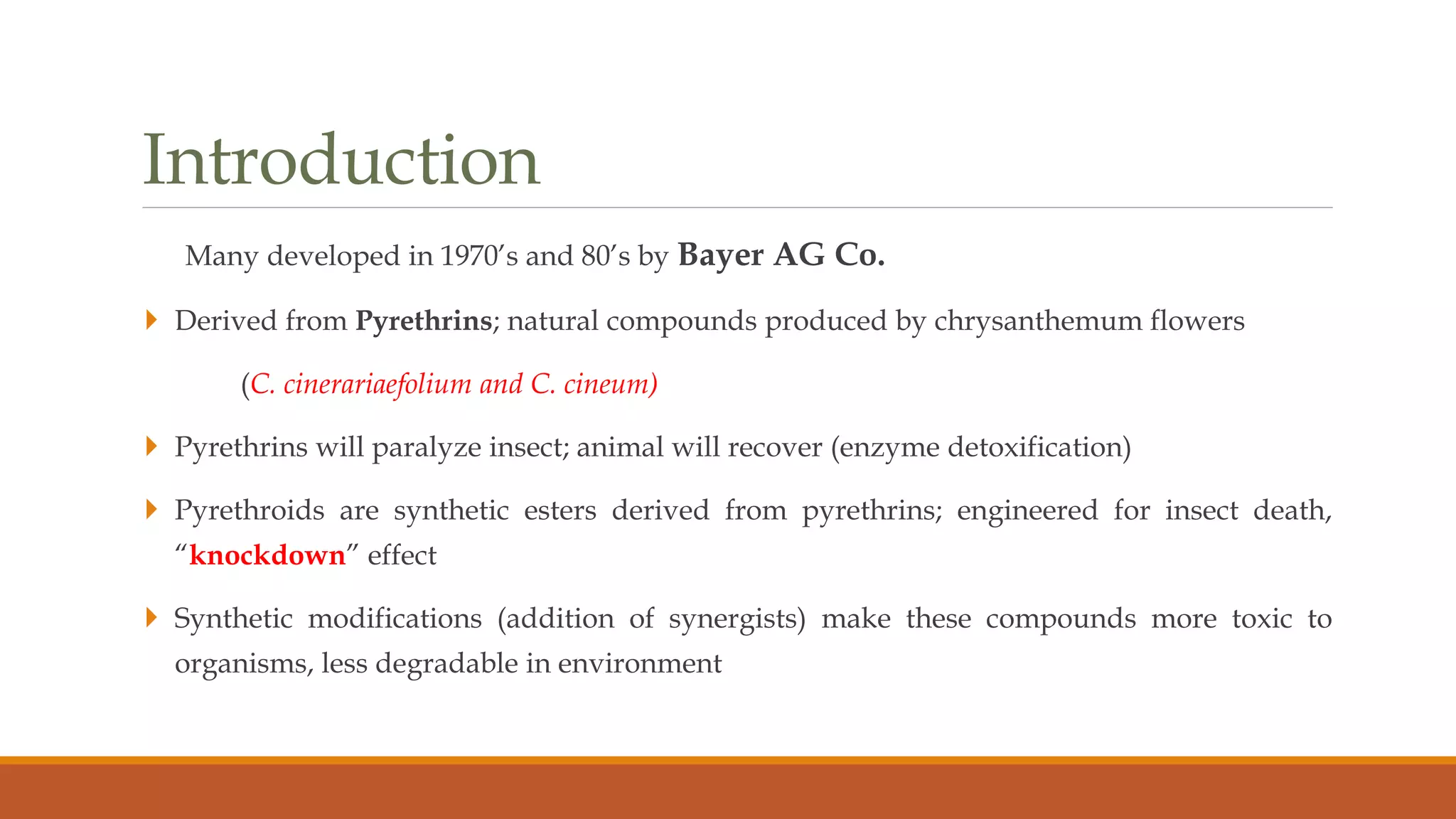
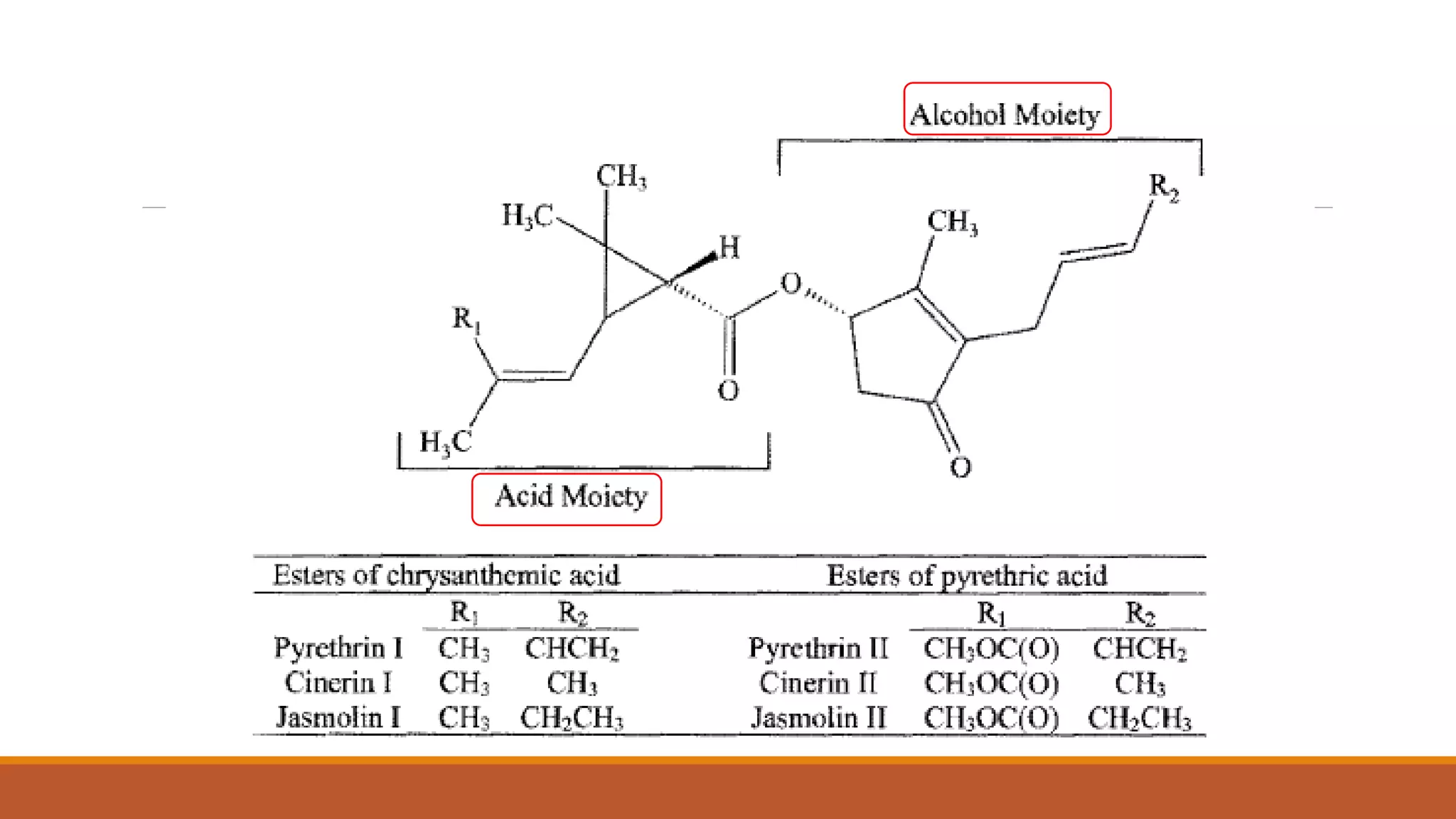
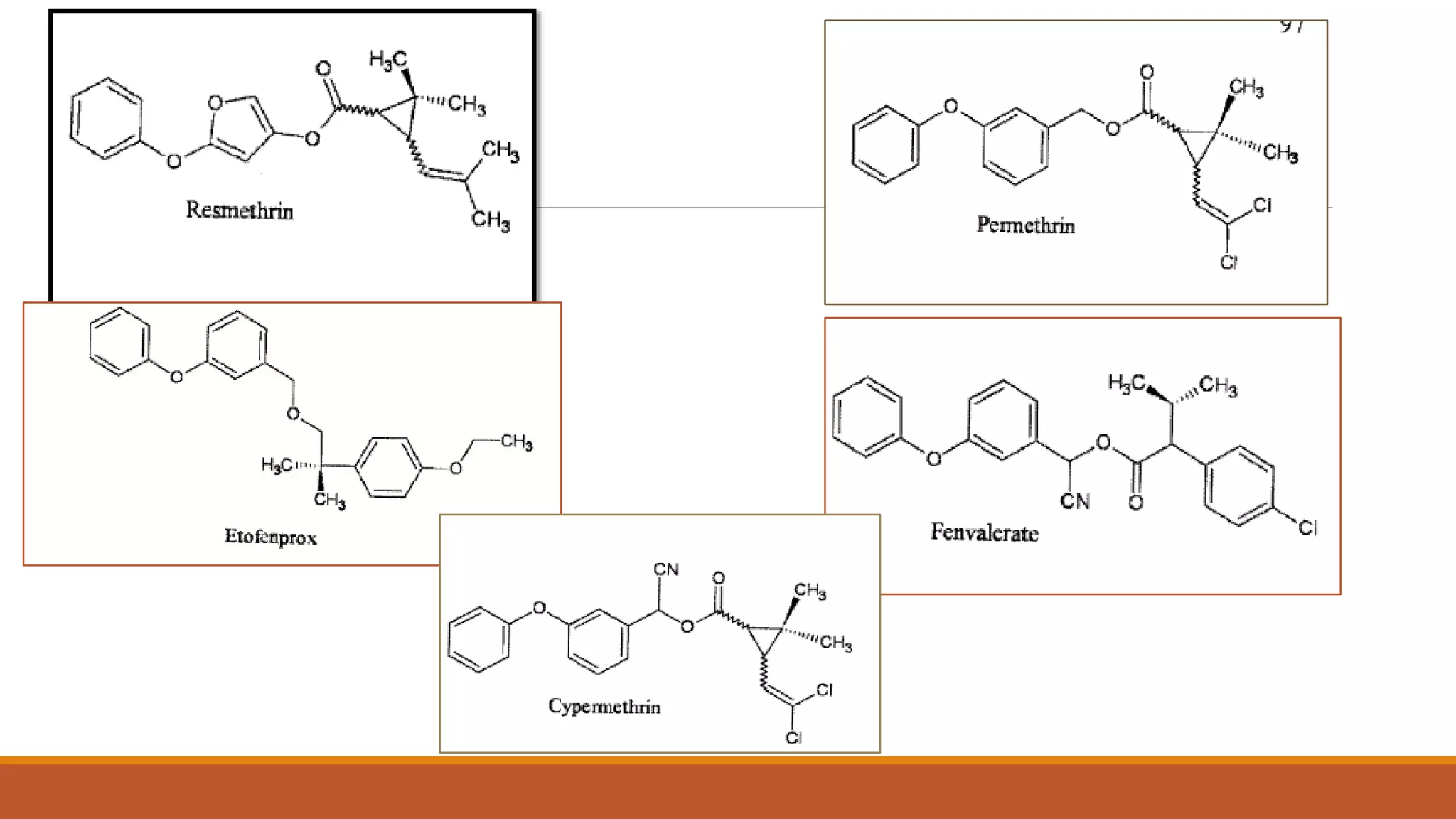
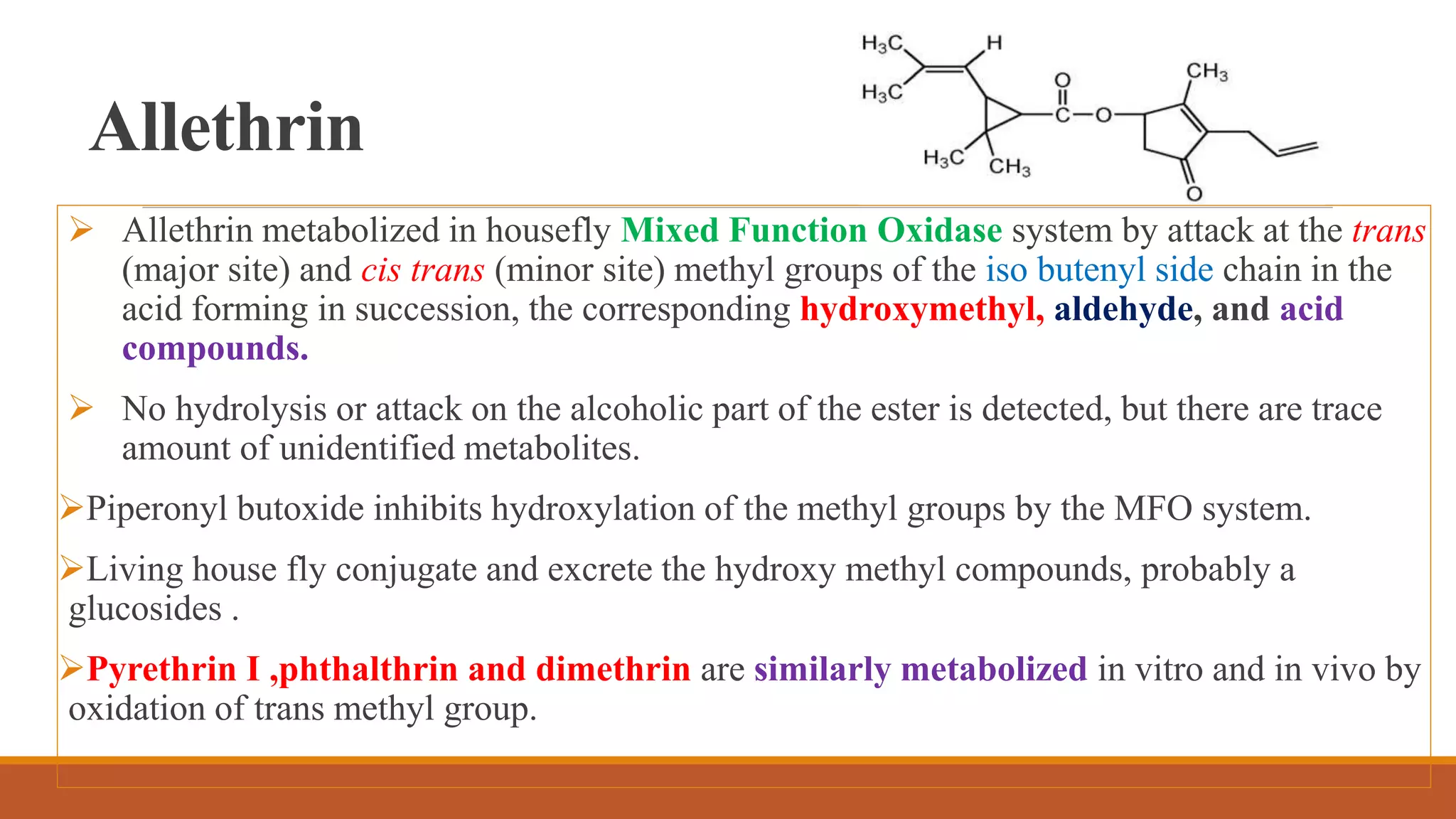
1) Synthetic pyrethroids are derived from natural pyrethrins produced by chrysanthemum flowers and were developed in the 1970s-80s to be more toxic to insects and less degradable.
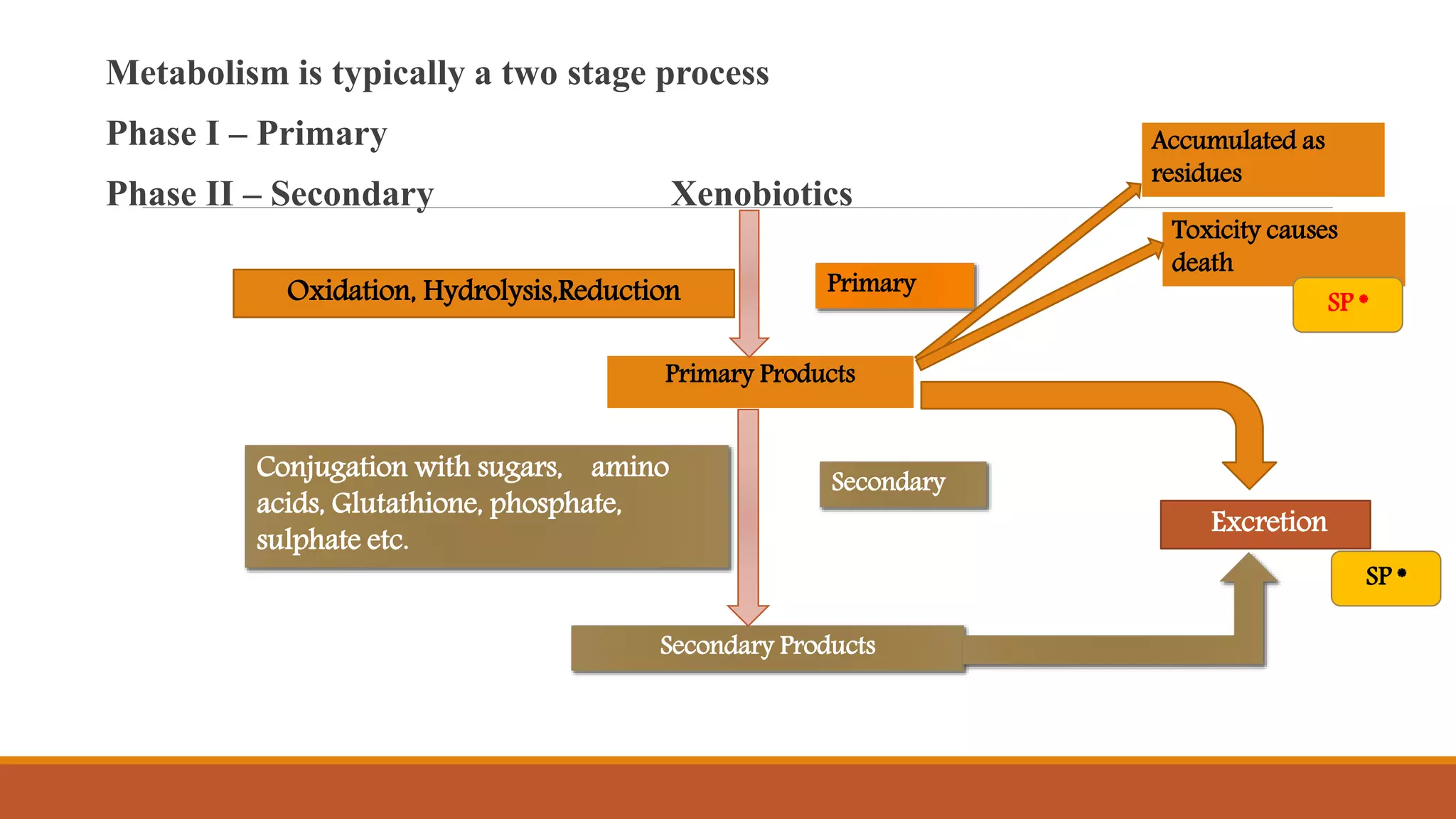
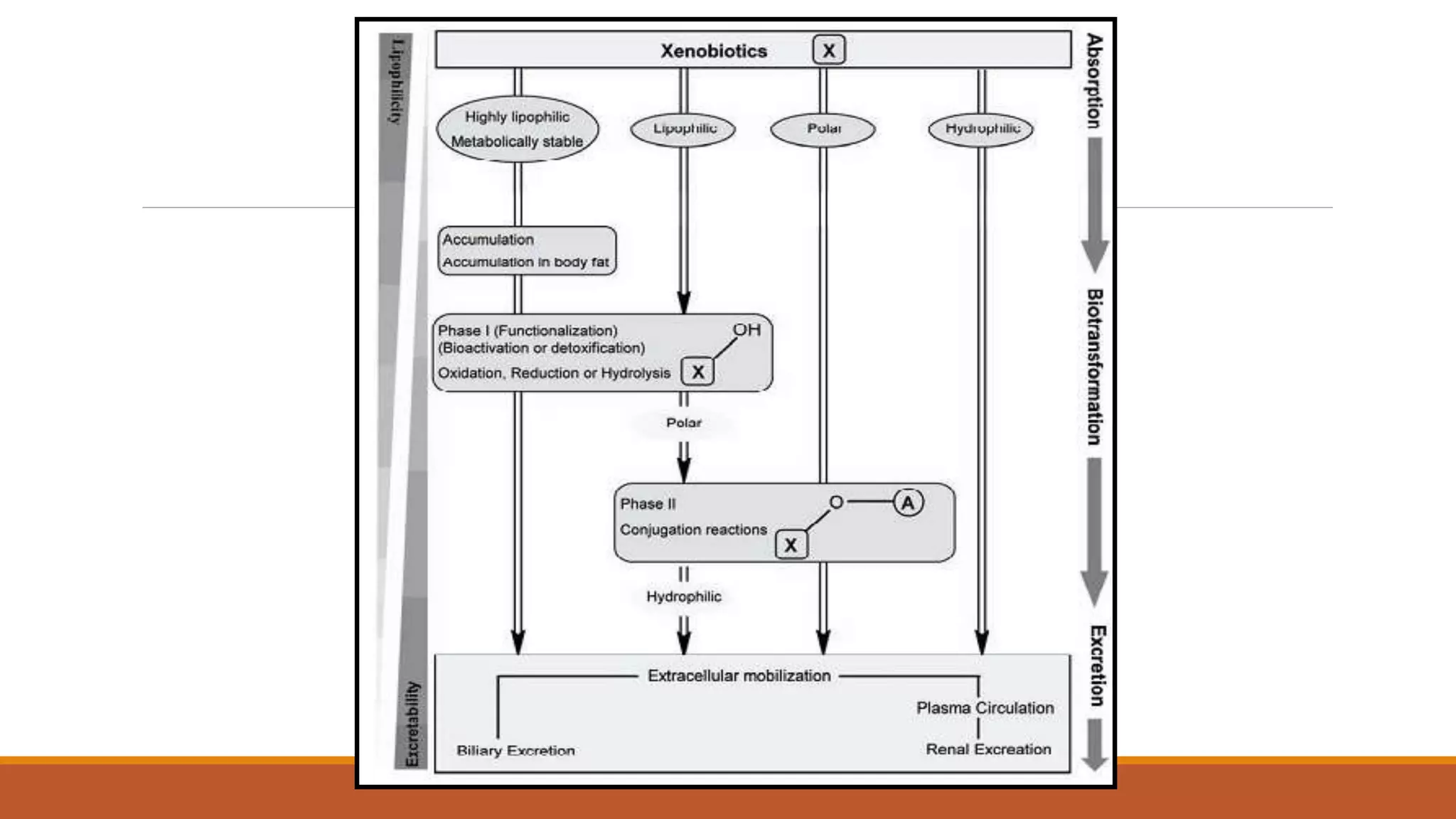
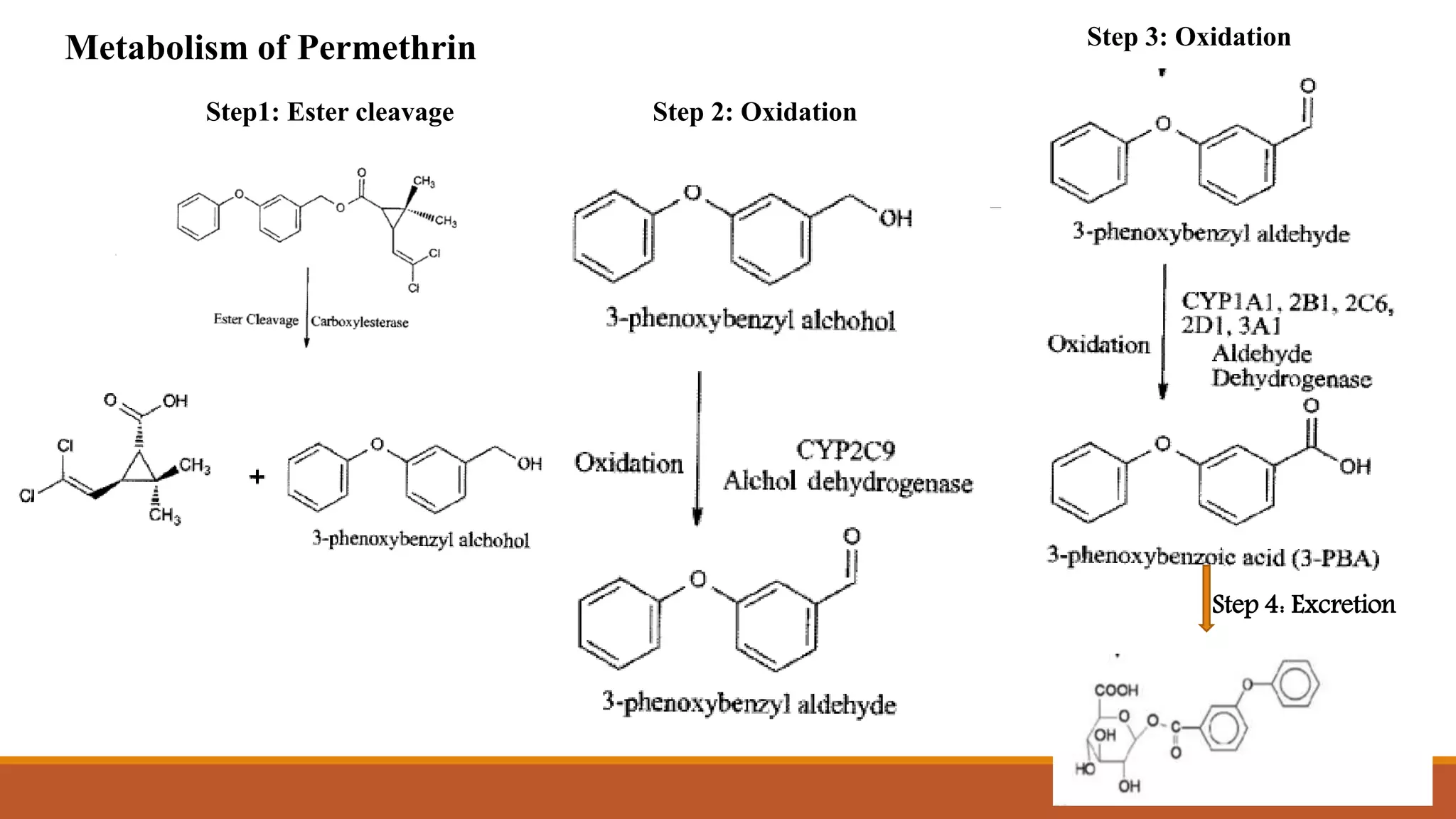
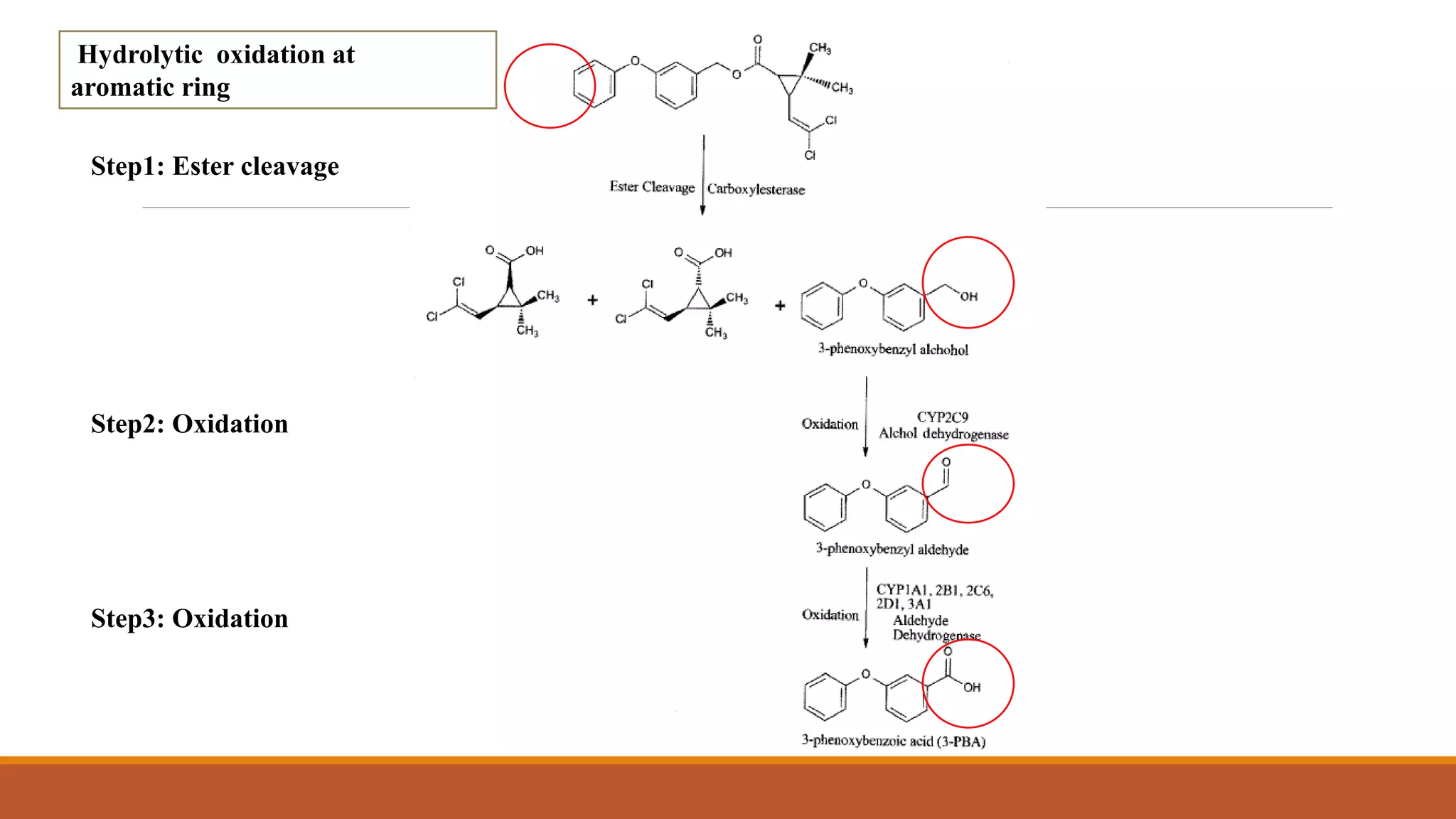
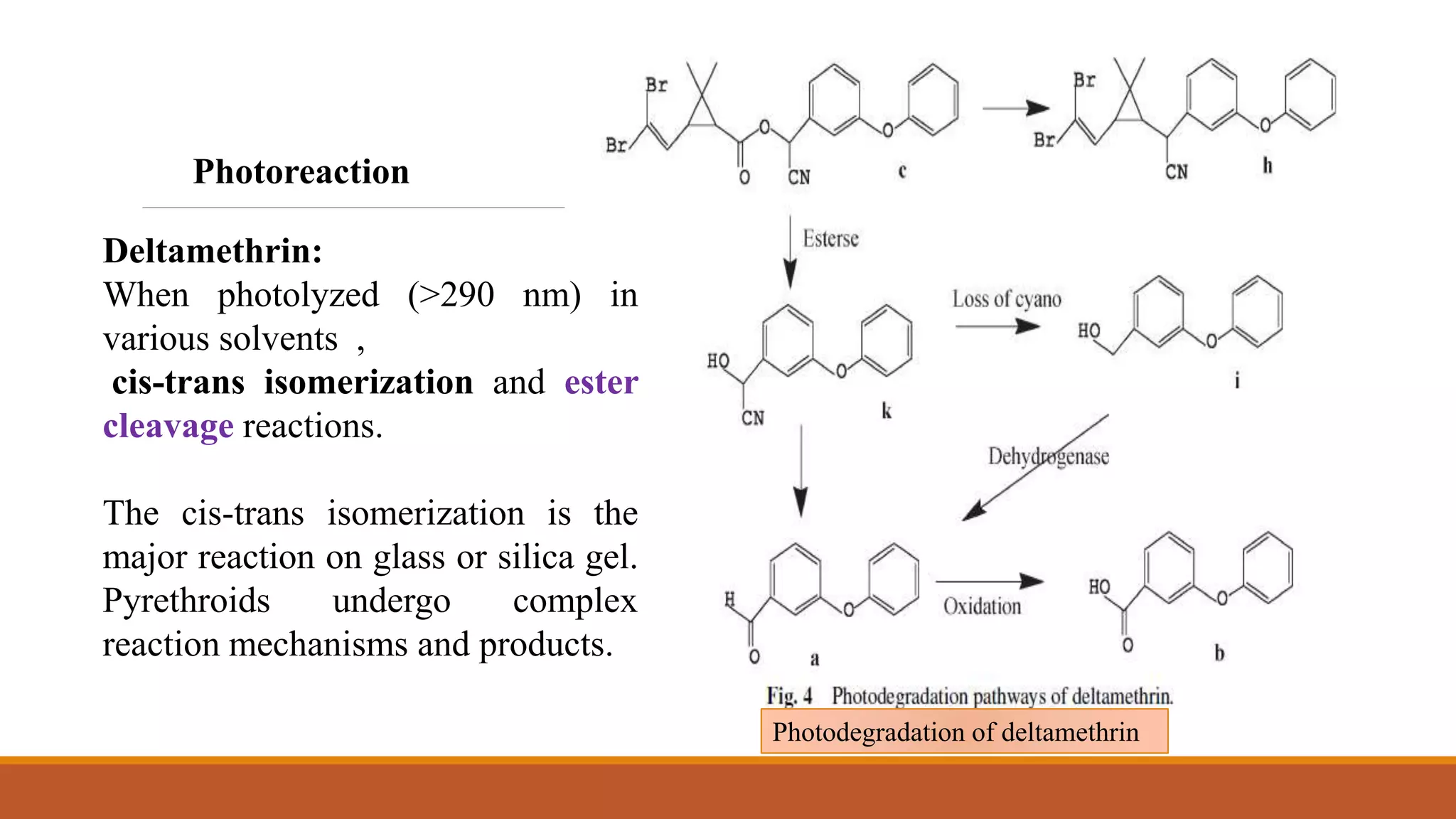
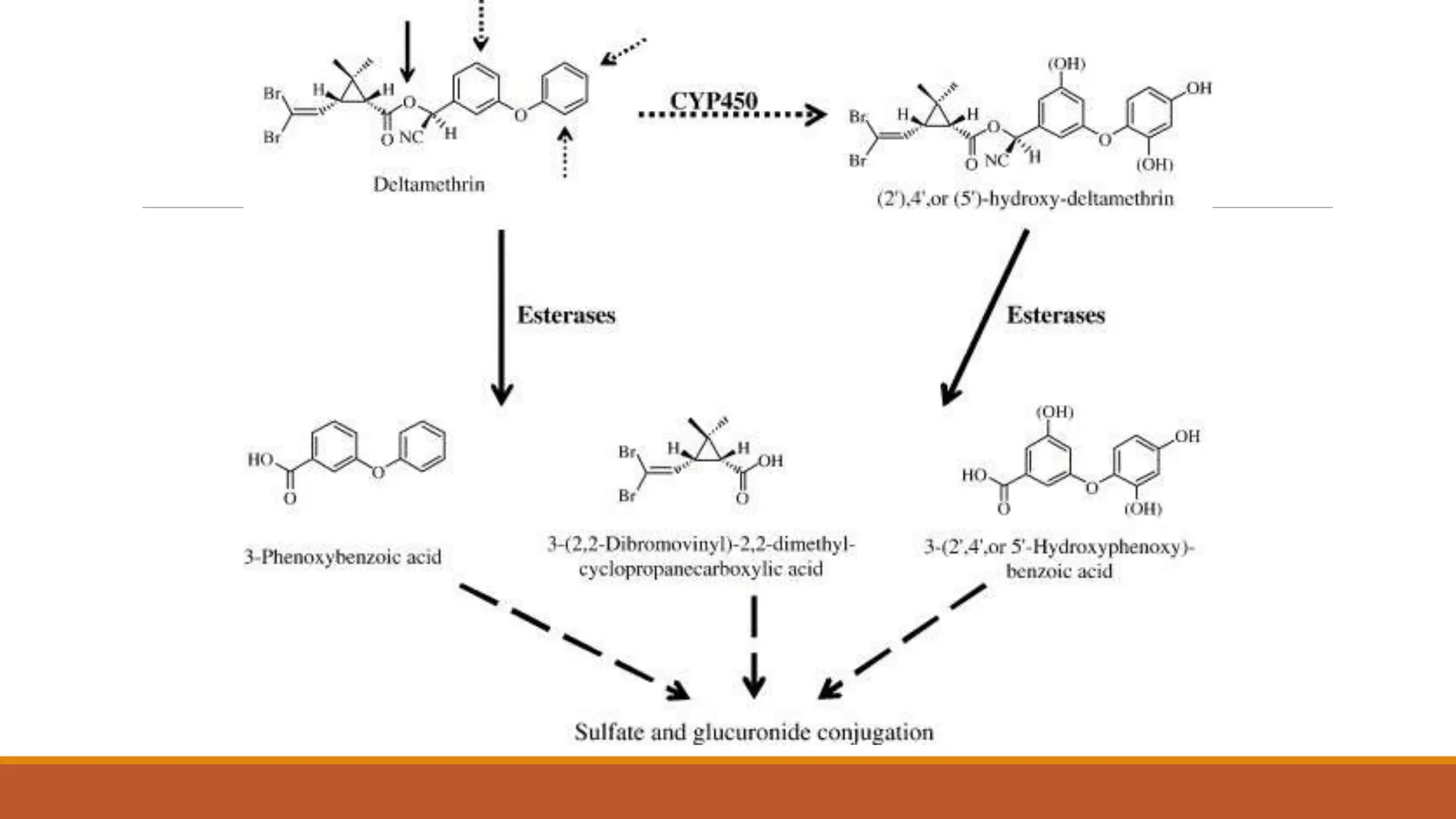
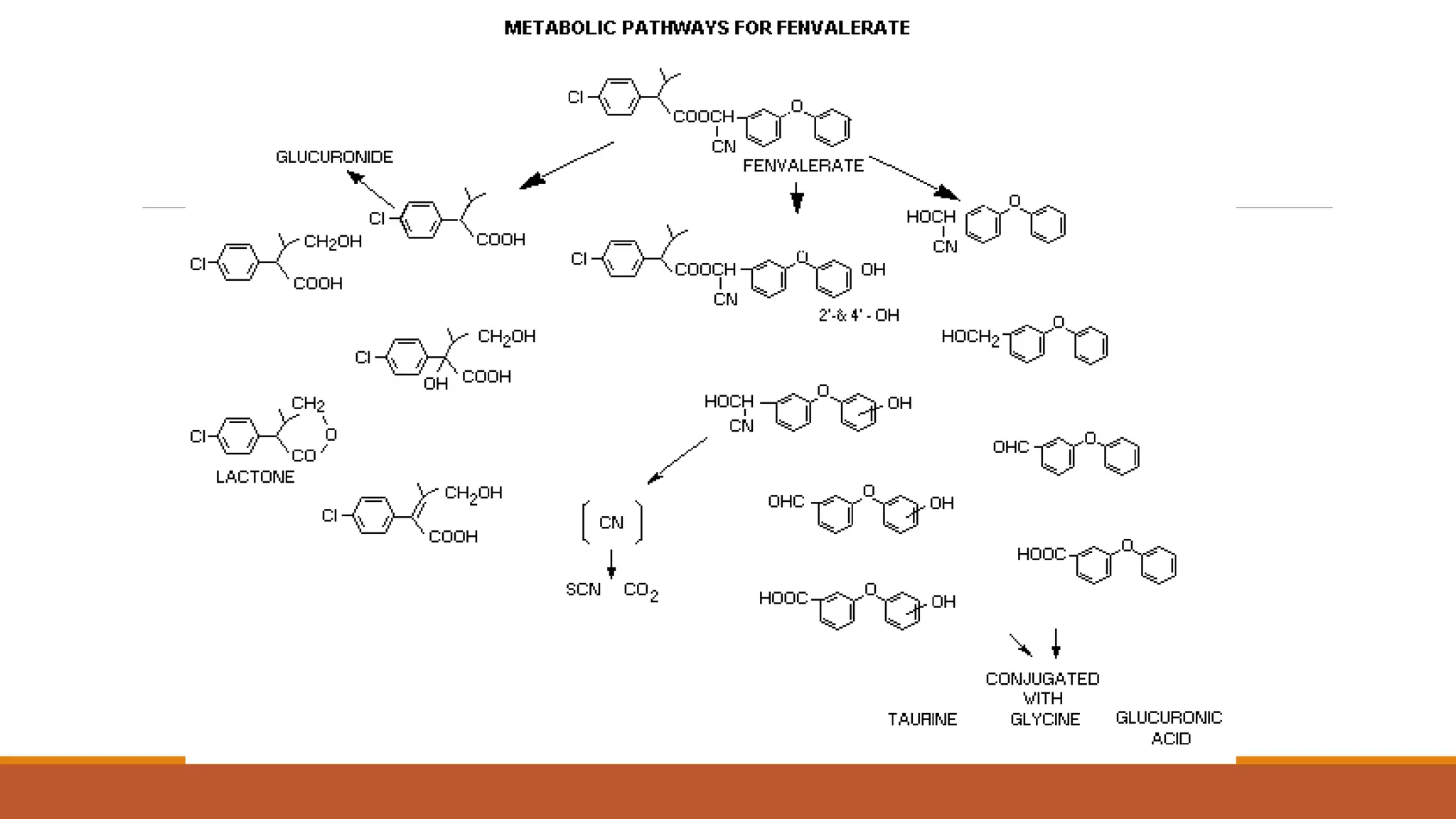
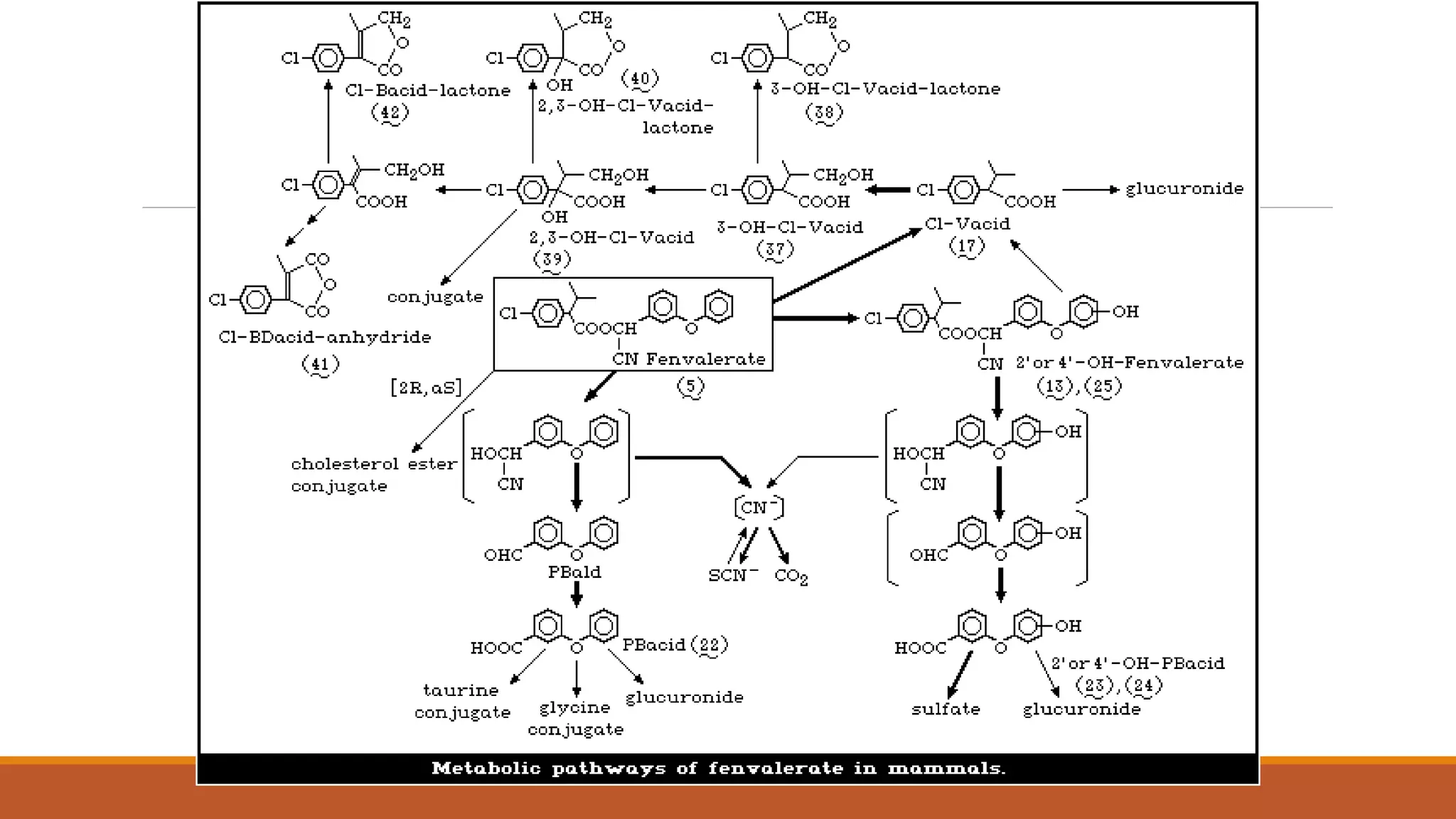
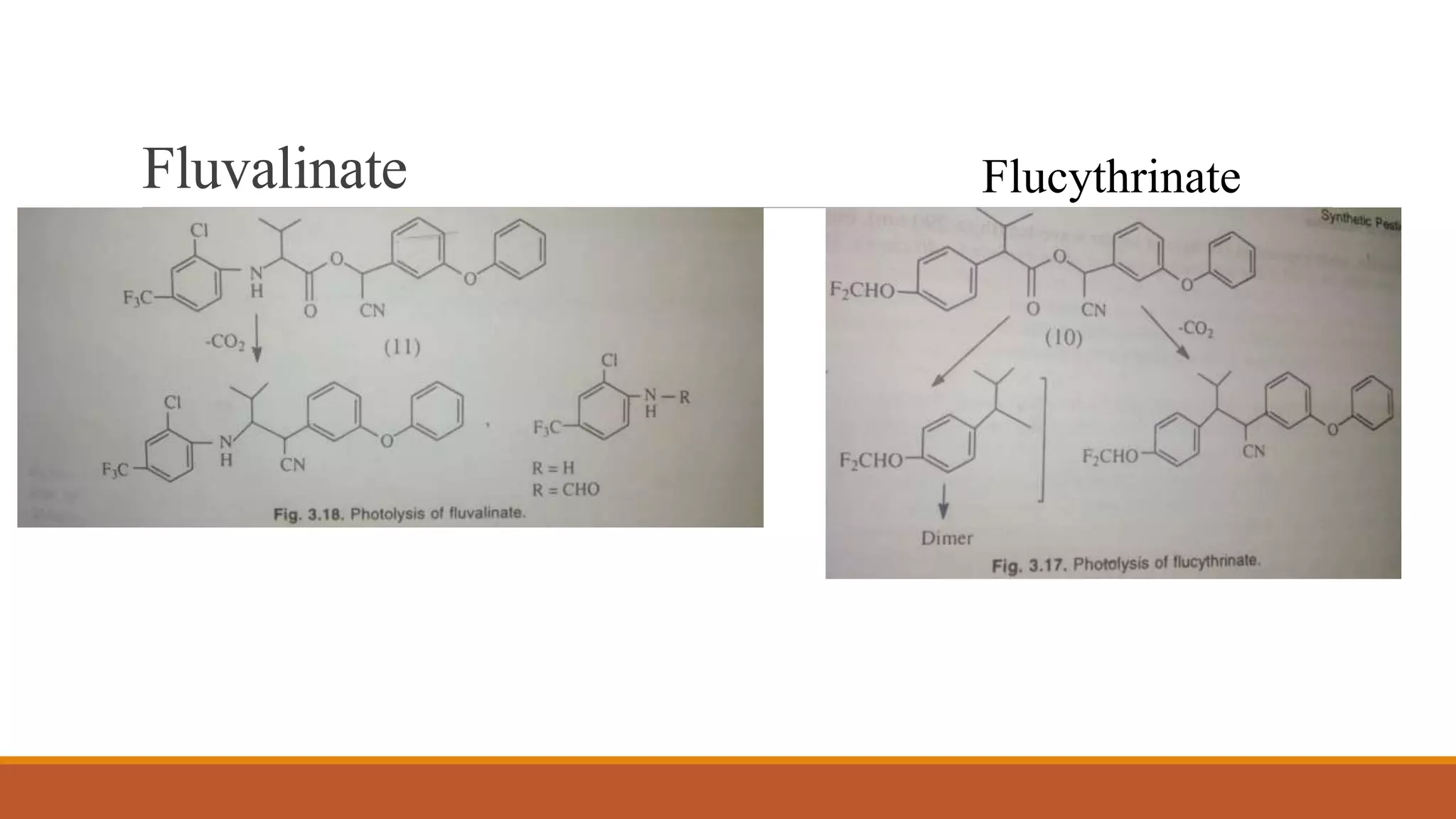
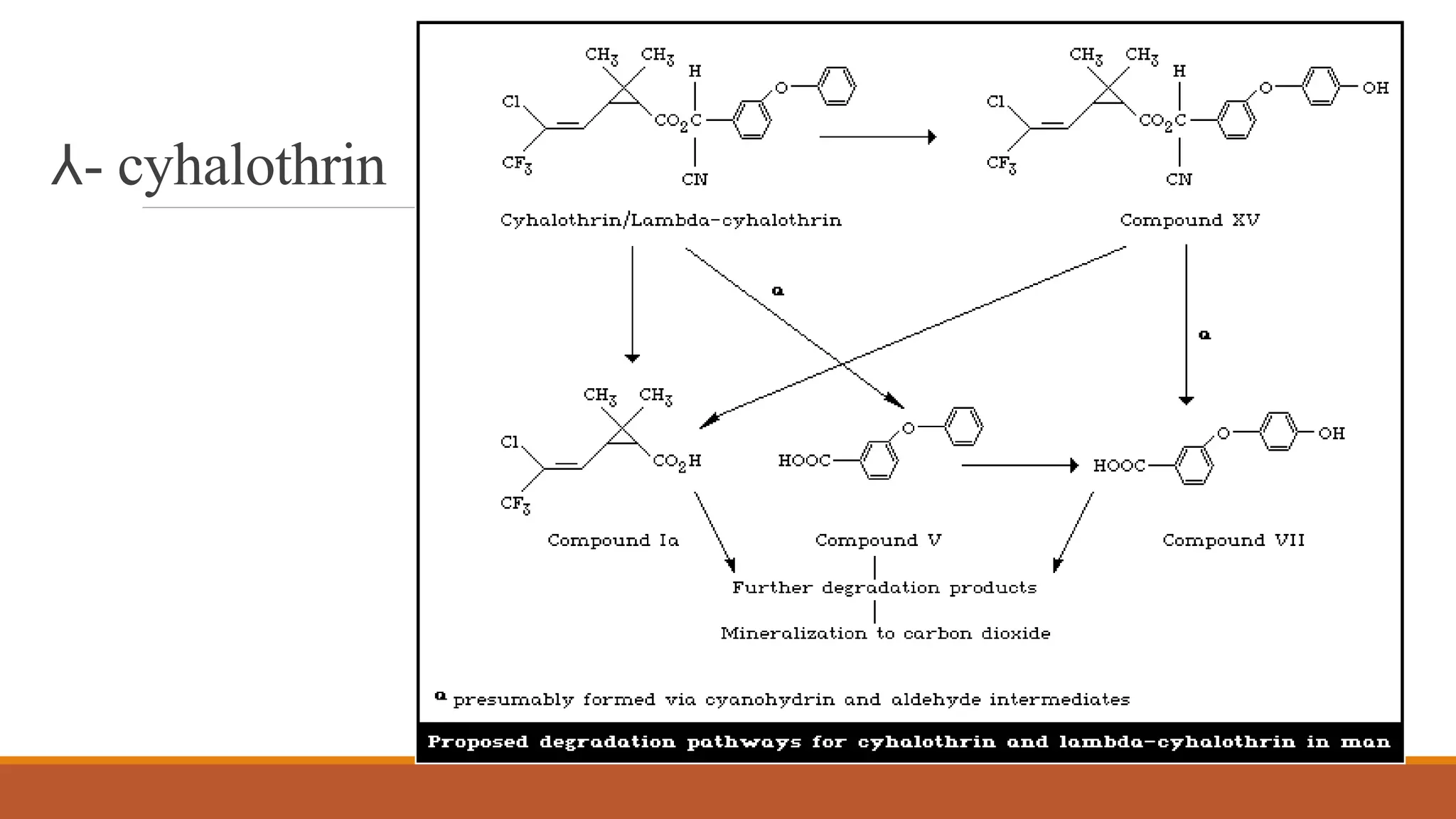
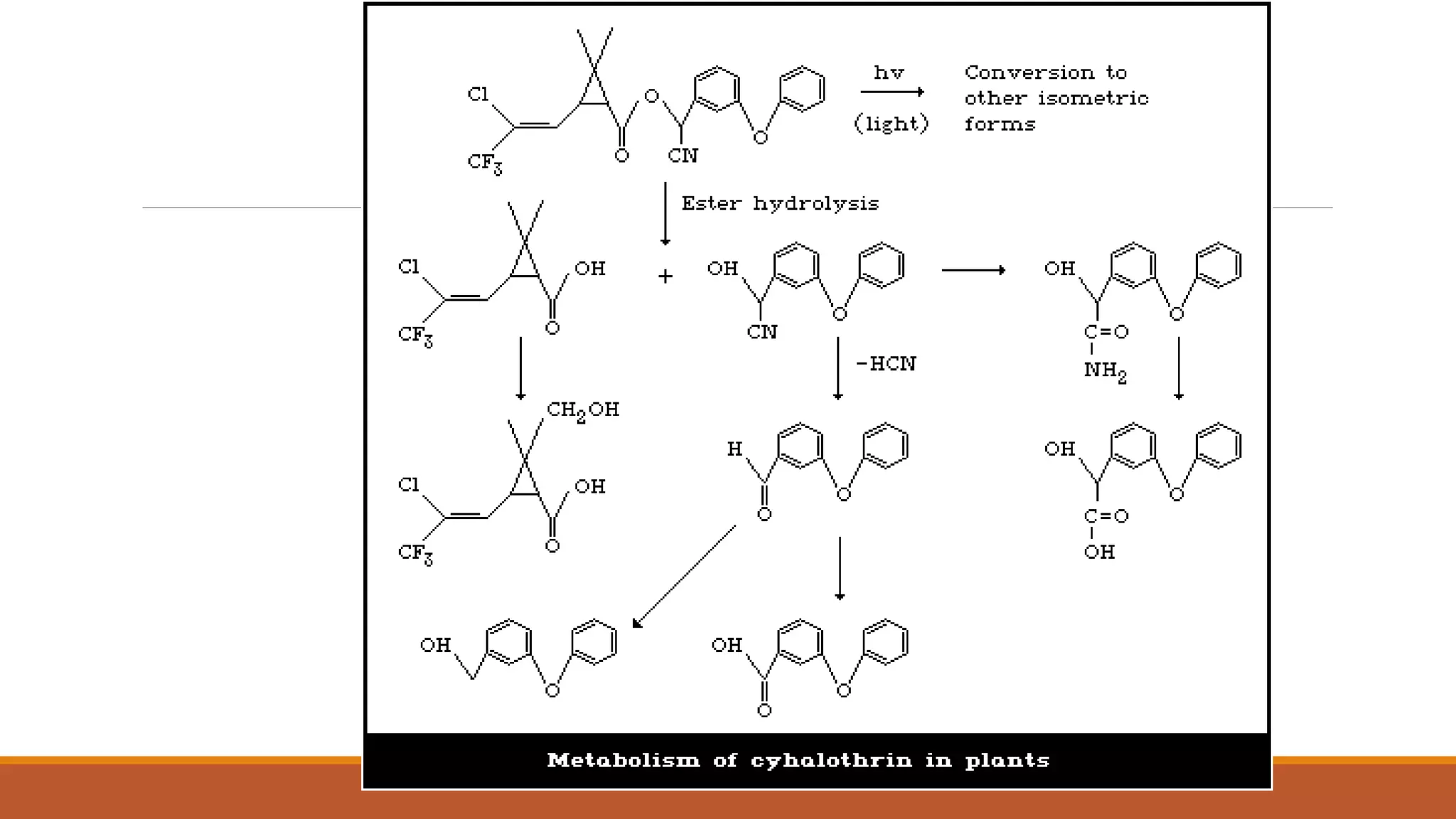
2) Pyrethroids are metabolized through ester hydrolysis and oxidation reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Metabolism typically proceeds through phase I oxidation and phase II conjugation and excretion.
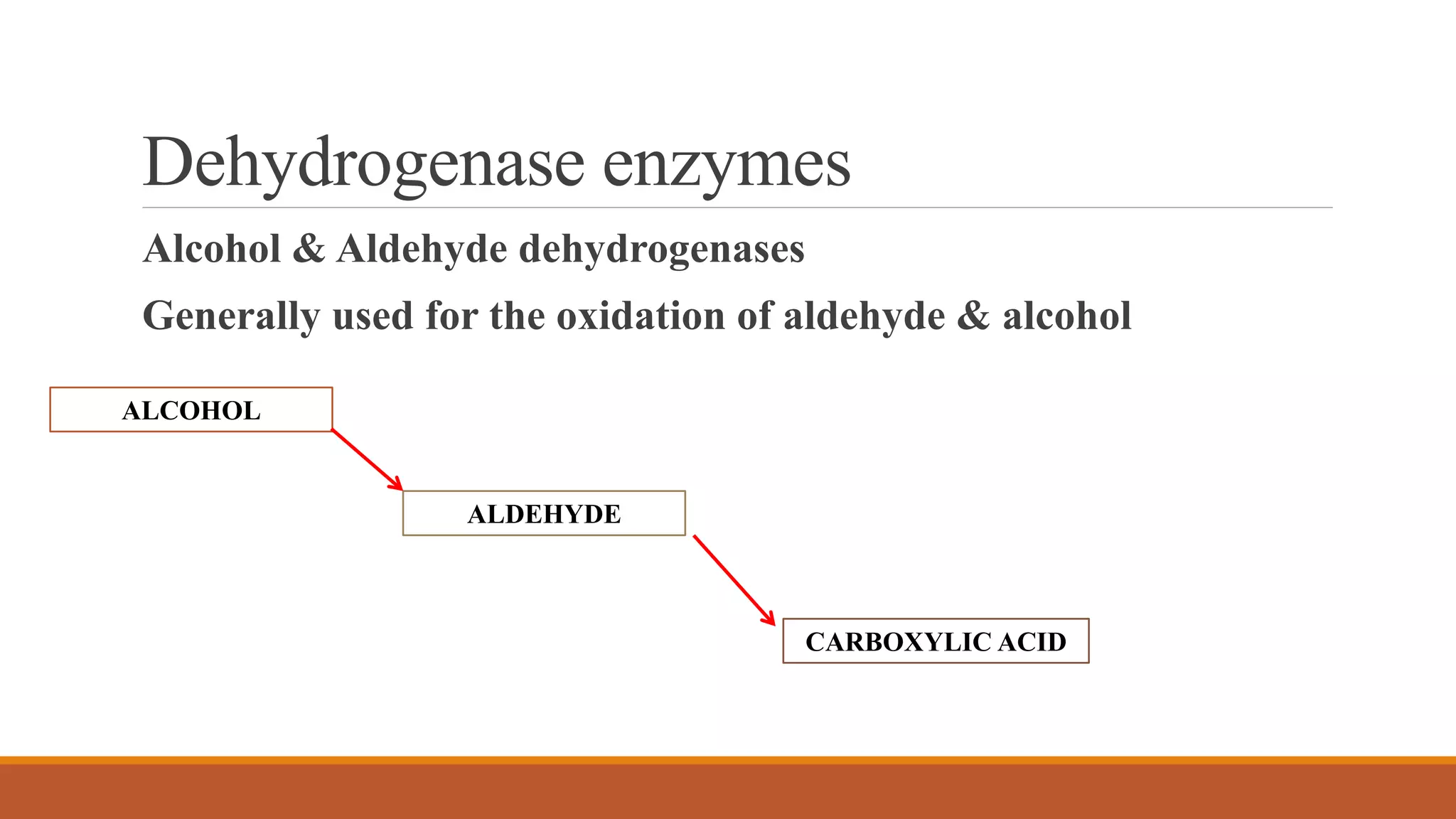
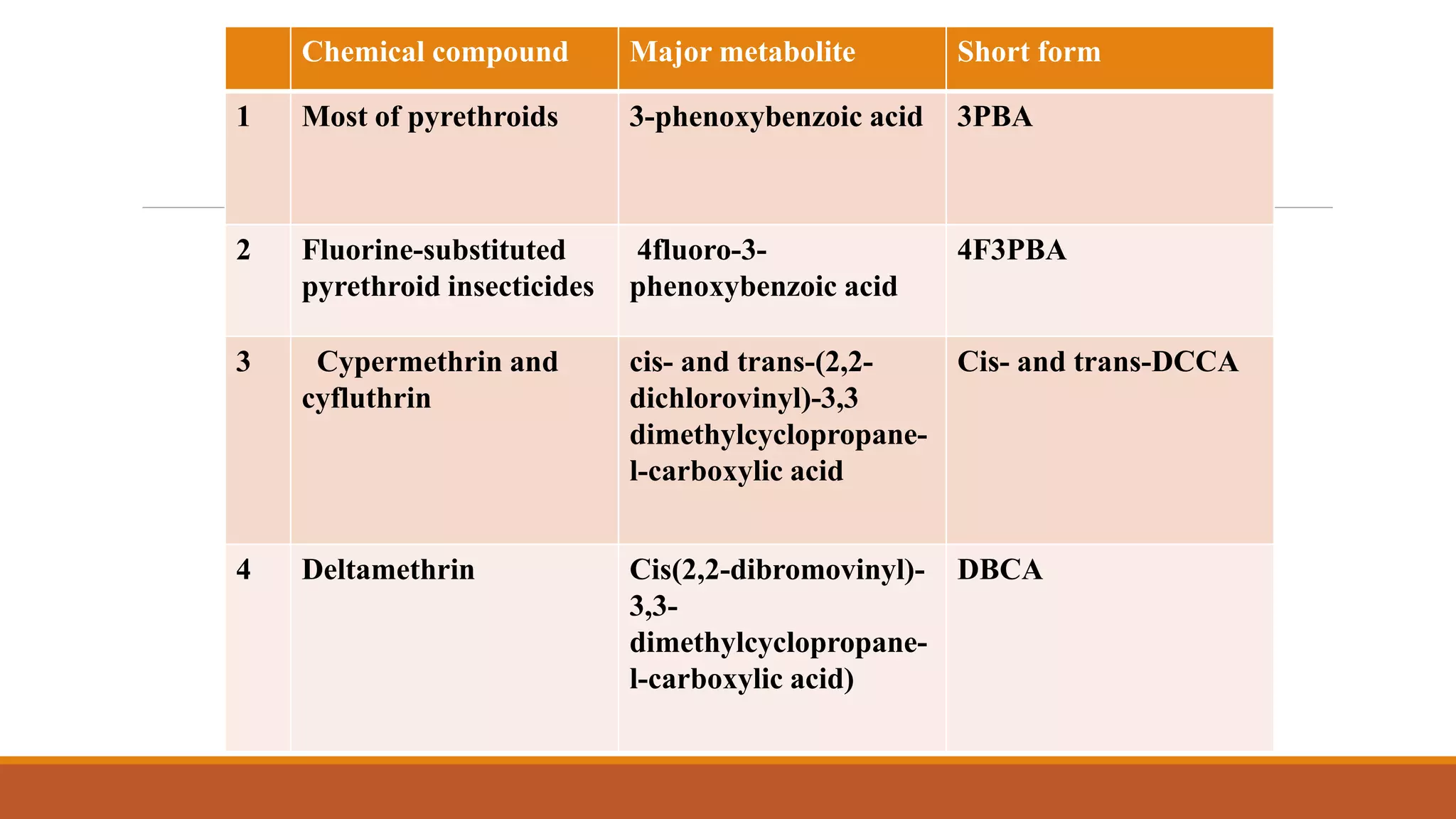
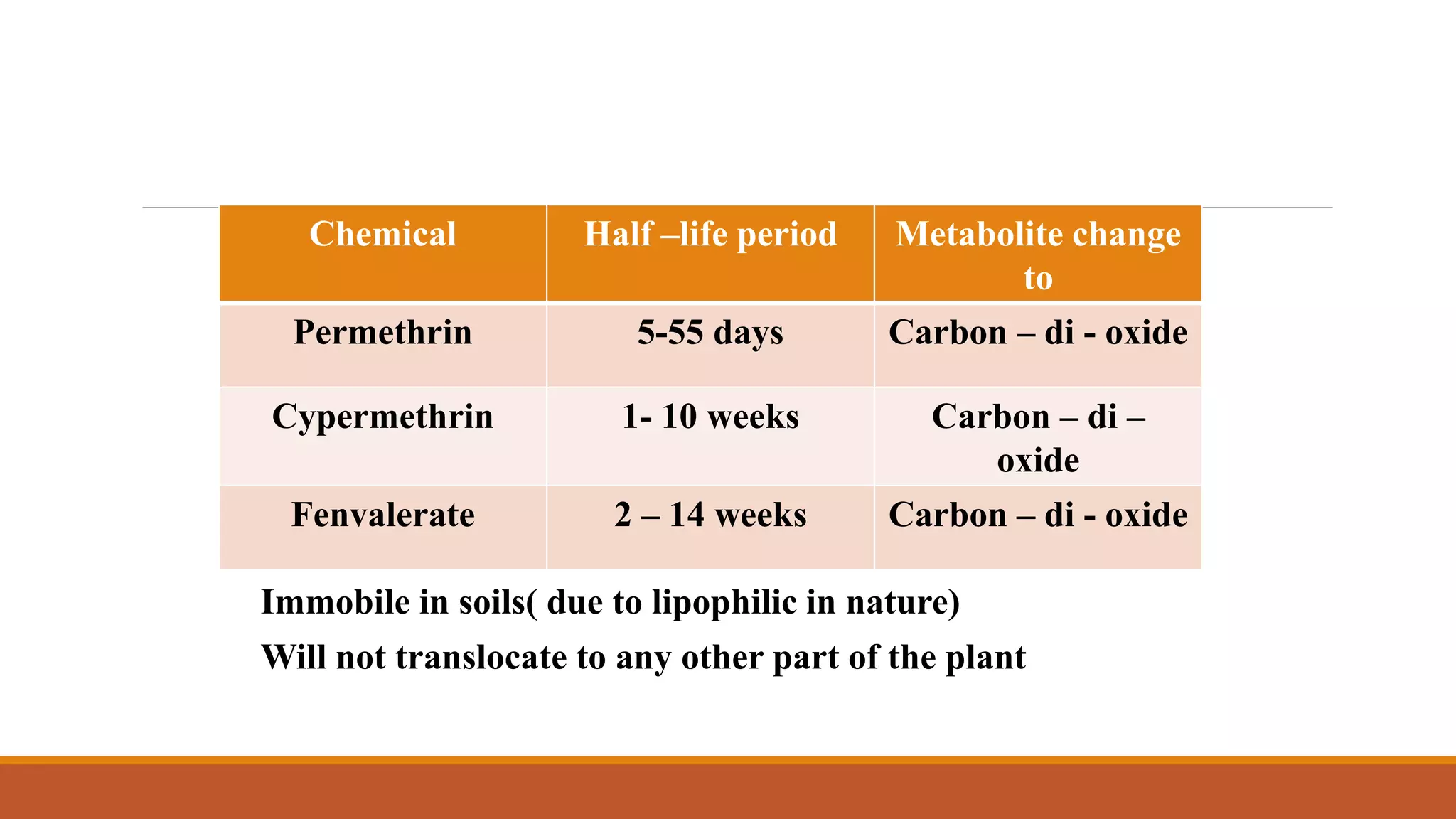
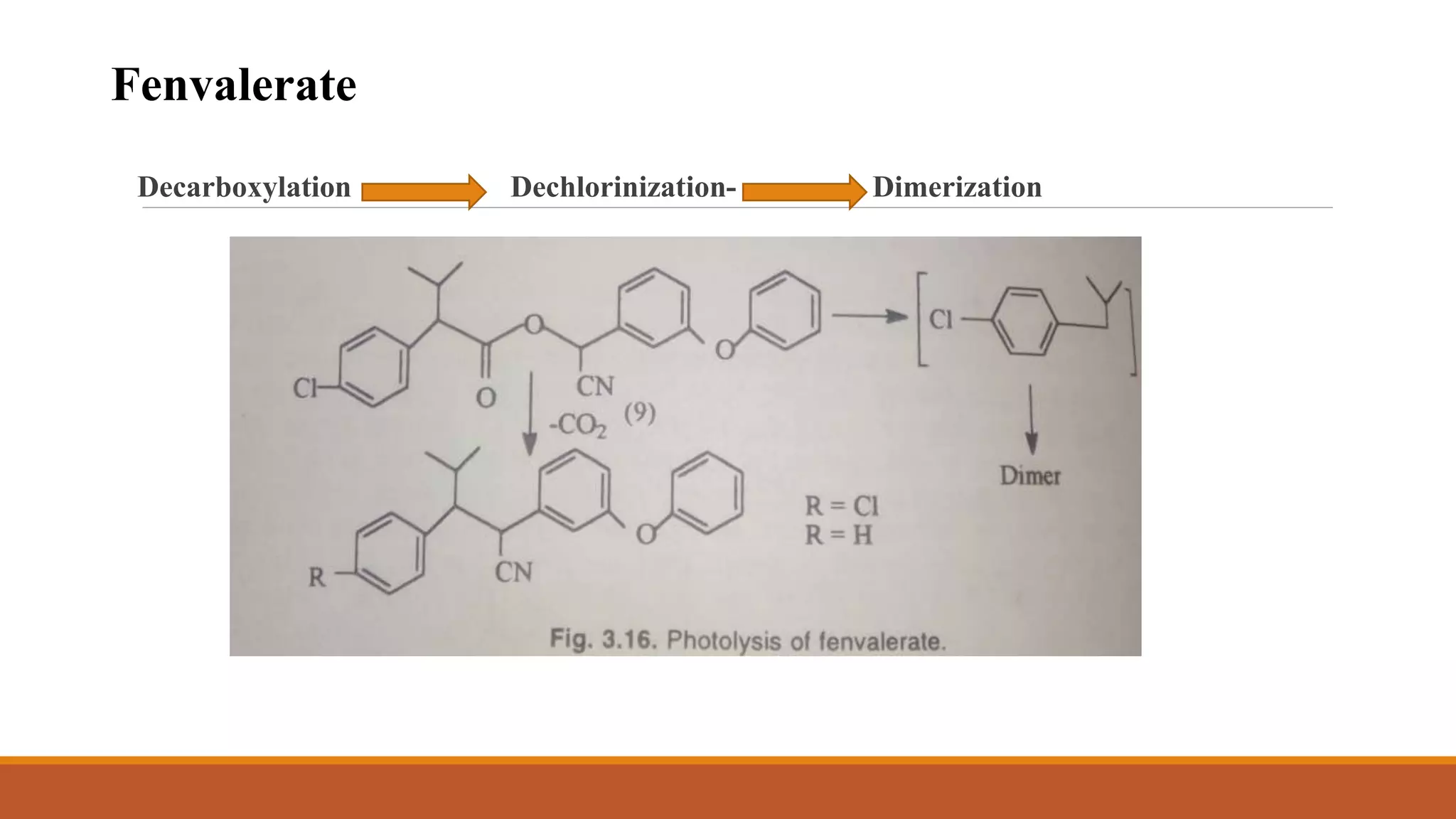
3) Major metabolites include various acids, alcohols, and carbon dioxide produced through ester cleavage and oxidation of different parts of the pyrethroid structure. Metabolism pathways can differ between species and individual pyrethroid compounds.