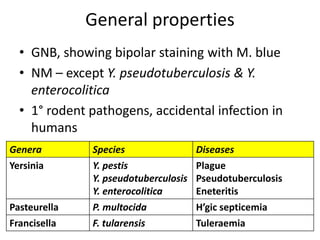
This document summarizes several bacterial genera - Yersinia, Pasteurella, and Francisella. It describes their general properties, species, diseases caused, morphology, culture characteristics, biochemical reactions, epidemiology, pathogenesis, laboratory diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis. Key points include Yersinia pestis causing plague, Pasteurella multocida causing septicemia, and Francisella tularensis causing tularemia.