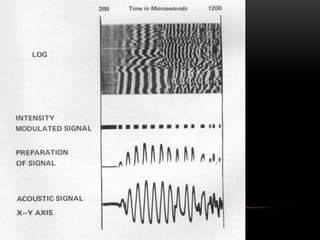
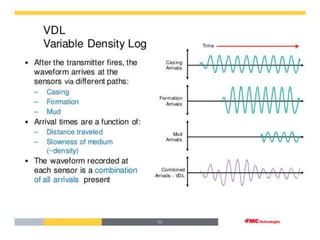
The Variable Density Log (VDL) displays acoustic waveforms to assess sonic or ultrasonic measurements, often used alongside cement-bond logs for better interpretation. It relies on gamma ray emissions and Compton scattering to measure formation density, with tools including long and short spaced detectors for accurate readings. The VDL is particularly reliable for identifying porosity in sandstones and limestones, though it has limitations related to uniformity of conditions in the borehole.