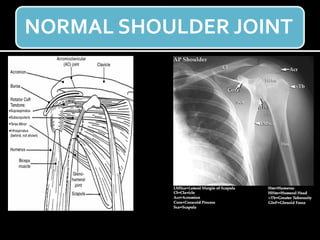
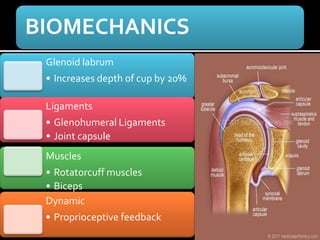
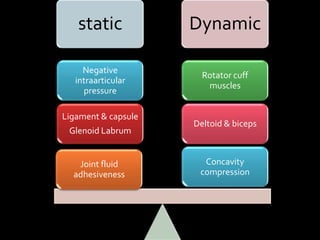
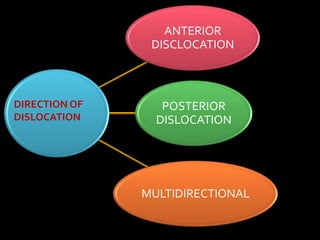
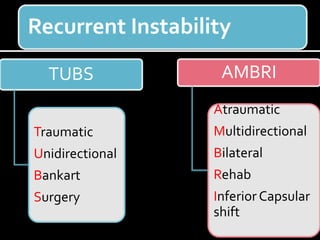
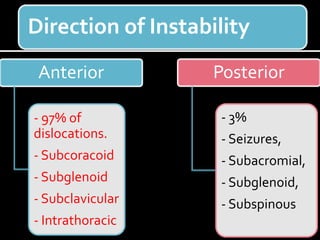
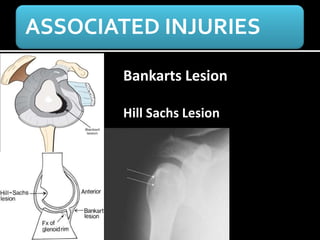
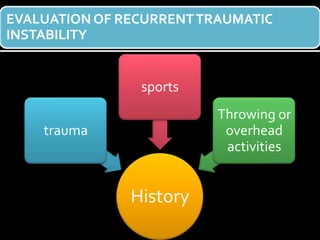
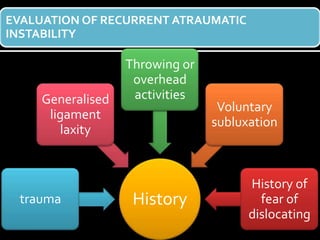
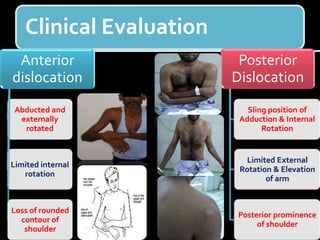
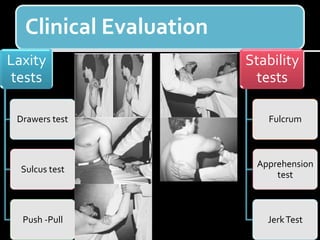
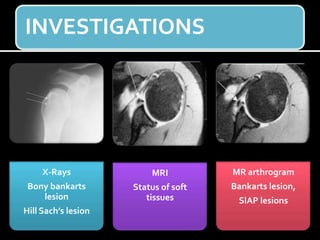
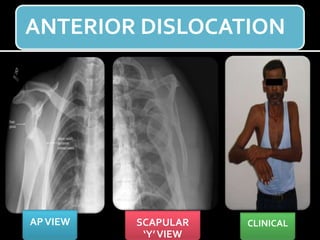
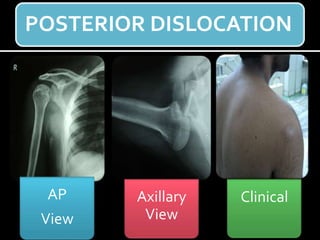
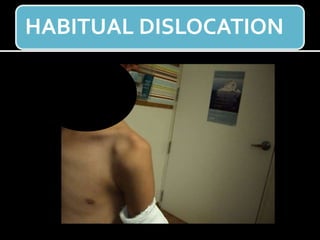
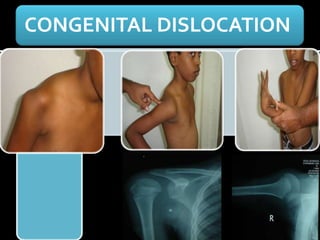
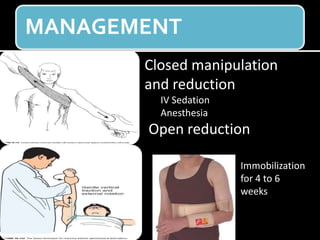
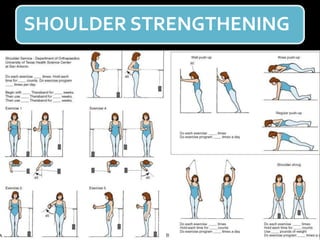
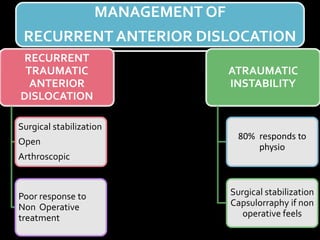
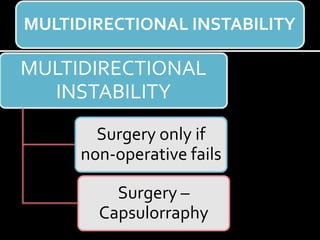
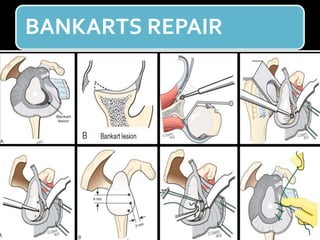
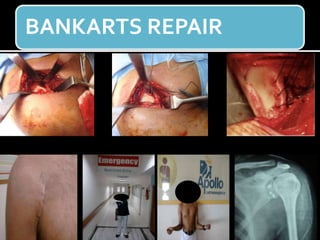
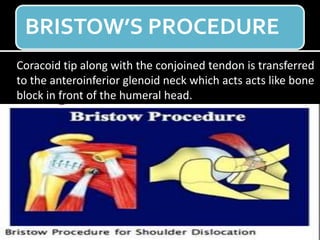
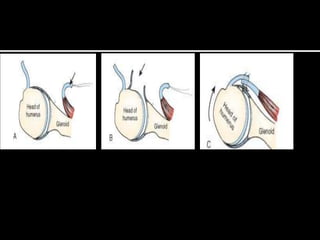
The document discusses unstable shoulder dislocations, including types, causes, biomechanics, and management approaches. It details evaluations for recurrent dislocation, associated injuries like Bankart and Hill-Sachs lesions, and outlines treatment options such as closed manipulation, surgical stabilization, and rehabilitation. The document emphasizes the importance of both non-operative and surgical interventions based on the specific instability type and patient response.