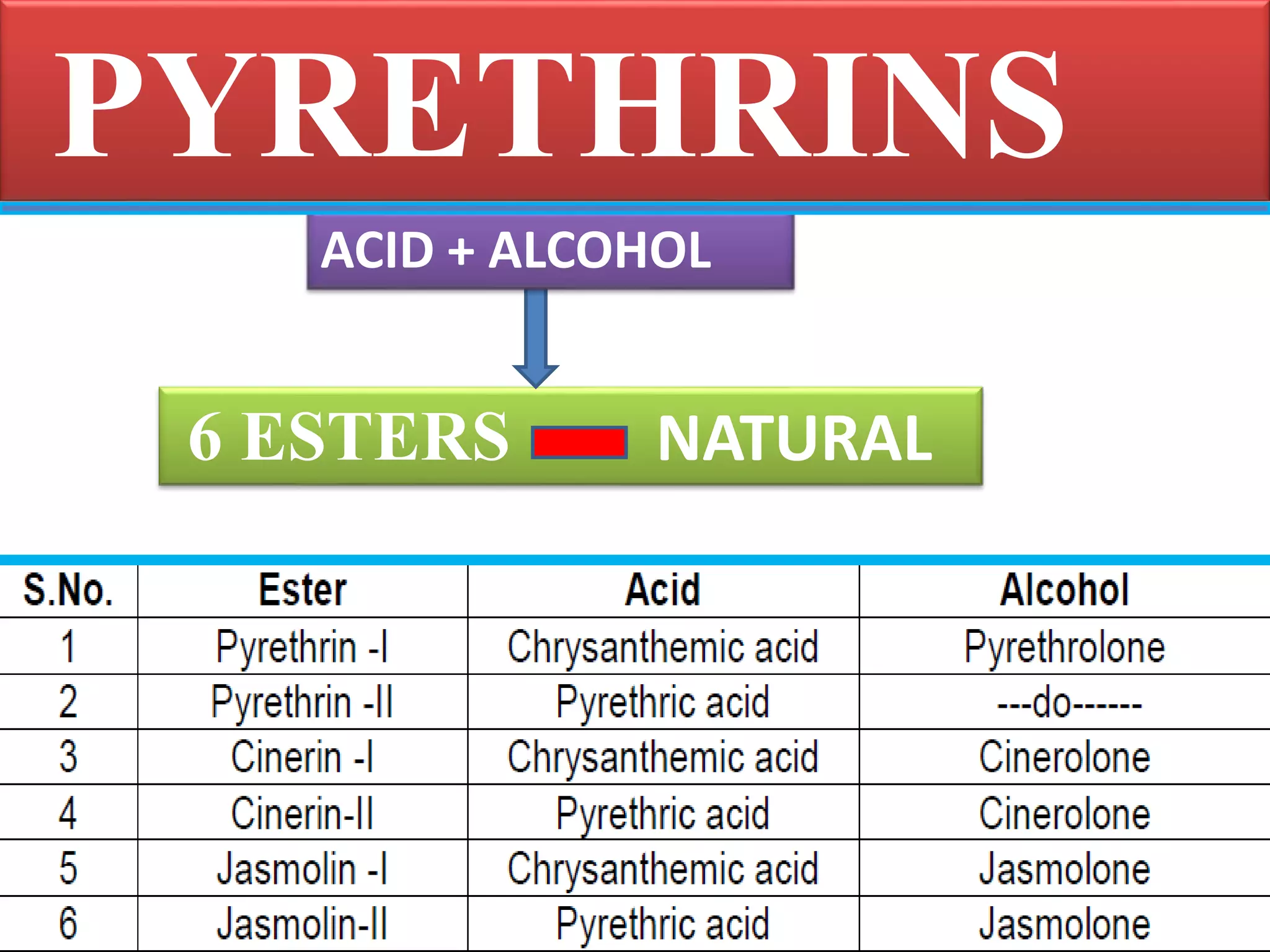
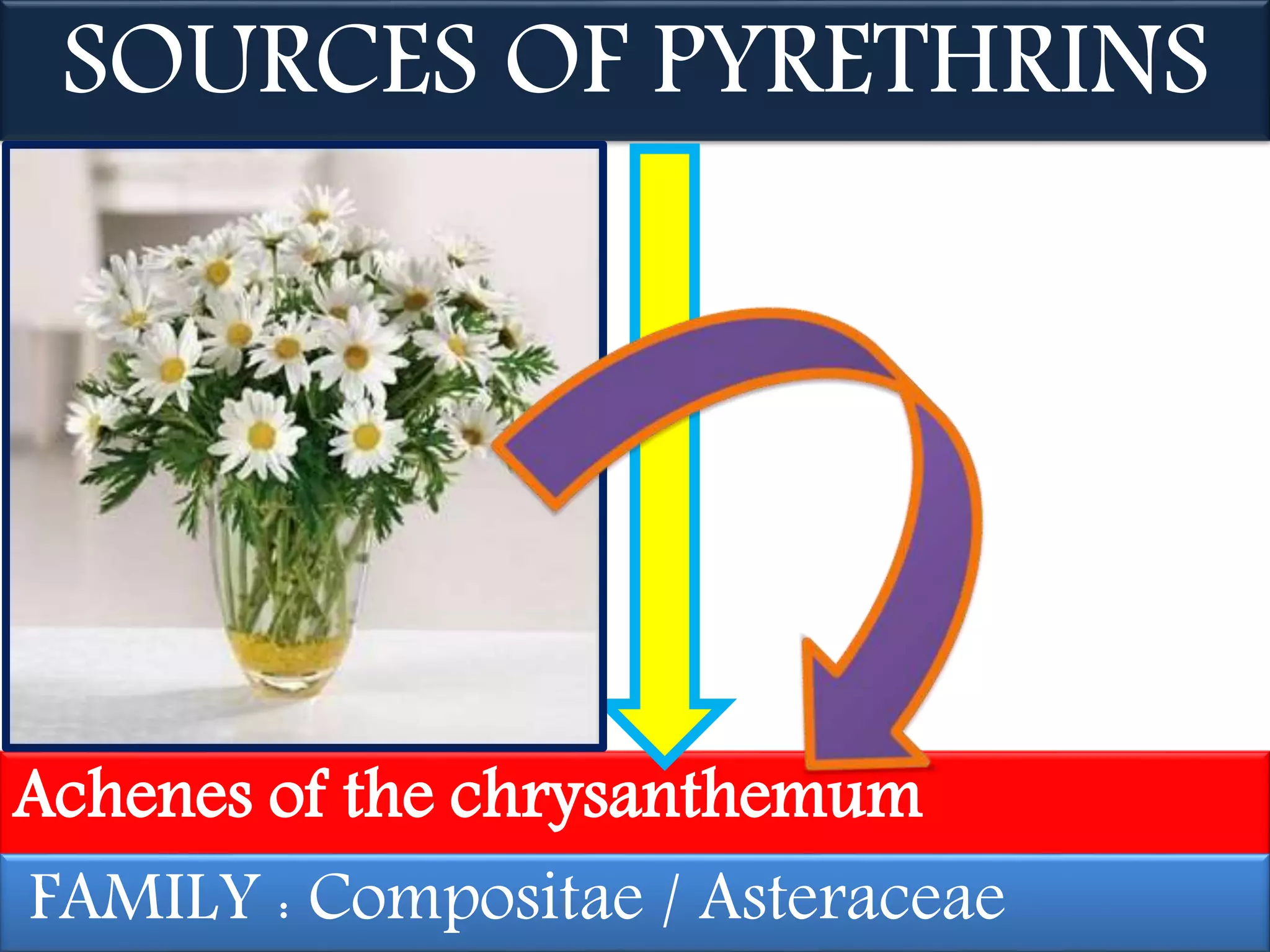
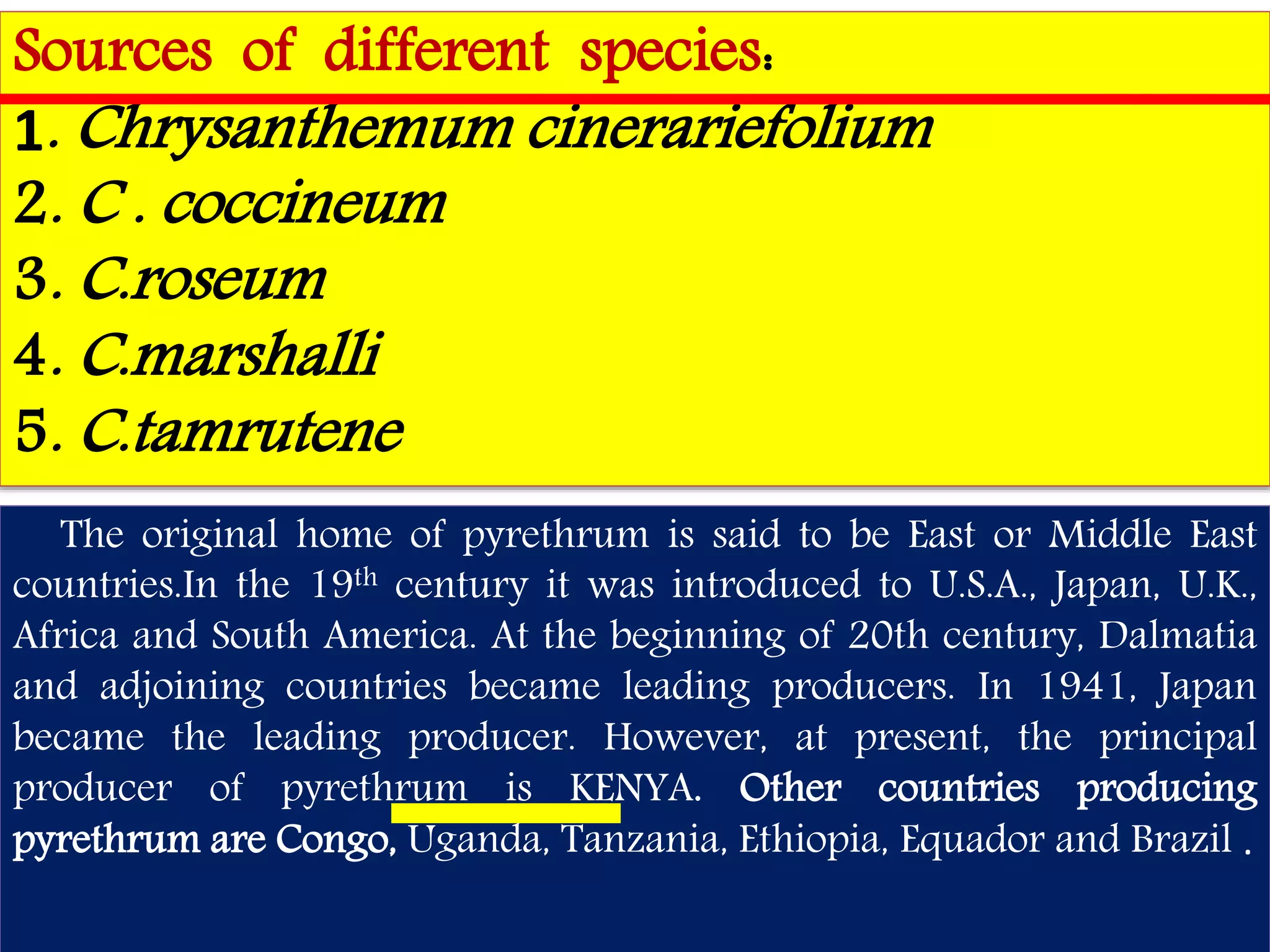
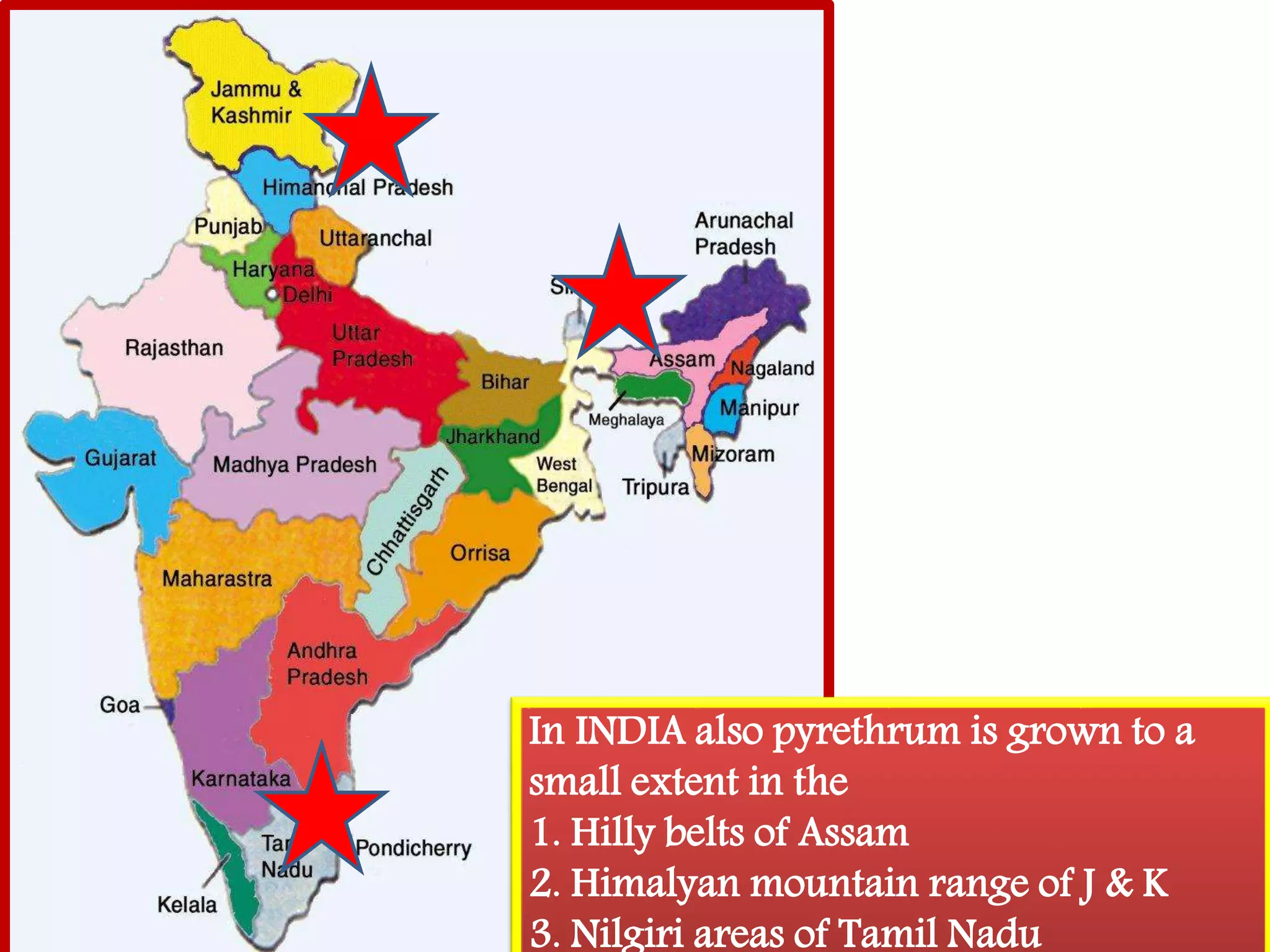
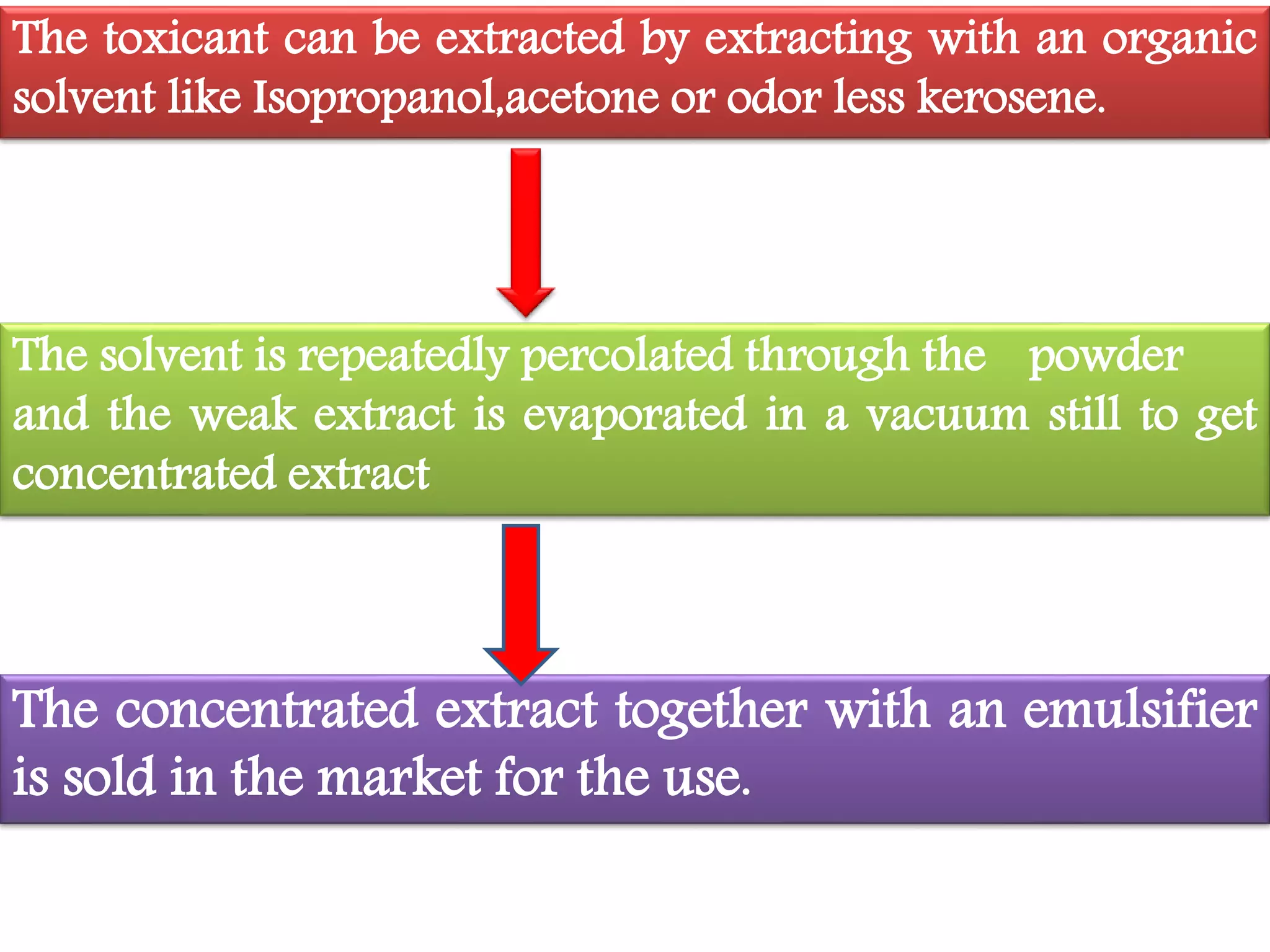
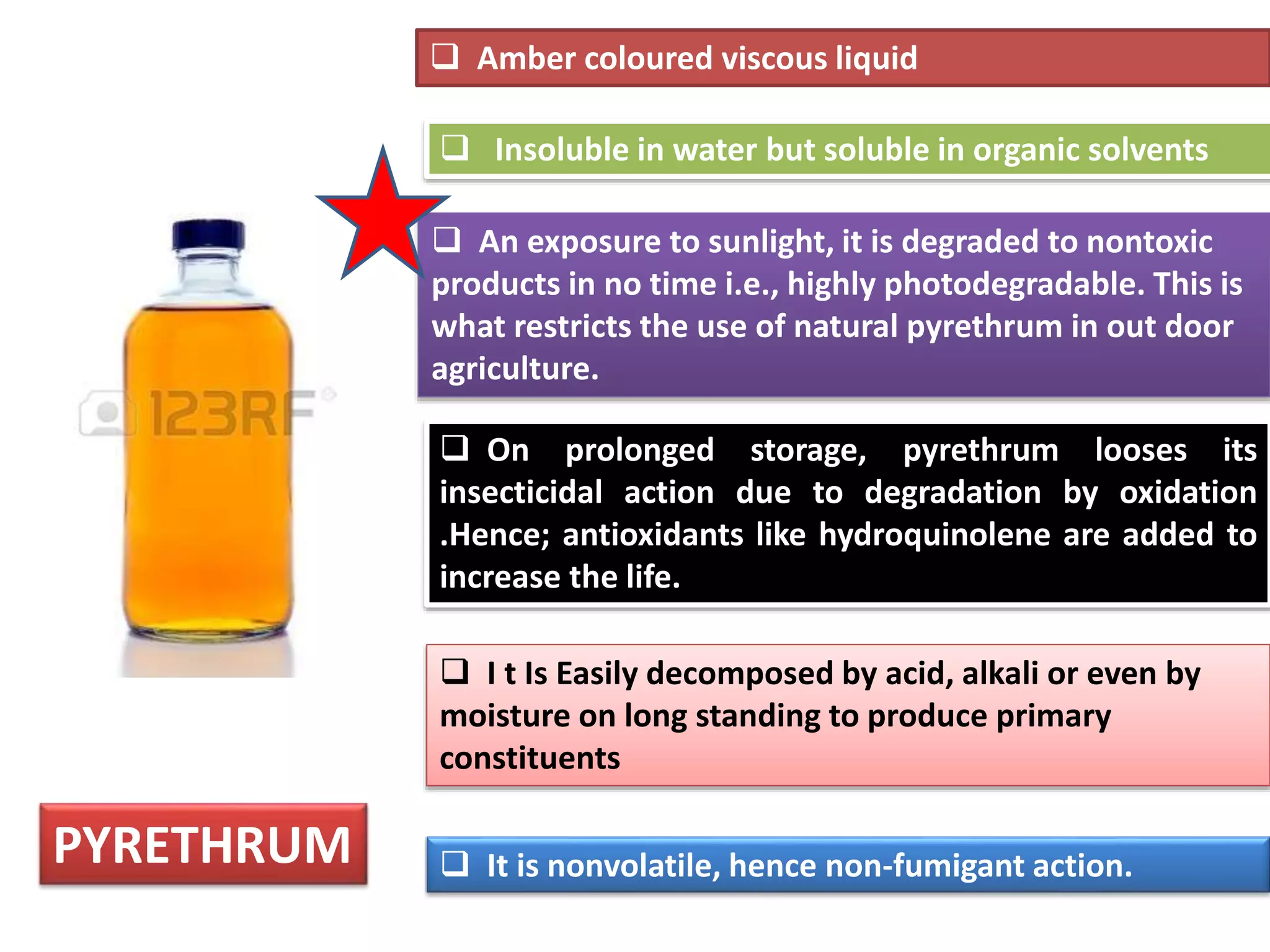
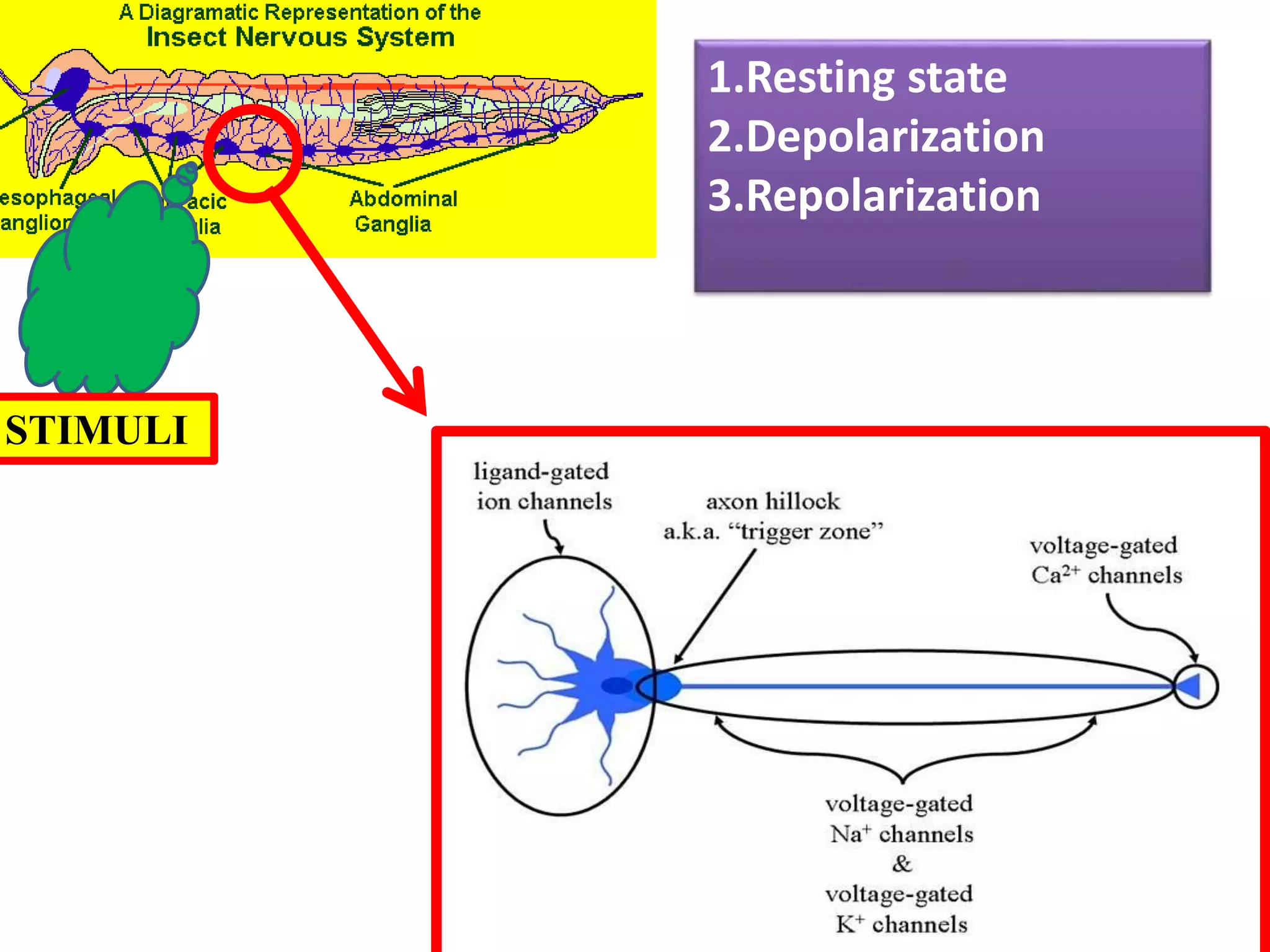
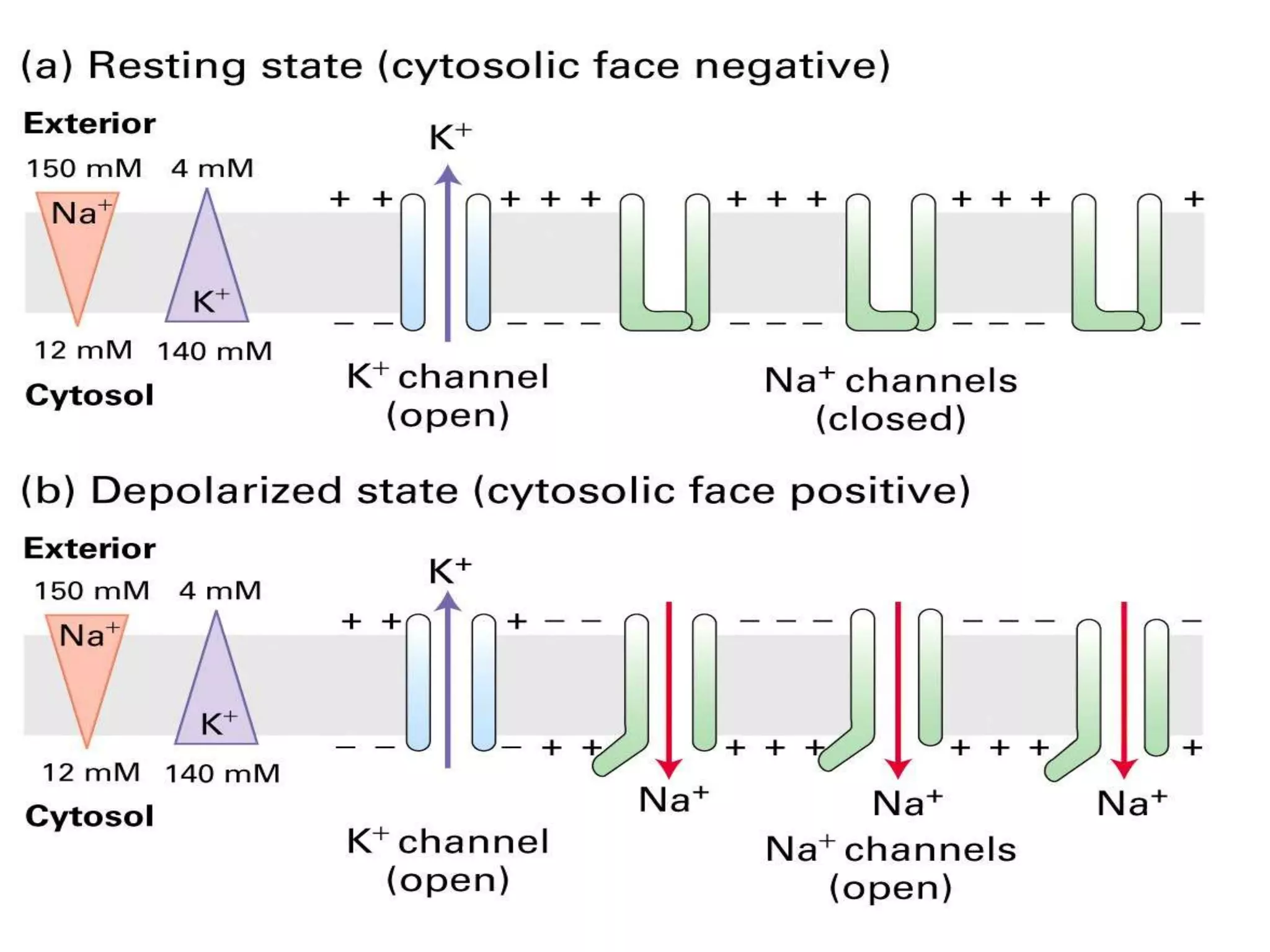
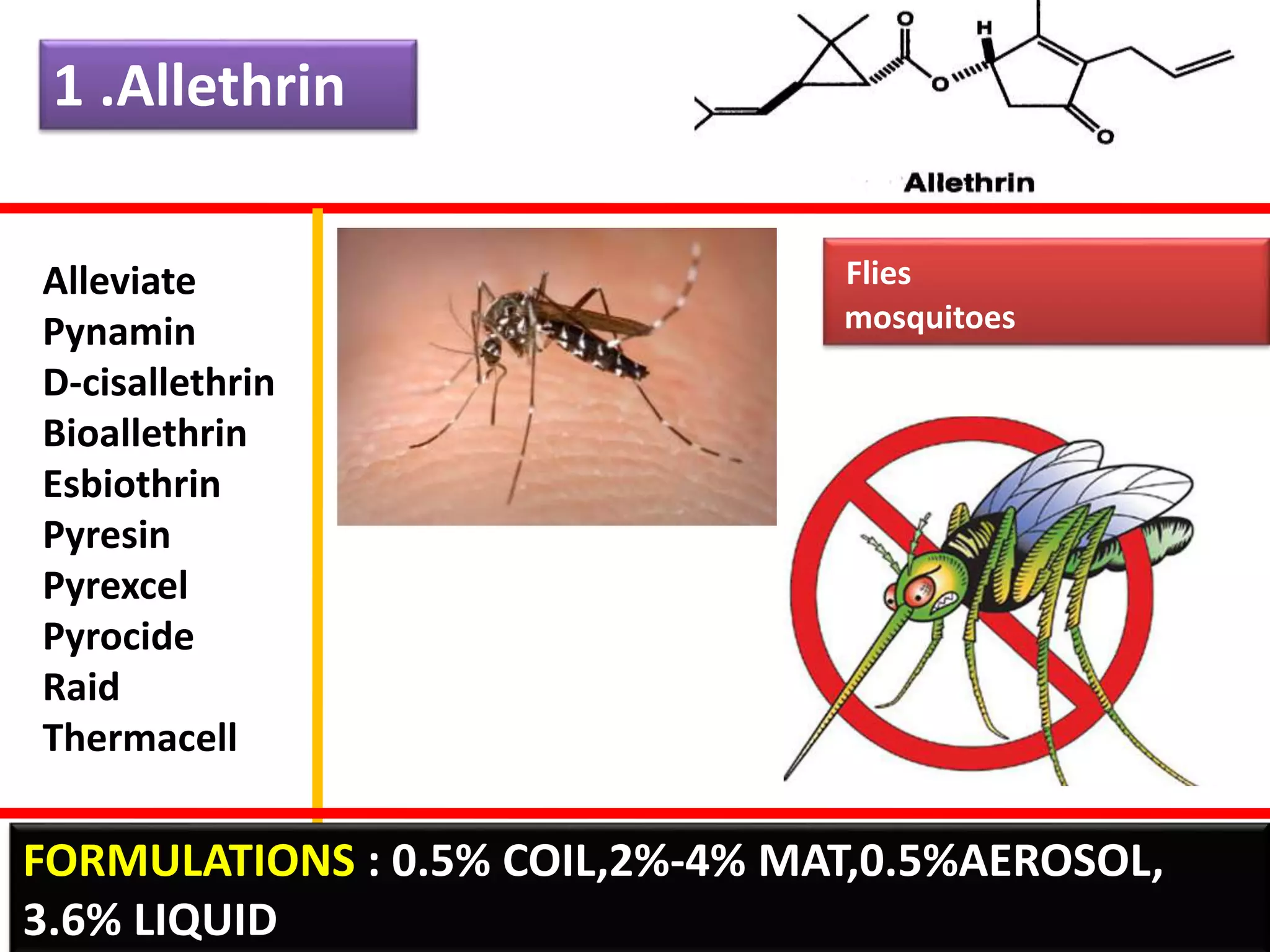
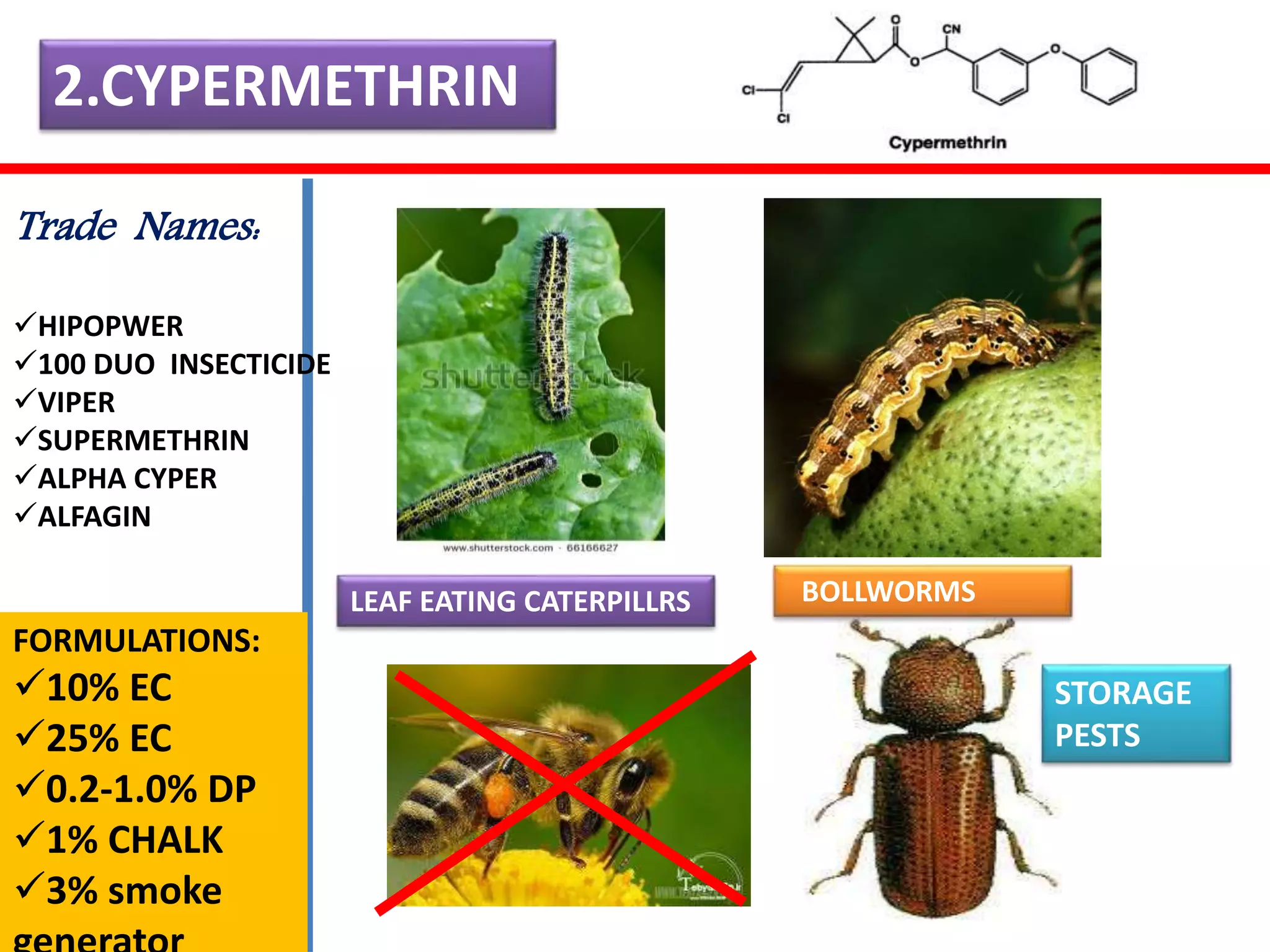
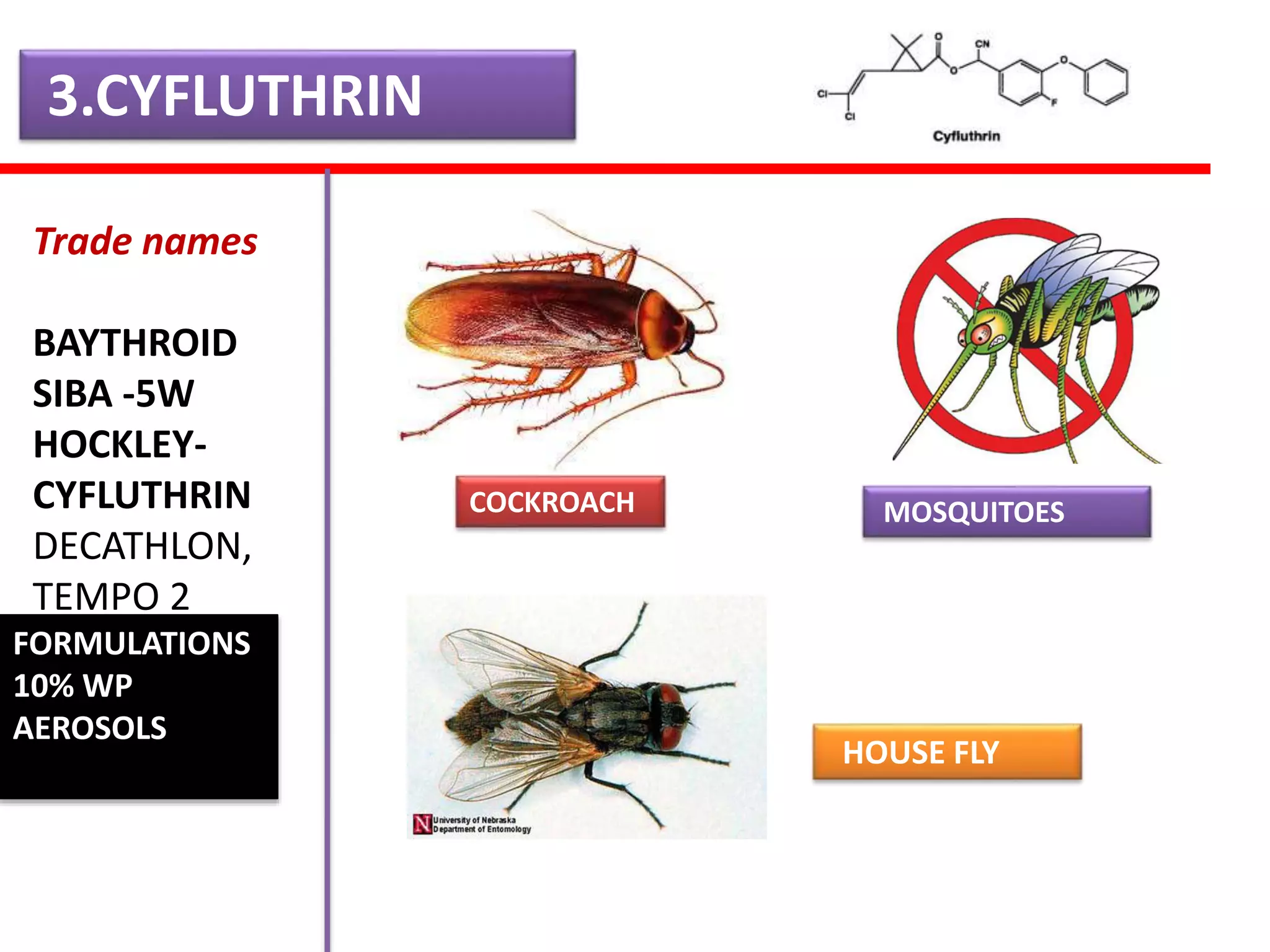
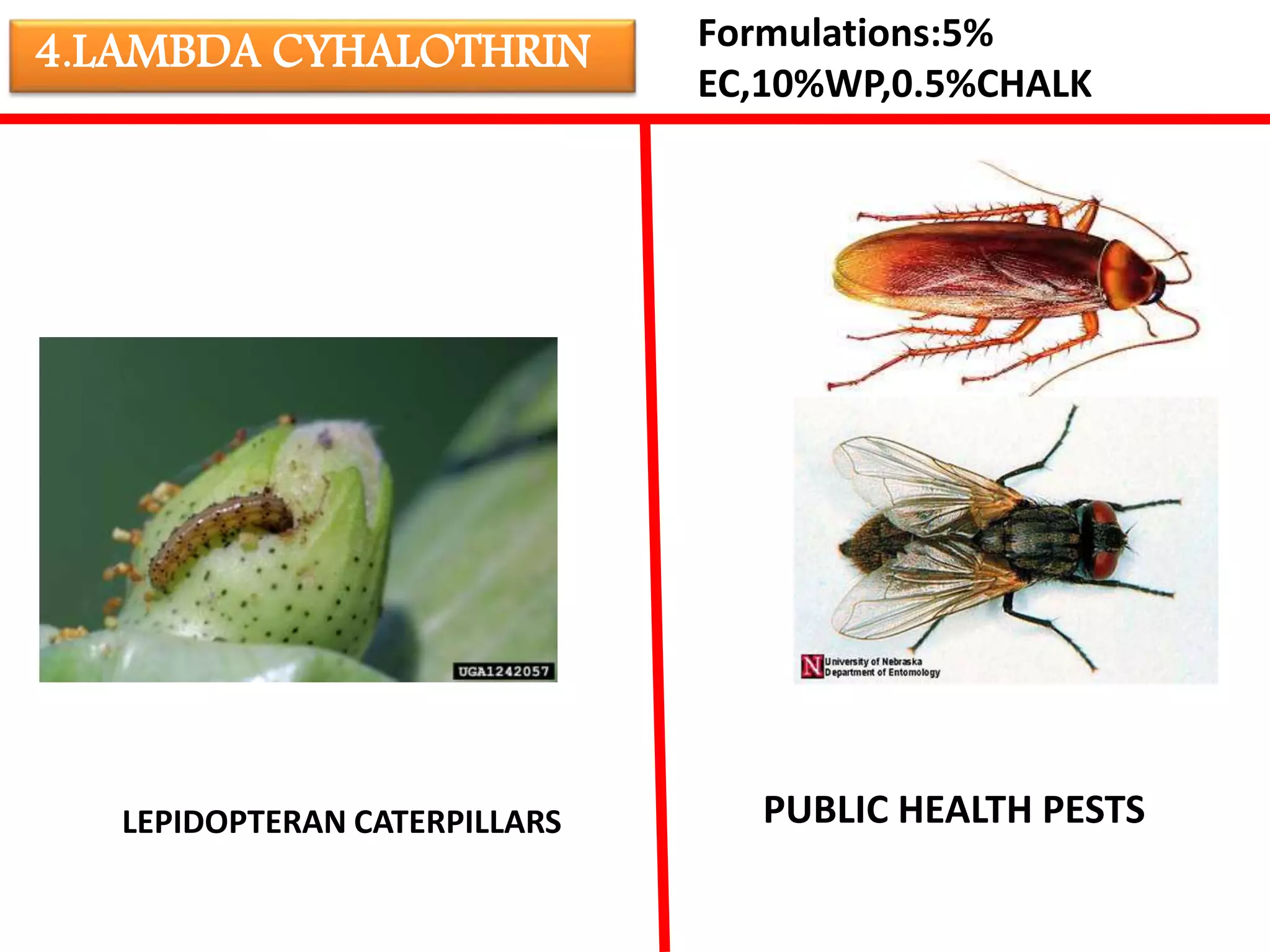
This document summarizes synthetic pyrethroids, a class of insecticides. It begins by classifying all insecticides and noting where synthetic pyrethroids fall. It then compares natural pyrethrins to synthetic pyrethroids. Examples of major synthetic pyrethroids are provided, along with their formulations and target insects. The document discusses the extraction of natural pyrethrins from chrysanthemum flowers and the modes of action of synthetic pyrethroids. It concludes with symptoms of poisoning and examples of common synthetic pyrethroid compounds.