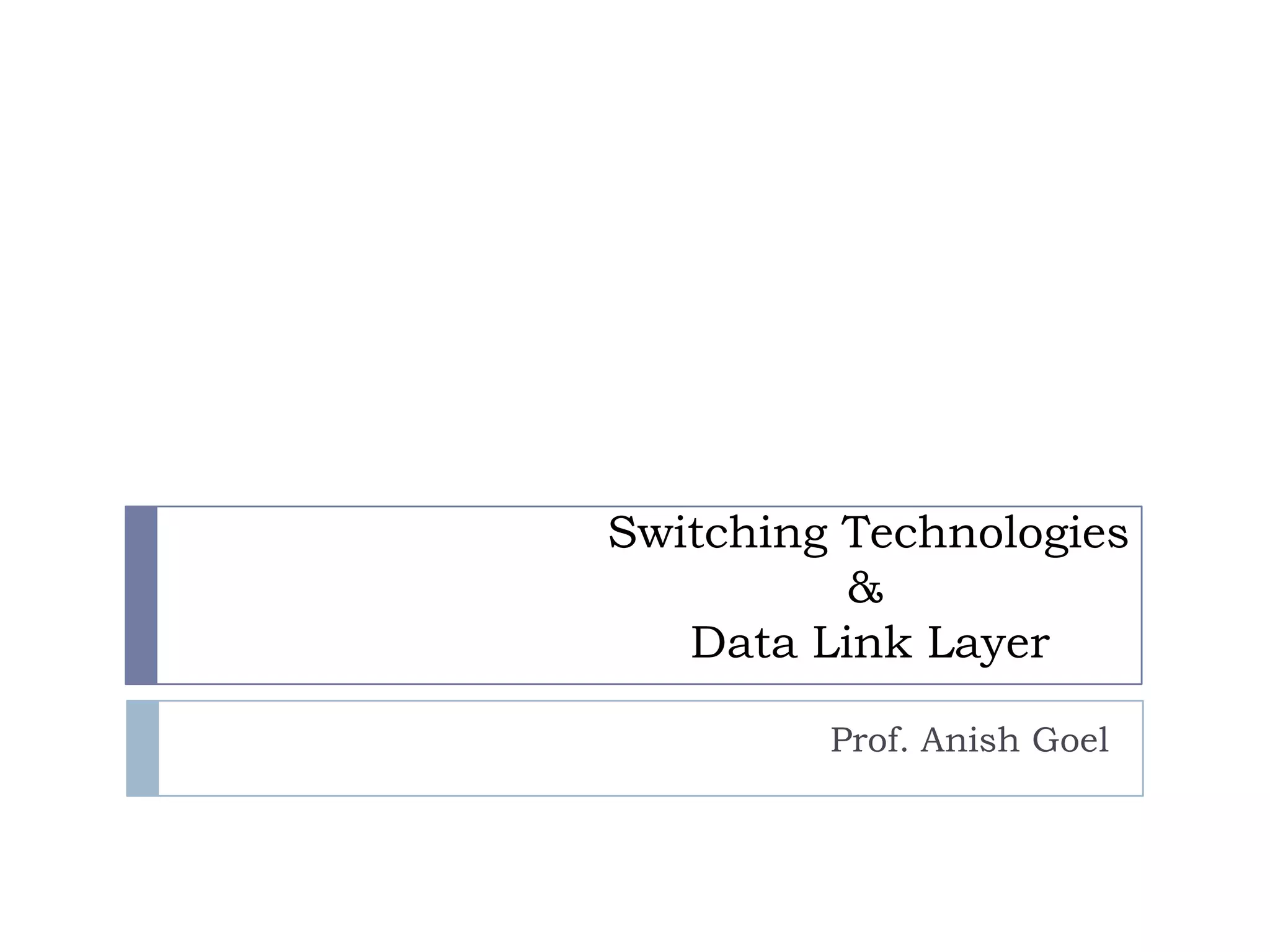
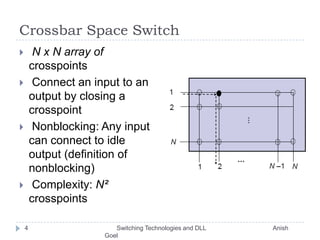
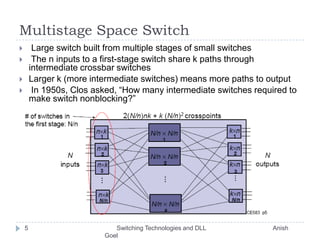
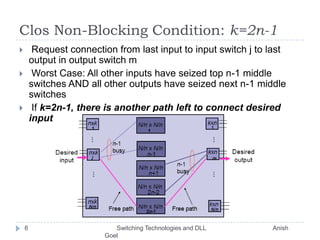
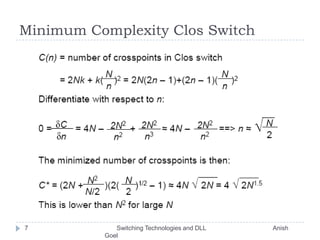
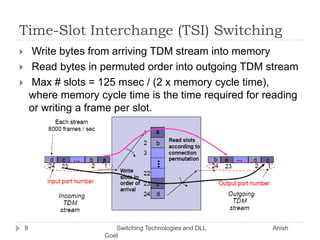
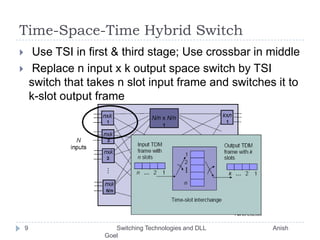
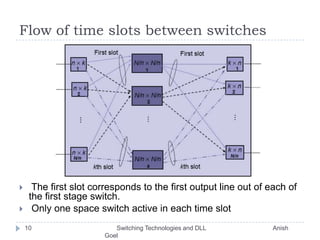
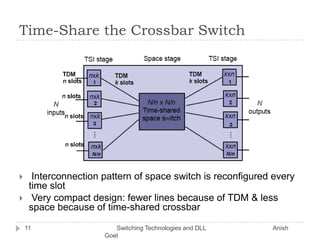
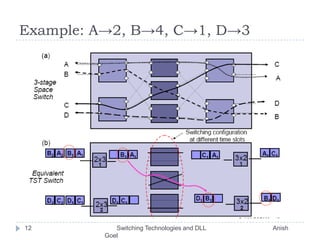
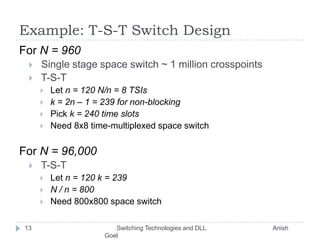
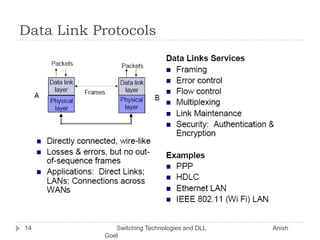
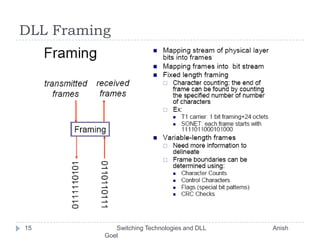
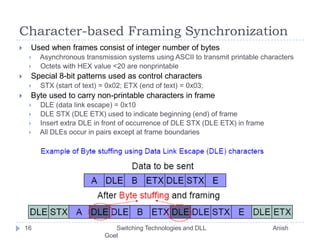
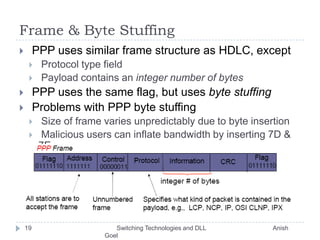
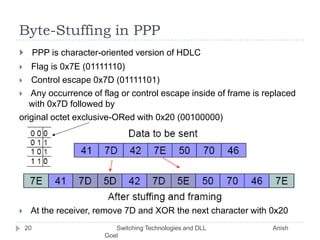
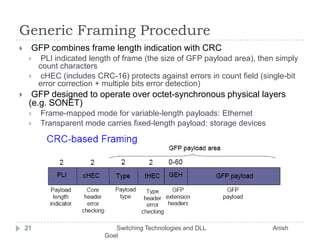
This document discusses various switching technologies and data link layer protocols. It describes circuit switching, space-division switches like crossbar switches and multistage switches, and time-division switches. It also covers data link layer framing techniques like character-based framing, bit stuffing, byte stuffing, and the Generic Framing Procedure (GFP). GFP uses a frame length indication, CRC, and scrambling for synchronization and error detection.