The entomopathogenic bacteria is isolated from insect cadavers or soil samples by heat treating the samples to kill vegetative cells and enrich for bacterial spores, plating the samples on growth media to obtain isolated colonies, and transferring colonies to liquid culture. The bacteria is mass cultured in flasks containing UG medium on an orbital shaker to induce sporulation and production of parasporal crystals. The spores and crystals are harvested through centrifugation, washing, and resuspension in water or saline for use in bioassays or storage.


![4
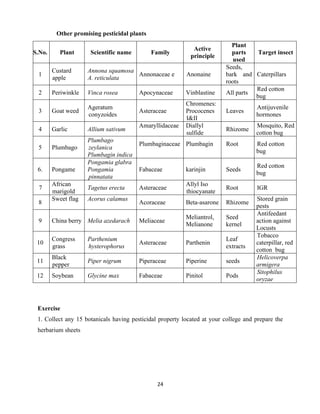
Ex. No: 01
TERMS, CONCEPTS, RULES AND REGULATIONS FOLLOWED
IN BIOPESTICIDE LABORATORY
Date:
AIM
The student should get acquainted with the terms, concepts, rules and regulations
followed in the biopesticide laboratory.
TERMINOLOGY
Entomopathogen/ Insect pathogen: Entomopathogens are infectious agents,
microorganisms that invade and reproduce in an insect and spread to infect other insects. Eg:
Fungi, bacteria, actinomycetes and nematodes etc.
Insect pathology: Insect pathology is the study of anything that goes wrong [i.e., disease
(“lack of ease”)] with an insect.
Infectivity: Ability of microorganism to enter the body of a susceptible insect and produce an
infection
Pathogenicity: The quality or state or being pathogenic, the potential or ability to produce
disease
Virulence: The disease producing power of an organism, the degree of pathogenicity within
a group or species
Dosage: A minimal number of infective propagules needed to pass through the portal of entry
for infection to occur in an insect
Sign: Physical or structural abnormality in an insect as a result of infection. Eg:
Abnormalities in the morphology or structure such as colour, malformed appendages or body
segments, fragility of the integument, etc.
Symptom: Functional and behavioural abnormality in an insect as a result of infection. E.g:
Abnormal movement, abnormal response to stimuli, digestive disturbances (vomiting or
diarrhoea), inability to mate, etc.
Syndrome: It refers to a system complex or a particular combination or sequence of signs
and symptoms (Group of characteristic signs and symptoms)
Course of infection: It is the time from when the entomopathogen infects/enters the host
until its death
Incubation period: It is the time from when the entomopathogen infects/enters the host until
the development of signs and/or symptoms
Acute infection: Acute infections are of short duration and usually result in the death of the
host (i.e., the period of lethal infection is short).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpracticalmanualelec230-converted-220416133957/85/Final-Practical-Manual-ELEC-230-converted-pdf-4-320.jpg)







![12
Mass culturing techniques
The growth of most commonly used entomopathogenic bacteria, B. thuringiensis and
B. sphaericus is typically done at 30 ºC and UG medium has provided reliable and
reproducible growth, sporulation and production of parasporal bodies in both cases.
Preparation of a 10-ml preculture
• From a stock or a colony from a fresh plate, is inoculated into the tube containing 10
ml UG medium to serve as a preculture.
• After inoculation, culture is incubated on a shaker for 48 h at 30ºC and then observed
for sporulation. After sporulation occurs, the preculture is heat-treated at 80 ºC for 10
minutes to kill vegetative cells. Heat treatment allows for a more consistent growth of
the new culture. This preculture will be used to inoculate the cultures for large scale
production.
Harvesting of spores/crystals
• Erlenmeyer flask (1 litre) containing 100 ml UG medium is subjected to sterilization
at 121ºC for 15 minutes. After sterilization, glucose is added to give 1%final
concentration. [Glucose stock solution of 10% that has been filter sterilized should be
used]
• Flask is inoculated with ~ 0.5 ml of a preculture and incubated at 30º C with orbital
agitation for 48 to 72 h until cell lysis is complete. Culture should be checked under a
phase-contrast microscope to monitor cell lysis, the sporulation rate and presence of
parasporal crystal proteins.
• Then culture is subjected to centrifugation at 5000 rpm for 15 to 20 minutes.
Supernatant is decanted and pellet of spores and crystals is collected
• The pellet of spores and crystals is resuspended with 0.5 M NaCl for 15 min to avoid
exoprotease activity.
• The resuspended spore crystal mix is centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 15 to 20 min. Again
the pellet is resuspended in distilled or deionized water and centrifugation is repeated.
• Finally, the pellet is resuspended in a water volume identical to the initial culture (i.e.
200 ml). This material can be used in bioassays to determine target insects or pellet
of spores/ crystals is freeze dried for long term storage
Exercise
1) Isolate entomopathogenic bacteria from insect cadaver and soil and culture it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalpracticalmanualelec230-converted-220416133957/85/Final-Practical-Manual-ELEC-230-converted-pdf-12-320.jpg)