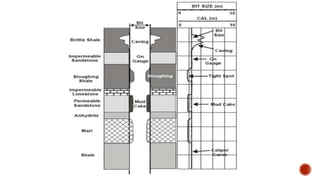
The document discusses self potential (SP) logs, which measure electrical potential differences between points on the ground caused by natural subsurface currents. SP logs have three main conditions: porous and permeable reservoirs bounded by impermeable layers, two different fluid types (e.g. oil, gas, brine), and differences in salinity between fluids. SP logs can be used to find oil and gas reservoirs, determine shale volumes, and understand aquifer levels. They work by detecting potential differences between shales and reservoirs using electrodes during drilling.