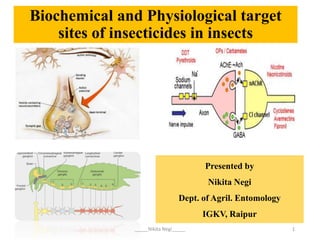
Biochemical and physiological target sites of insecticides on insect
- 1. Biochemical and Physiological target sites of insecticides in insects Presented by Nikita Negi Dept. of Agril. Entomology IGKV, Raipur 1 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 2. Insect Nervous system 1. Sensory neuron 2. Interneuron 3. Motor neuron Passage of information (electrical signal) 2 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 3. INSECT NERVOUS SYSTEM Insect Neuron 3 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 4. Mechanism of Impulse conduction Axonic conduction • Ionic composition (Na+ and K+) varies between inside and outside of axon resulting in excitable conditions, which leads to impulse conduction as electric response Synaptic conduction • Neurochemical transmitters are involved in the impulse conduction through the synaptic gap. Neurotransmitters (Ach, GABA, Octapomine) and the type of reactions help in the impulse conduction 4 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 5. Axonic conduction Action Potential STAGES OF NERVE CONDUCTION 1. Resting potential 2. Depolarisation 3. Repolarisation 4. Hyperpolarisation (more influx of negative ion) it is required to inhibit the hyperexcitation of nerve 5 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 7. 1. Insecticide affecting voltage gated sodium channels • DDT group • Pyrethroids • Indoxacarb • Sabdilla • Metaflumizone 7 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 8. MOA of DDT group and Pyrethroids, • DDT and Pyrethroid Insecticides bind to sodium channels • Delay sodium channel closing • Axon doesn’t readily recover to its resting stage • Repetitive discharges of axonal action potential • Excessive neuroexcitation cause Hyperactivity, tremors and rigid paralysis (Matsumura.,1985) 8 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 9. DDT Repetitive discharges of axonal action potential Axon doesn’t readily recover to its resting stage 9 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 11. Cross section of Sodium gate Acting site of DDT and Pyrethroid 11 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 12. Type I Pyrethroid Type II Pyrethroid Repetitive discharge of neurons Do not induce repetitive discharge - Cause slow depolarization of nerve membrane - Reduce amplitude of the action potential Negative temperature coefficient Positive temperature coefficient Behavioral arousal, Body tremor Profuse salivation and tremors leading to seizures Examples-Permethrin Examples- Cypermethrin 12 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 13. Sabadilla Veratridine Cevadine Prolong the opening of Sodium channels by delaying the channel closing (Bloomquist.,1999) Sabadilla is an insecticide produced from the seeds of the sabadilla plant, Schoenocaulon officinale 13 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 14. Indoxacarb • Metabolized by esterases/amidase to N decarbomethoxylated metabolite (DCJW) • Metabolite is Sodium channel blocker in insect • Binds to sodium channel and prevents sodium ions from flowing into Axon 14 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 15. Metabolite Indoxacarb is proinsecticide that is readily metabolized by an esterases to DCJW 15 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 16. 2. Insecticide affecting Ryanodine receptors Ryanodine • RyRs -Class of intracellular calcium channels • Muscle contraction is mediated by calcium channels • Depolarization activates these channel and stimulate the release of chemical transmitter, Amino acid glutamate 16 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 17. How muscle contraction take place? Glutamate Synaptic cleft Bind to receptor influx of sodium and calcium ion sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium channel calcium into protein filaments Muscle contraction 17 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 18. Flubendamide (pthalic diamide insecticide) and chlorantraniliprole (Anthranilic diamide) • Chlorantraniliprole – Selective RyRs activator • It activates RyRs through binding to receptor site • Stimulate release of ca ion cause impaired regulation of muscle contraction • It affect cardiac muscle causing feeding cessation and immobility • Cyantraniliprole- share same mode of action 18 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 20. 3. Insecticide inhibiting acetylcholinesterase Organo- phosphates - Binding of OP - Phosphorylation of Ache - Dephosphorylation NOTE: Dephosphorylation is slow Reversible Days or even weeks 20 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 21. Carbamates -Binding of carbamate -Carbamylation of Ache -Decarbamylation NOTE: Decarbamylation is very fast Irreversible Minutes 21 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 22. 4. Insecticide interfering with chloride channels 1. GABA gated chloride channel 2. Glutamate –gated chloride channel γ-Aminobutyric acid, or GABA Reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system. 22 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 23. • Increase Cl permeability results in Hyperpolarisation • Effect of hyperpolarization is to maintain the membrane at its resting value so that excitability decreased • Cyclodeines (BHC) and Phenyl Pyrazole (Fipronil) Bind and block activation by GABA- Hyperexcitation CNS 23 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 24. Avermectins • Open Cl channel by binding to GABA • The avermectins open the GABA receptor chloride channel by binding to the GABA recognition site (receptor protein) and act as partial agonists (Abalis et al., 1986). • Continuous flow of Chloride – This chloride permeability increase can significantly hyperpolarize (make more negative) the membrane potential- Loss of sensitivity- Paralysis • Emmamectin benzoate and milbemectin share same mode of action Streptomyces avermitilis 24 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 25. Glutamate –gated chloride channel • Influx of chloride ion – hyperpolarize the membrane potential – maintain membrane at resting value • Signs of poisoning- Ataxia( poor mucle control) paralysis and death • Fipronil – block glutamate gated chloride channels GABA Both Invertebrate and Vertebrate Glutamate –gated chloride channel Invertebrate 25 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 26. 5. Insecticide that bind to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors • nAChR – both presynaptic and post synaptic nerve • Examples: nicotine, neonicotinoids (immidacloprid, acetamiprid, thiamethoxam, clothianidin), Sulfoxaflor (Sulfoxamine) and Spinosyn (Spinosad and Spinotram) • Mimic ach (Agonist)- activate nAChR • Activation cause influx of Sodium ion and generation of action potential 26 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 27. Overstimulation • Hyperexcitation • Convulsion • Paralysis • death 27 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 28. 6. Insecticide interfering with respiration • Cell respiration describes the metabolic reactions and process that occur in cell to produce ATP 28 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 29. Inhibitors of the mitochondrial electron transport system 29 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 30. Oxidative phosphorylation • Sulfluramid is first N-deethylated by cytochrome P450 monooxygenases to become perfluorooctane • This oxidative metabolite acts as a potent inhibitor (uncoupler) of oxidative phosphorylation, disrupting the proton gradient, thus inhibiting ATP production (Schnellman and Manning, 1990) 30 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 31. • Chlorfenapyr is activated by herbivores via oxidative removal of the N- ethoxymethyl group to become CL 303,268, which acts as an uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation. • It disrupts the proton gradient across mitochondrial membranes and subsequently impairs the ability of mitochondria to produce ATP, which in turn leads to the death of affected cells and ultimately to the death of the organism (Hunt and Tracy, 1998) 31 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 32. 7. INSECTICIDES DISRUPTING INSECT MIDGUT • Bt ( Bacillus thuringiensis) By disturbing cell osmotic balance 32 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 33. In experiments with gypsy moth larvae, Broderick et al. (2006) proposed a new mode of action for Bt. According to these authors, δ-endotoxin causes the formation of pores in the larval digestive tract. These pores allow naturally occurring enteric bacteria such as Escherichia coli and enterobacter to enter the hemocoel where they multiply in the hemolymph and causes sepsis. Midgut bacteria are required for Bt insecticidal activity. Thus, Bt induces death by septicemia. Septicemia is a term referring to the presence of pathogenic organisms in the bloodstream, leading to sepsis. Sepsis is the condition or syndrome caused by the presence of microorganisms or their toxins in the bloodstream or the tissue. 33 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 34. CHITIN SYNTHESIS 8. Insecticides affecting chitin biosynthesis 34 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 35. 8. Insecticides affecting chitin biosynthesis • Benzoylphenylureas(diflubenzuron,hexaflumur on, teflubenzuron, flufenoxuron, and lufenuron) and thiadiazines (buprofezin) are inhibitors of chitin biosynthesis. • These insecticides inhibit the final step of chitin synthesis, that is, the polymerization of N- acetylglucosamine 35 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 36. • Affect the elasticity and firmness of the endocuticle. • As a result, the cuticle is unable to support the insect and withstand the rigors of molting, leading to the death of the insect. • Example- in cabbage white butterfly (Pieris brassicae) larvae, diflubenzuron treatment causes an obliteration of the connection between epidermal cells and cuticular layers. The space in between contains scattered globules of apparently coagulated material (Gijswijt et al., 1979). • It was reported that chitin synthesis was blocked within 15 min after the application of diflubenzuron in the cuticle of Pieris brassicae larvae (Deul et al., 1978). 36 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 37. • Cyromazine does not inhibit the biosynthesis of chitin, but it is a molting disruptor. It affects cuticle sclerotization by increasing the cuticle stiffness in insects. • It has been reported that the cuticle of cyromazine-treated tobacco hornworm larvae rapidly becomes less extensible and is unable to expand to the degree normally observed. The larvae show impaired growth, eventually developing cuticular lesions, and die after a period of days (Reynolds and Blakey, 1989; Reynolds and Kotze, 1992). 37 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 38. 9. INSECTICIDE ACTING AS JUVENILE HORMONE Juvenile hormone • It prevent premature metamorphosis • JH tends to drop when as larva proceed to next instar • In adults insects it control reproduction i.e. oocyte development and vitellogenin production 38 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 39. Effects of the juvenile hormone (JH) analog insecticide methoprene on mosquito development. Under normal conditions 4th instar larval mosquitoes undergo a larval- pupal molt following a rapid reduction in haemolymph JH levels and concurrent spikes in molting hormone. When 4th instar Cx. quinquefasciatus are exposed to methoprene at exceptionally low levels (60 to 120 ng liter−1) unique morphologies are observed including larval-pupal monsters (A) and insects that are unable to complete pupal-adult eclosion (B). Kamita et al., 2011 39 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 40. • JH mimics (methoprene, hydroprene, fenoxycarb, and pyriproxyfen) act like JH and exhibit the highest toxicity when applied at the onset of metamorphosis, that is, in the last larval or early pupal stage • Pyriproxyfen affects the hormone balance in a wide range of insects, resulting in the inhibition of embryogenesis, metamorphosis, and adult formation (Ishaaya, 2001). • It strongly supports the notion that JH analogs act as JH agonists (Wilson, 2004). 40 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 41. Morphological abnormalities observed in ACP adults caused by exposure of late instars (fourth and fifth) to the two higher concentrations of pyriproxyfen (32 and 64 µg mL−1). a–f, twisted wings (tw); a–d, unable to emerge completely from exuvia (ex); c and d, wide abdomen (wa); e, deformed (thicker) antennae (da); f, deformed body (db). (Boina et al., 2010) 41 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 42. 10. Insecticide acting as ecdysone agonists • The ecdysone receptor (EcR) is a nuclear receptor that is involved in insect development • Diacylhydrazine insecticides (tebufenozide, methoxyfenozide, halofenozide, and chromafenozide) act as nonsteroidal ecdysone agonists. • They bind to specific ecdysteroid receptor binding proteins, interrupting the normal events from proceeding. Consequently, they induce an incomplete precocious molt, resulting in the mortality of the larva (Wing, 1988; Wing et al., 1988). 42 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 43. • Azadirachtin affects the brain–corpus cardiacum complex by inhibiting the release of the morphogenetic brain peptide, prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH), and other peptide hormones related to molting, such as eclosion hormone or bursicon, thereby blocking molting hormone activity. As a result, it suppresses fecundity, molting, pupation, and adult formation (Luntz et al., 2005). 43 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 44. 11. INSECTICIDE ABRADING INSECT CUTICLE • Boric acid is an absorber of insect cuticle wax and a stomach poison. • Its mode of action on insects has not been clearly established. Two major hypotheses have been proposed: 1. Abrasion of the cuticle followed by slow desiccation (Ware and Whitacre, 2004) 2. Destruction of the cellular lining of foregut after ingestion, causing the death of the insect by starvation (Cochran, 1995). 44 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 45. Examples • Cochran reported that when feeding boric acid to German cockroaches, the foreguts became empty and slightly enlarged on days 1 and 2 after treatment. By day 3 after treatment, the foregut cells of treated insects were completely destroyed, and by day 4, only the basement membrane remained. The author concluded that the most probable cause of death from ingested boric acid is starvation due to destruction of the foregut. 45 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 46. • Habes et al. (2006) also reported that dietary boric acid altered the midgut epithelial cells of the German cockroach. • Sumida et al. (2010) found that boric acid caused cell death in the midgut epithelium of the leaf-cutting ant Conti… 46 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 47. • Silica aerogels kill insects by absorbing waxes from the insect cuticle, resulting in slow desiccation and death by dehydration. • The wax layer normally prevents insects from losing water through their exoskeleton and desiccating. By adsorbing the wax layer, silica gel increase the permeability of the exoskeleton, resulting in insect death by dehydration • Pesticidal soaps disrupt the cuticle and break down cell membranes, resulting in rapid death of insects 47 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 48. 12. INSECTICIDE ACTING AS SELECTIVE FEEDING BLOCKERS • Pymetrozine (pyridine azomethine) is a selective feeding blocker against plant-sucking insects such as aphids, whiteflies, leafhoppers, and planthoppers. • In aphids (Myzus persicae) pymetrozine prevents insects from inserting their stylet into the plant vascular system. The feeding disruption appears to be related to the nervous regulation of feeding behavior, which consequently results in death due to starvation (Harrewijn and Kayser, 1997) • Pymetrozine also found to inhibit phloem ingestion in the rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (He et al., 2011). 48 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 49. Morita et al. 2007 Flonicamid inhibits aphid feeding by inhibition of stylet penetration to the plant tissue The feeding disruption appears to be related to the neurological effect of flonicamid on aphids, resulting in death from starvation. Flonicamid-treated aphids also displayed uncoordinated locomotion, walking staggeringly with their legs stretched 49 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 50. 13. INSECTICIDES CAUSING SUFFOCATION • The primary mode of action of pesticide oils such as paraffinic oil is through suffocation. • The spray forms a coating of oil on the insect’s body, which blocks the spiracles or breathing opening, resulting in the death of the insect by suffocation. 50 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 51. Target site Insecticide/Insecticide class Mode of action Voltage- gated Na channels DDT, Pyrethroids, Sabadilla Na channel modulator Indoxacarb, Metaflumizone Na channel blocker AChE Organophosphates and carbamates AChE inhibitors GABA-gated chloride channels Cyclodienes, Phenylpyrazoles, lindane Antagonism Glutamate- gated chloride channel Avermectins, Emamectin benzoate, milbemectin Activation Fipronil Channel blocker Biochemical and physiological target sites of insecticides on insects 51 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 52. Target site Insecticide/insecticide class Mode of action RyRs Ryanodine,flubendamide, chlorantraniliprole, Cyantraniliprole Modulator Mitochondrial electron transport system Rotenone, HCN, Tolfenpyrad, Fenazaquin, Phosphine, pyrimidifen, Tebufenpyrad, Fenpyroximate Inhibition Sulfluramid, Chlofenapyr Uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation Midgut cell membrane Bacillus thuringiensis Midgut membrane disruption Insect cuticle Benzophenylureas, Buprofezin Inhibition of chitin biosynthesis Cryomazine Molting disruption Boric acid, Silica aerogels Abrasion of cuticle Biochemical and physiological target sites of insecticides on insects 52 _____Nikita Negi_____
- 53. Target site Insecticide/insecticide class Mode of action JH receptors Juvenoids, fenoxycarb, pyriproxyfen JH mimic Azadirachtin Molting disruption Nervous system Pymetrozine, Flonicamid Selective feeding blocker Biochemical and physiological target sites of insecticides on insects 53 _____Nikita Negi_____