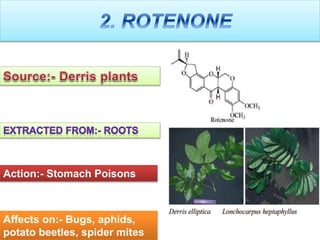
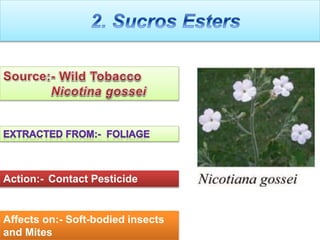
This document discusses various botanical insecticides, including their source, mode of action, and effectiveness against certain pests. It describes the 1st generation botanical insecticides such as nicotine, rotenone, ryania, and pyrethrum, and the 2nd generation including synthetic pyrethroids and neem products. It also outlines potential new botanicals like annonaceous acetogenins and sucrose esters. The document provides details on the extraction and application of each botanical insecticide and notes their advantages like being non-toxic and rapidly degrading, as well as disadvantages like lack of residual effect and need for multiple applications.