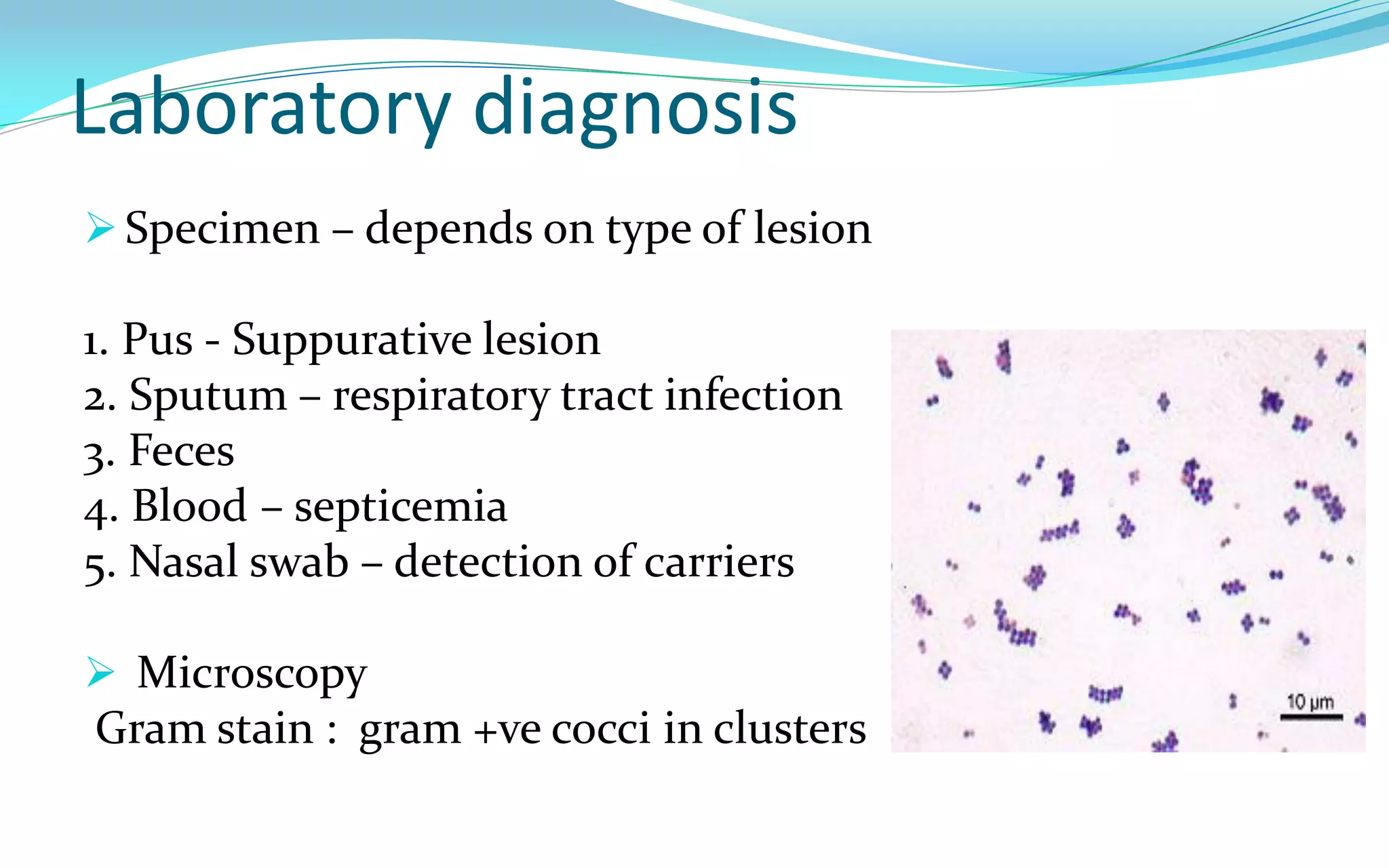
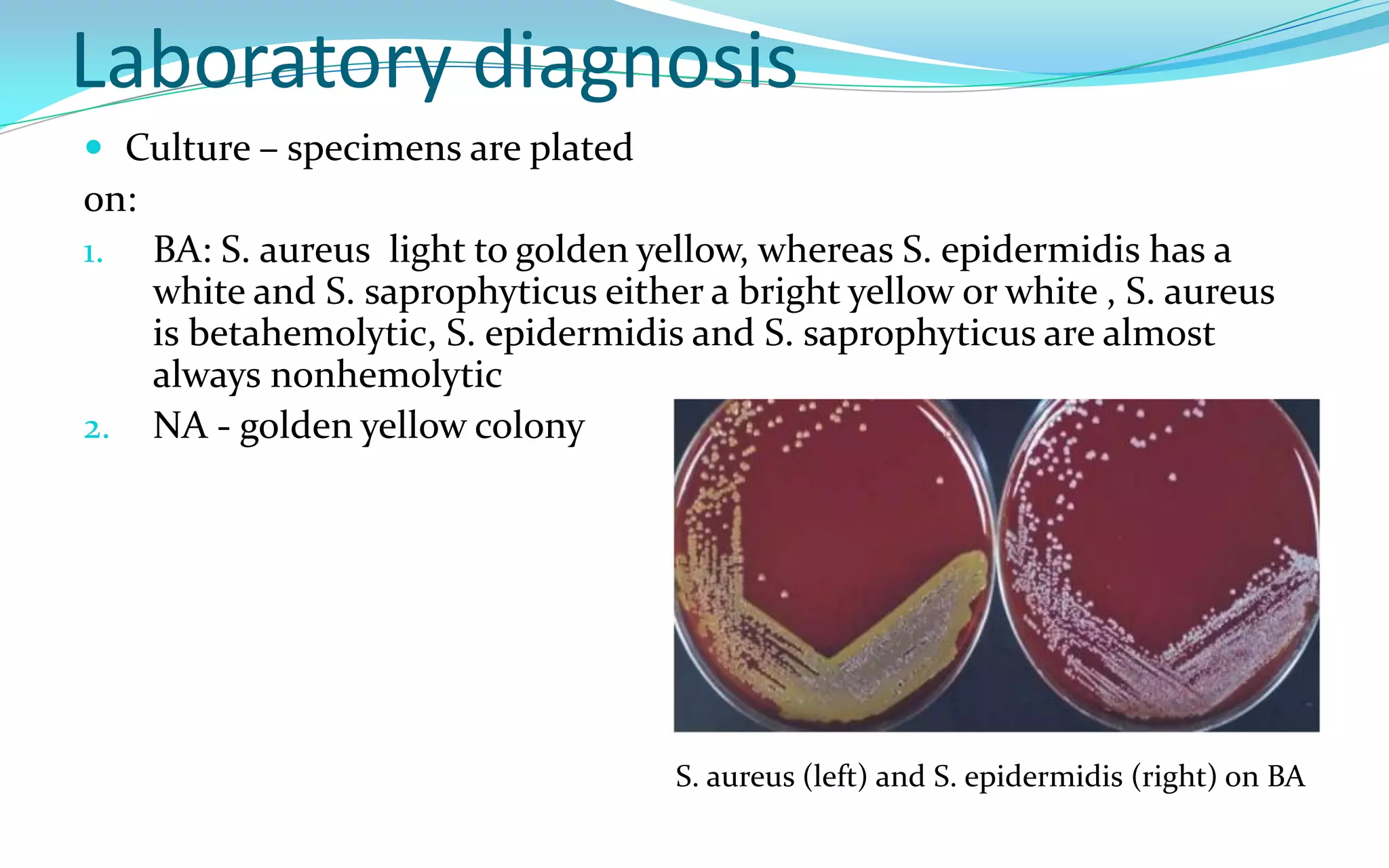
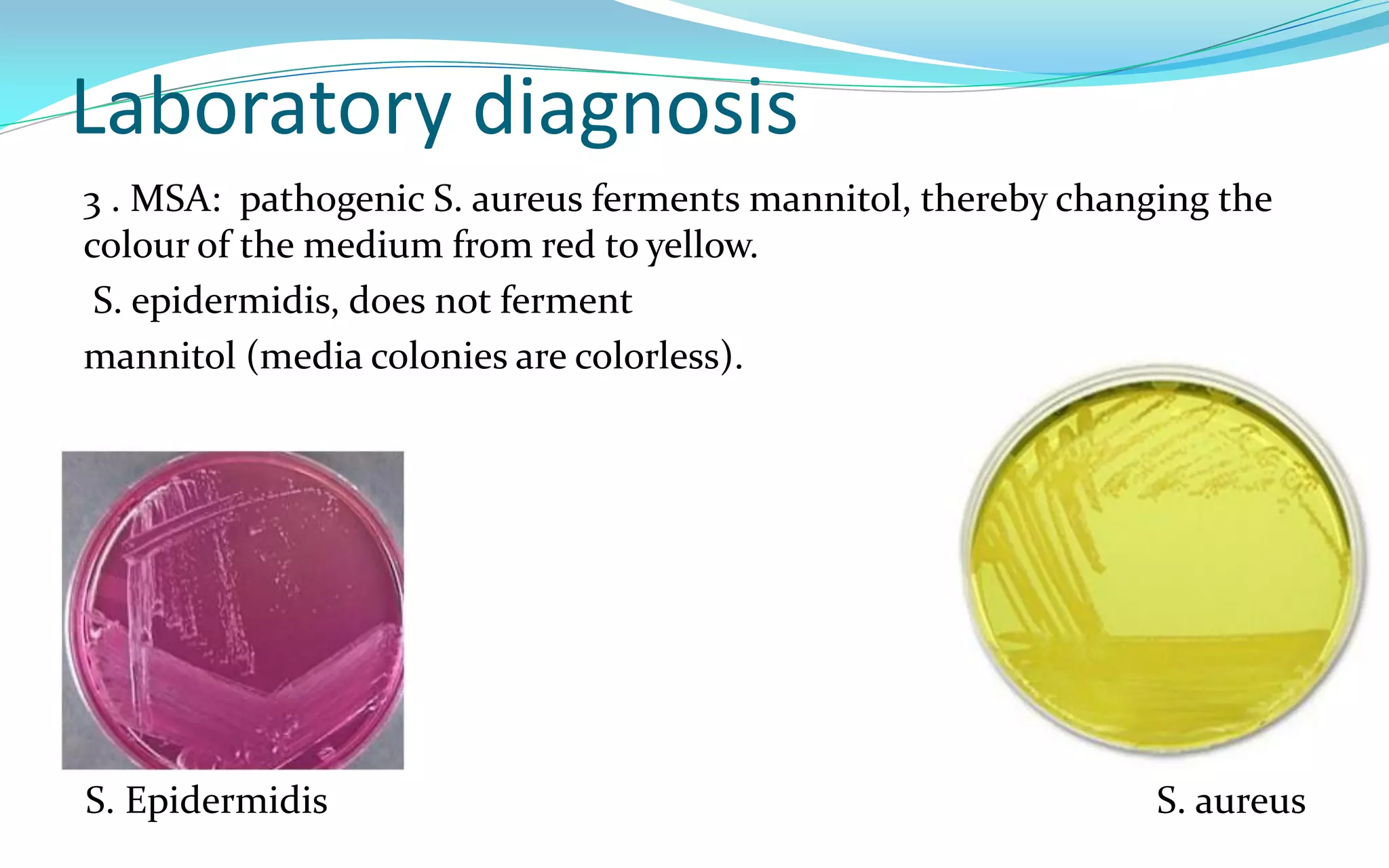
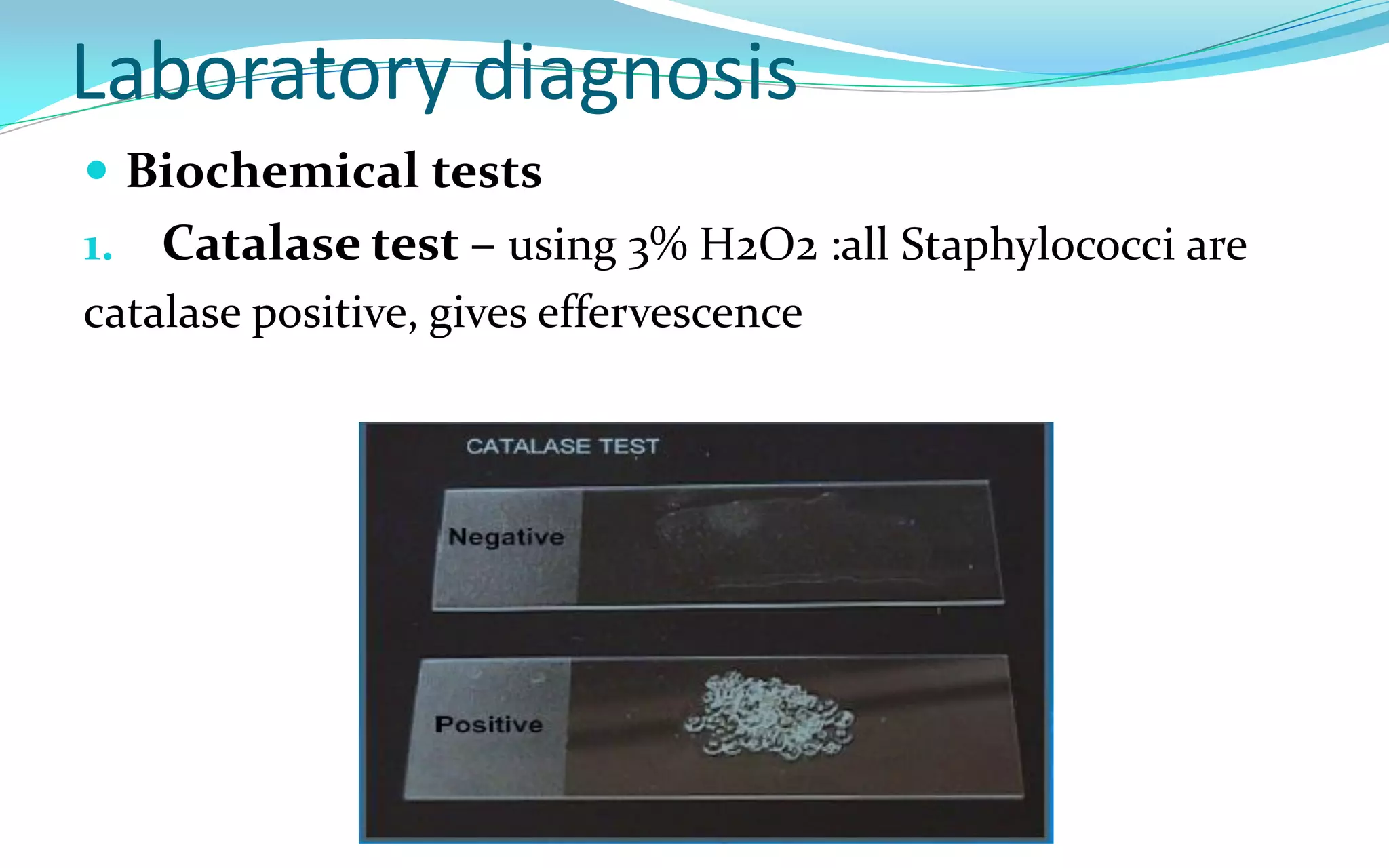
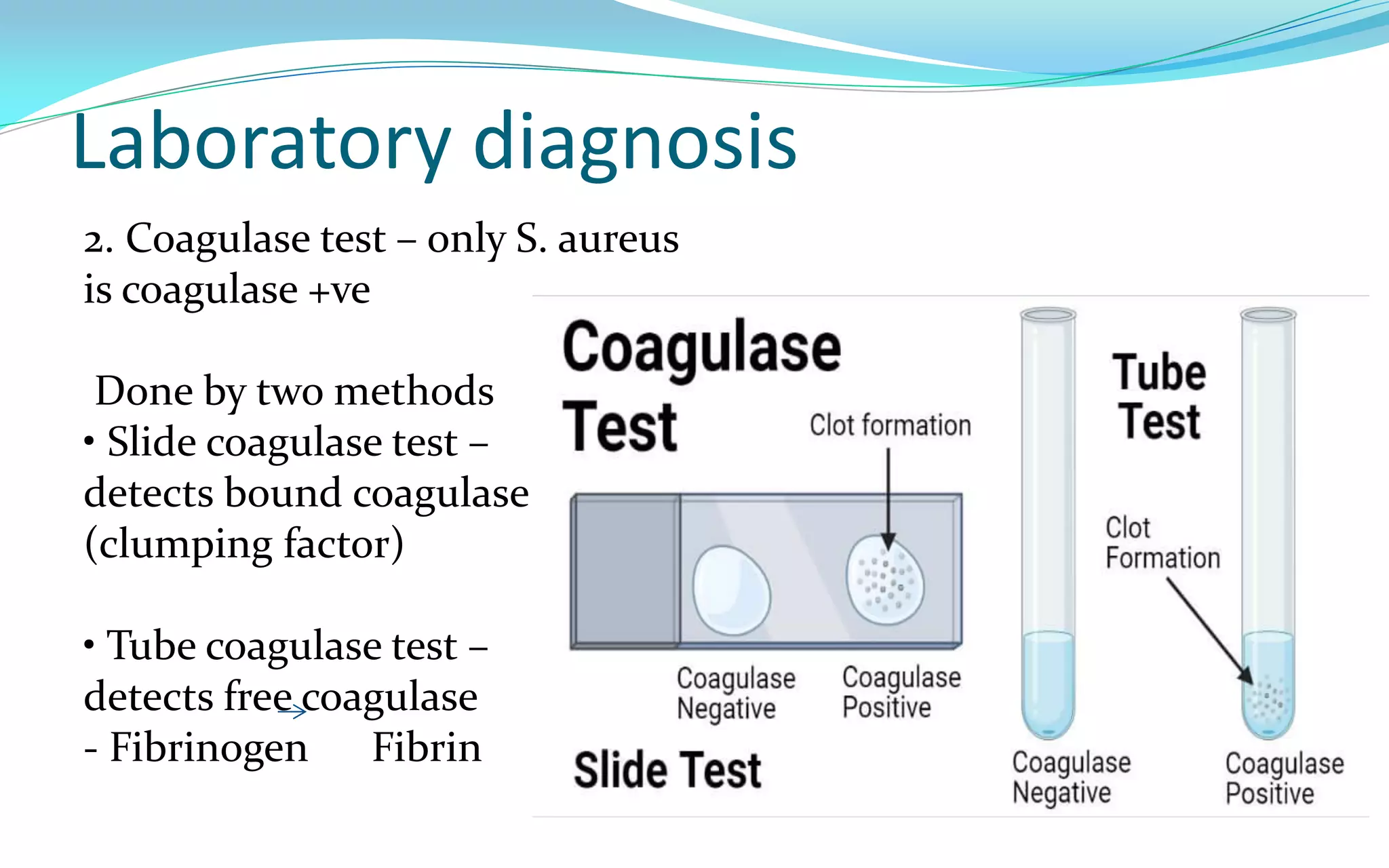
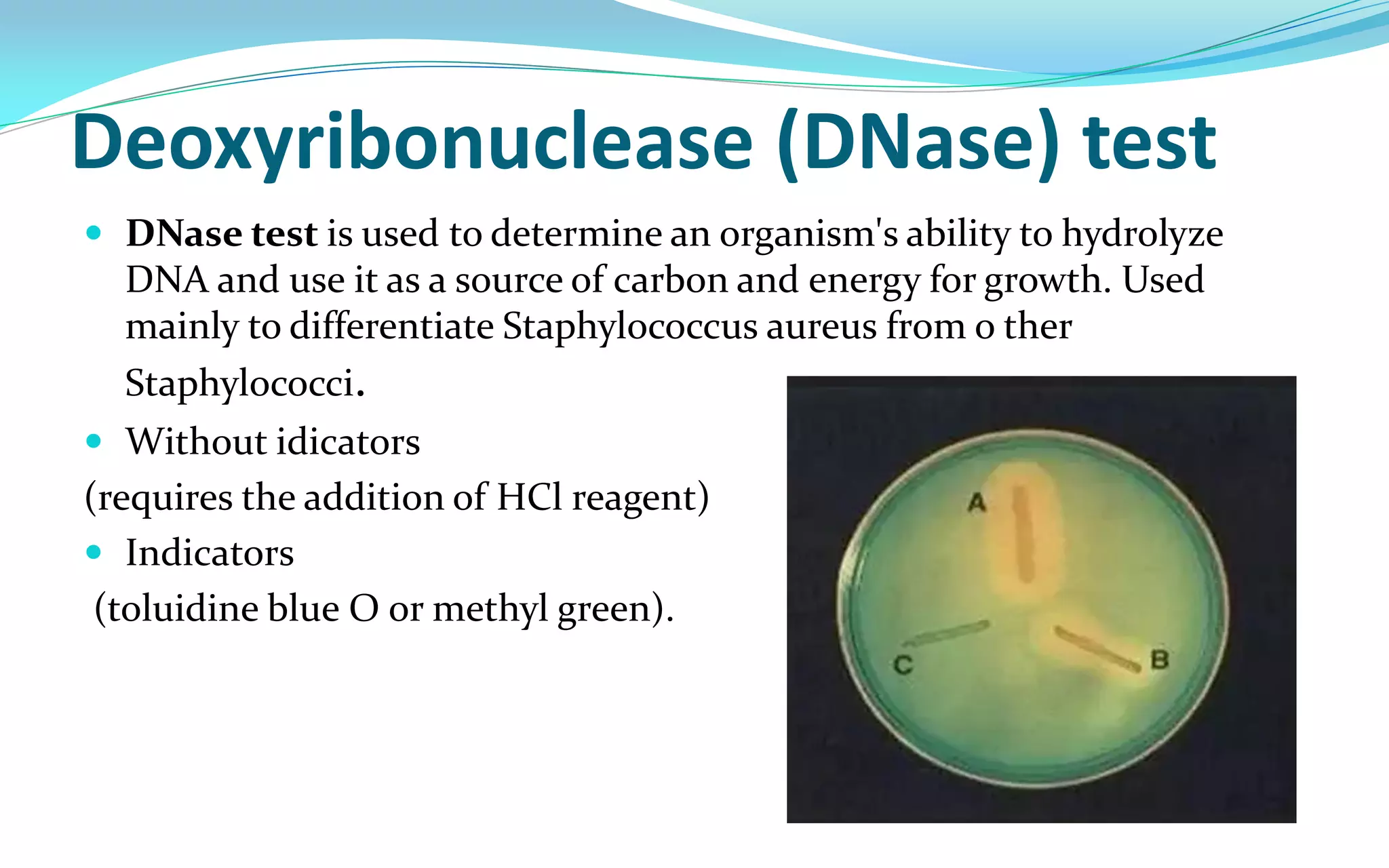
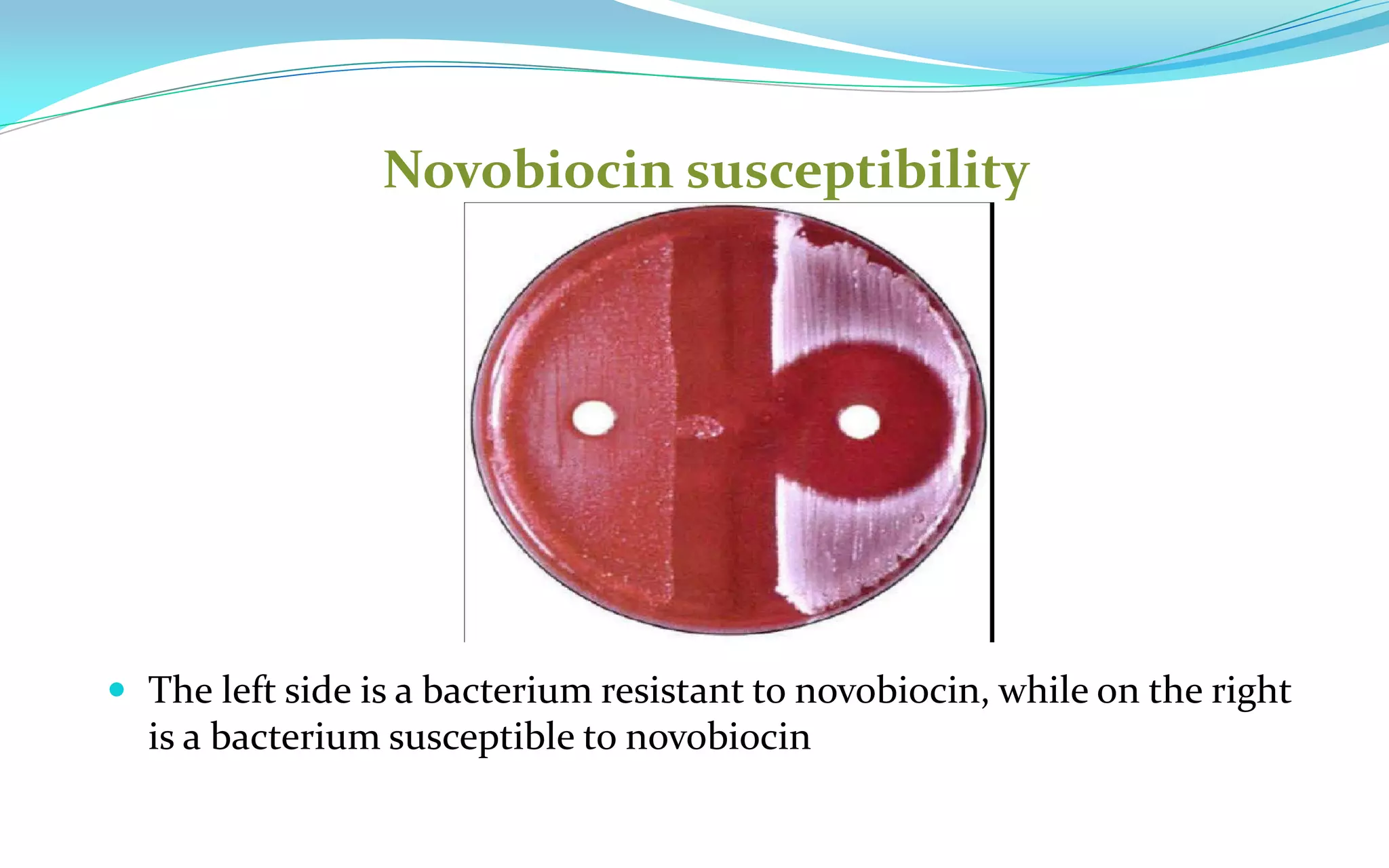
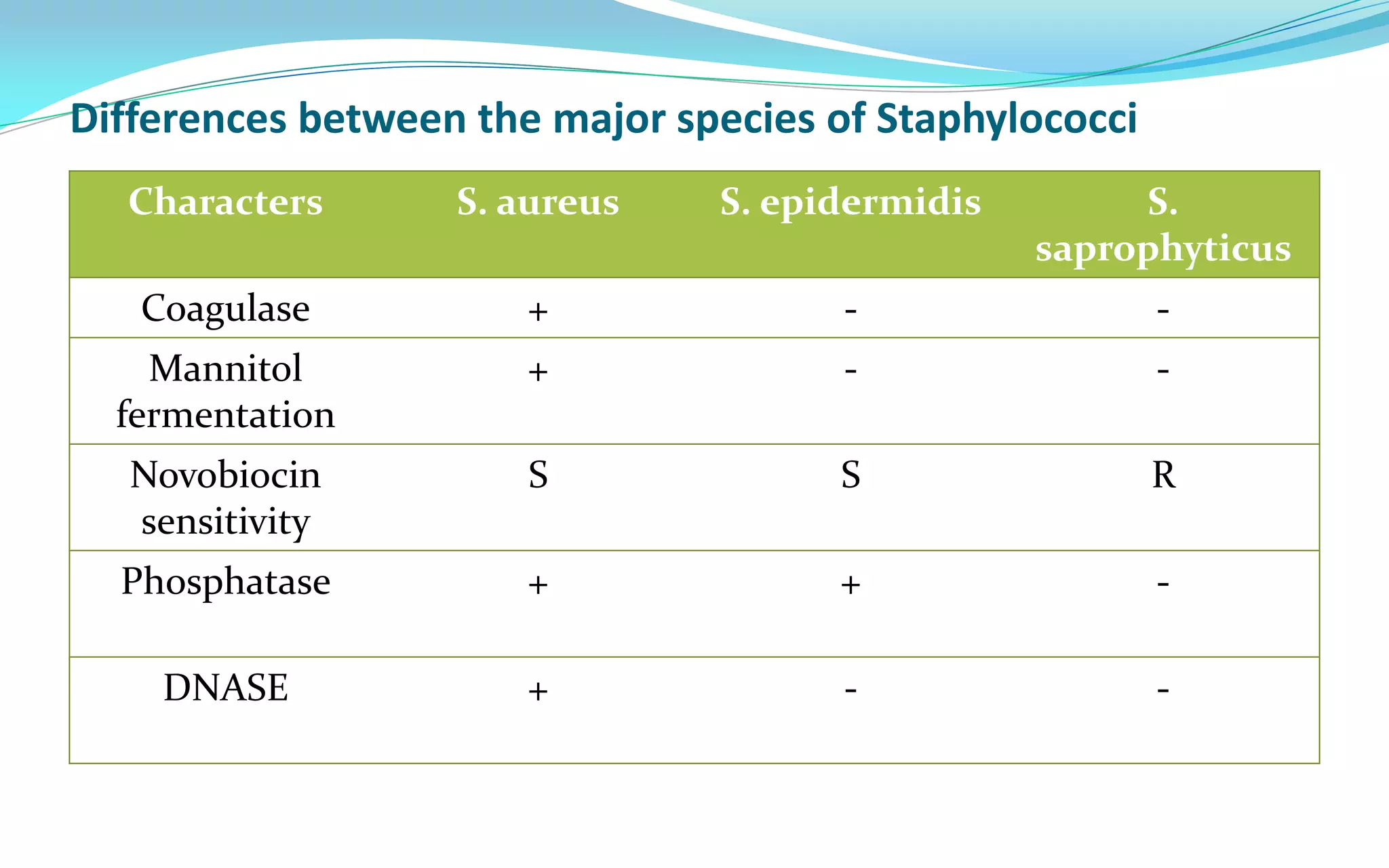
This document discusses Staphylococci bacteria, including their general features and important medical species. Staphylococci are gram-positive cocci that form grape-like clusters and are facultative anaerobes. Three medically important species are described: Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, and S. saprophyticus. S. aureus is the most virulent and causes a variety of infections through various cell-associated and secreted virulence factors. Laboratory diagnosis involves culturing specimens on selective media and performing tests like catalase, coagulase, and DNase.