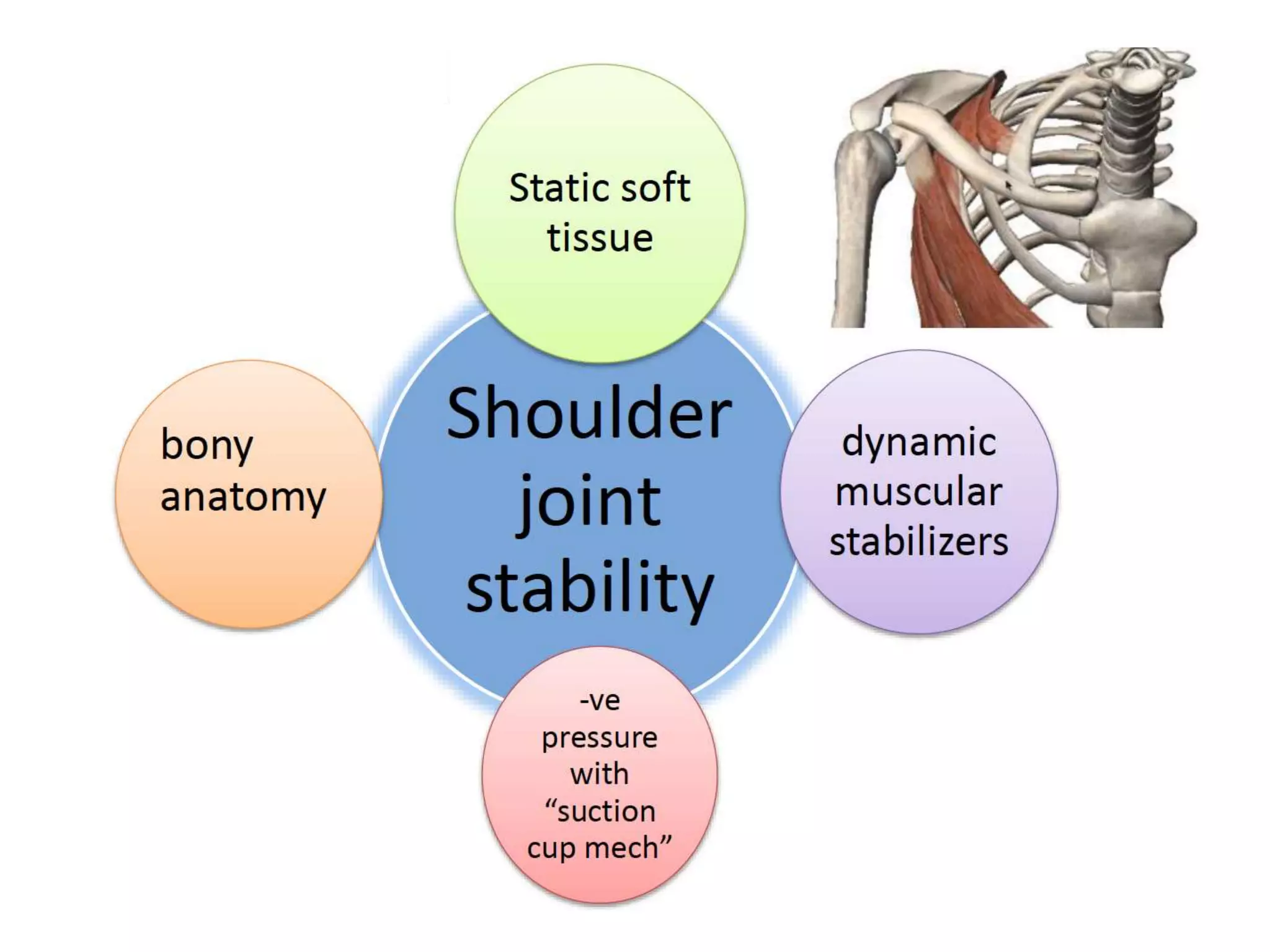
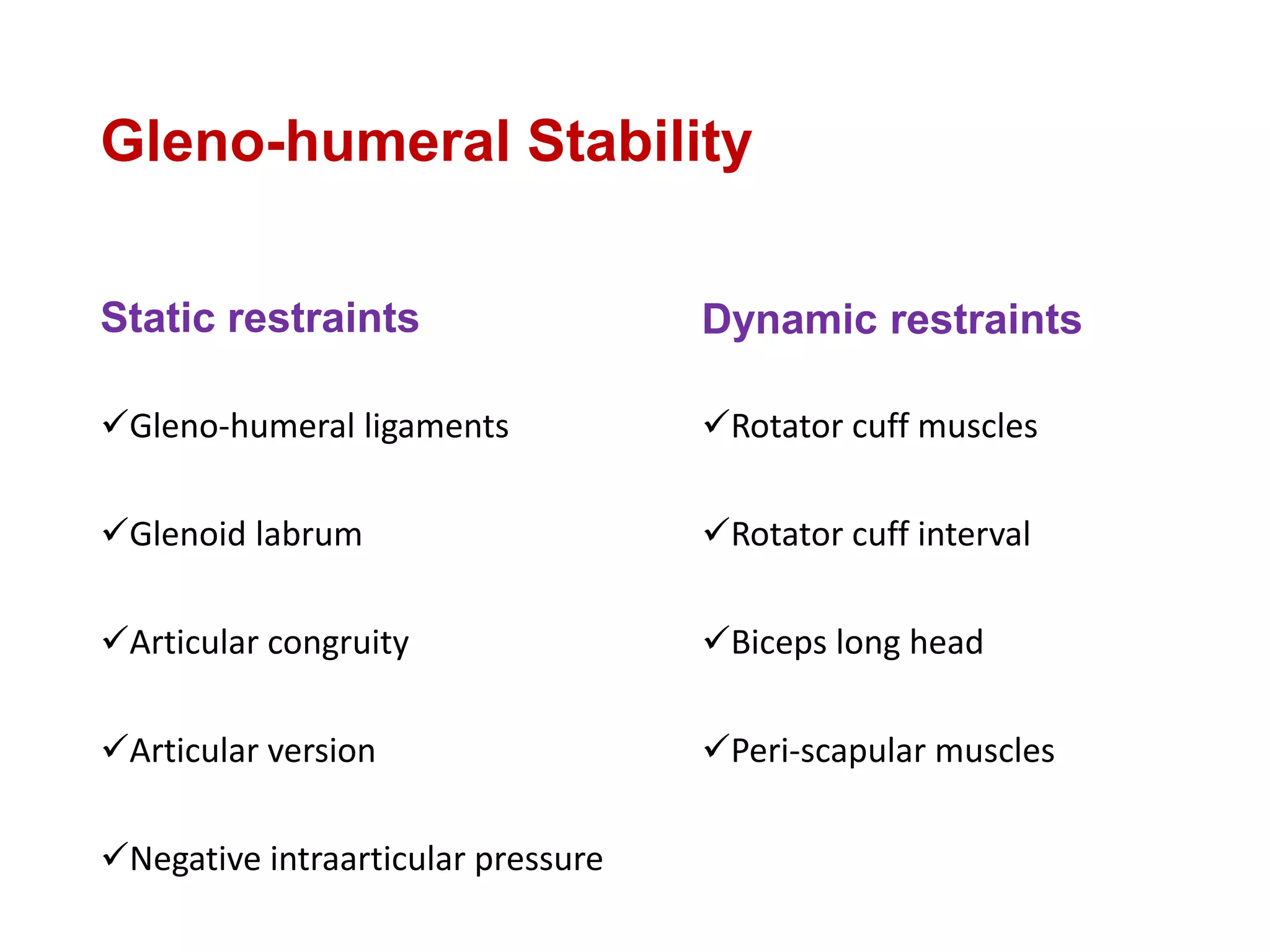
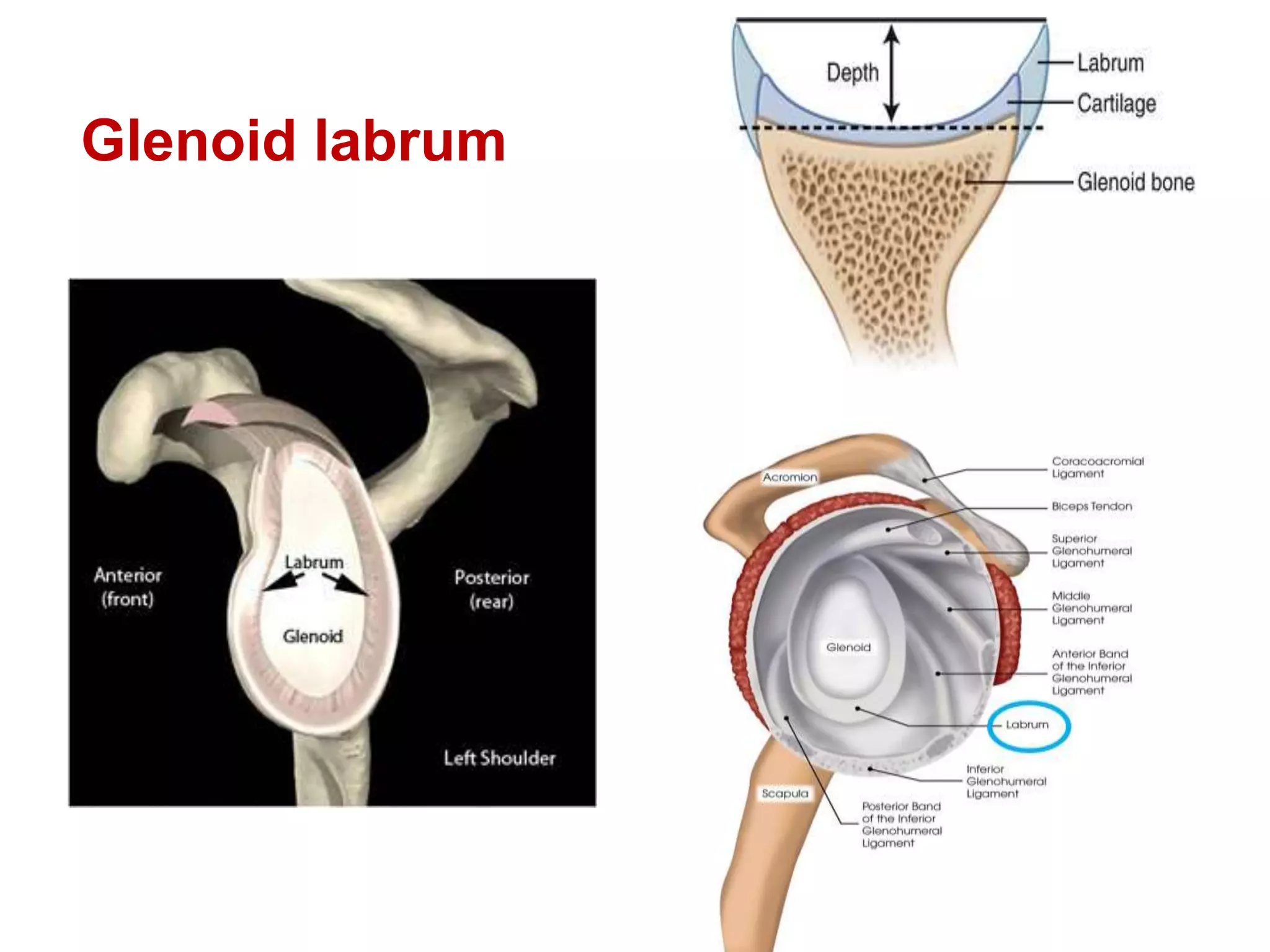
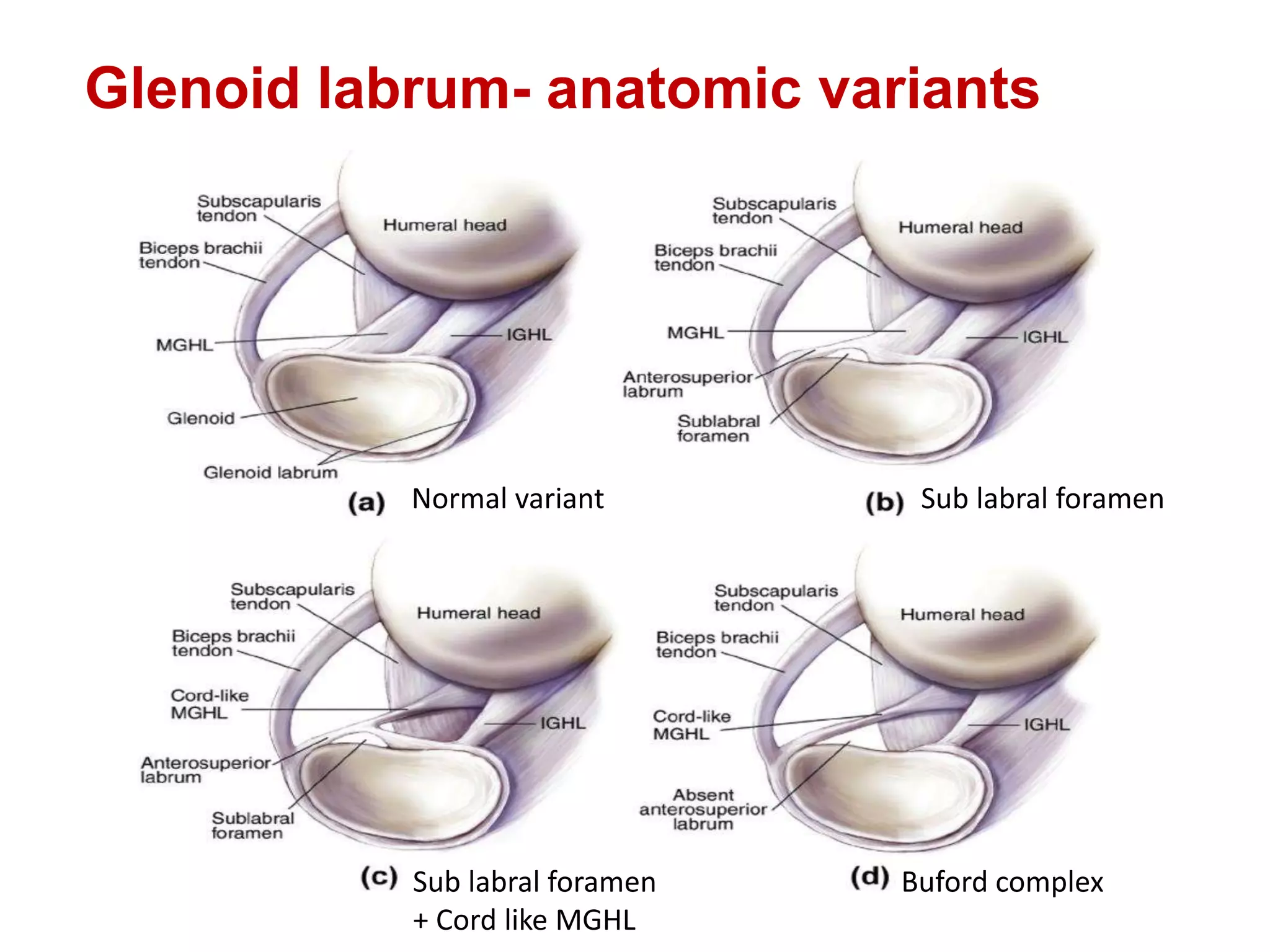
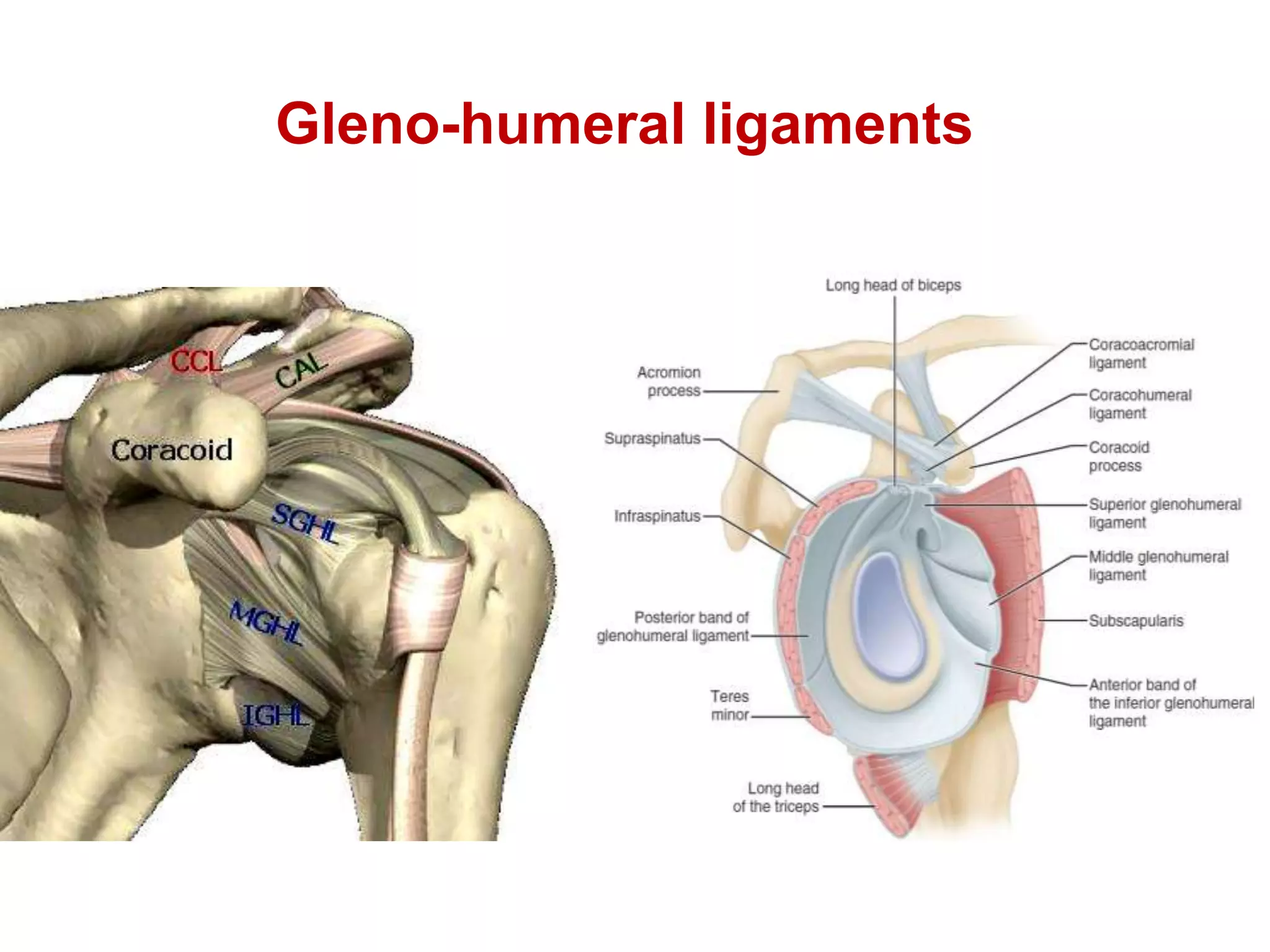
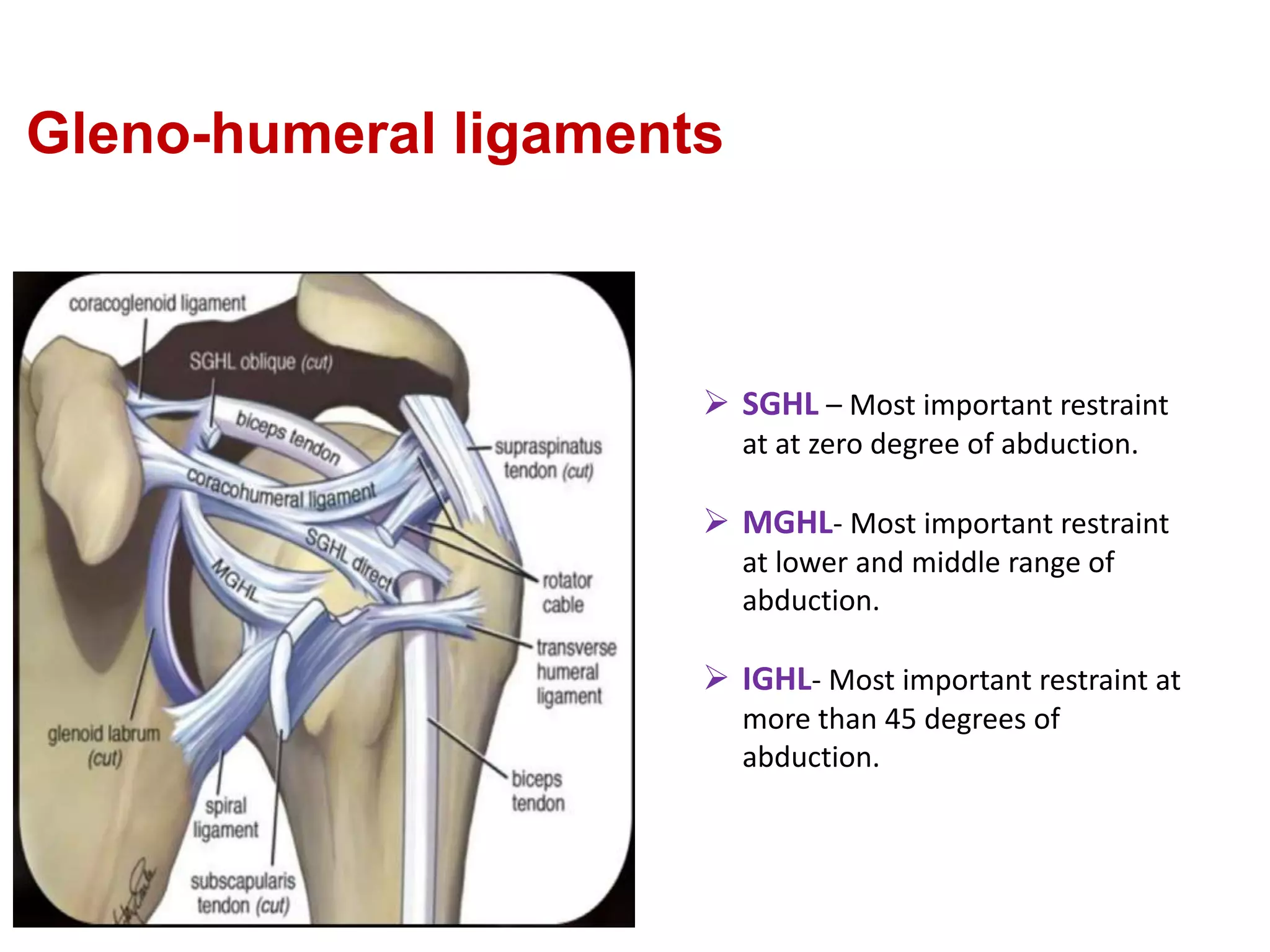
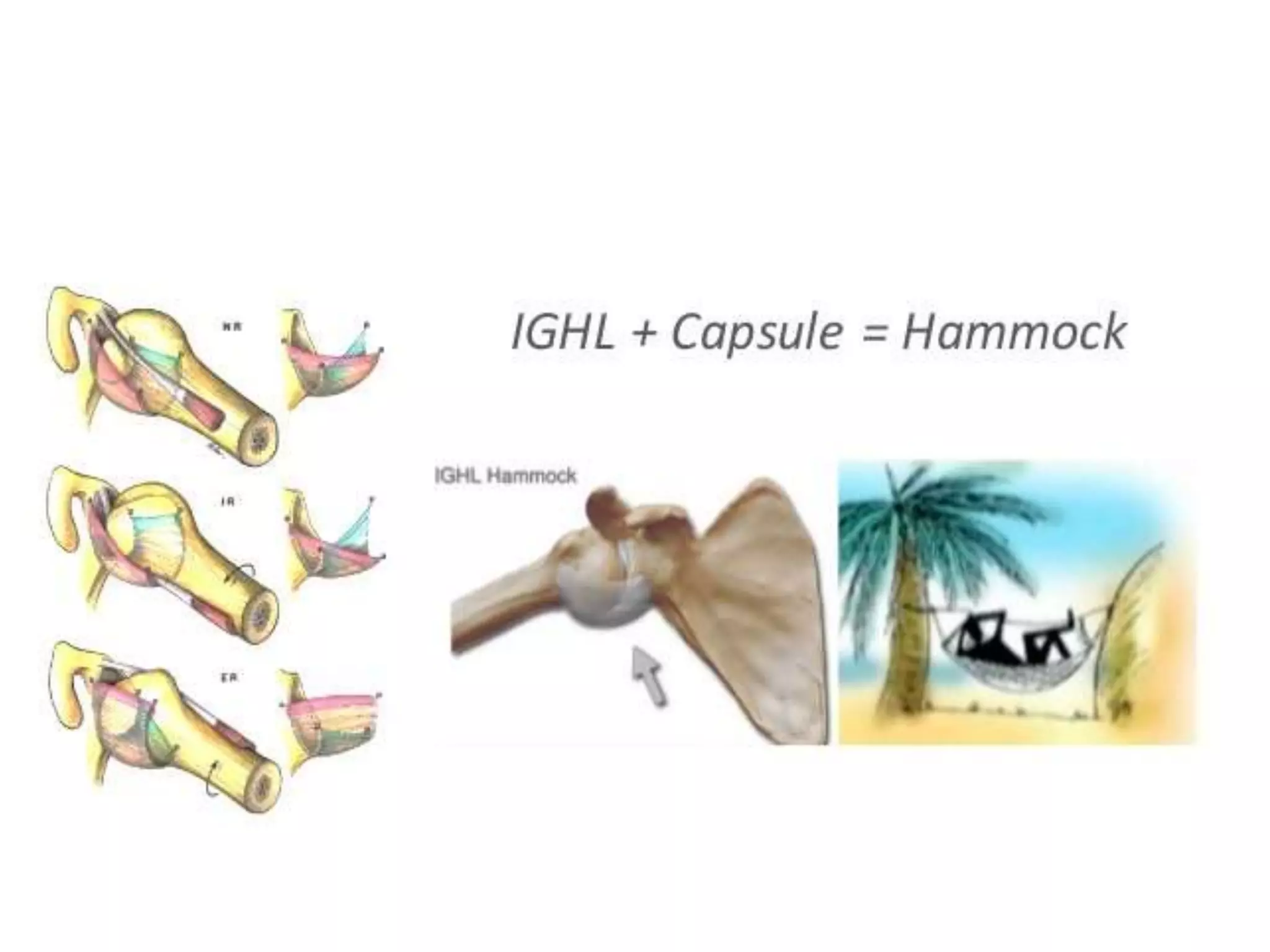
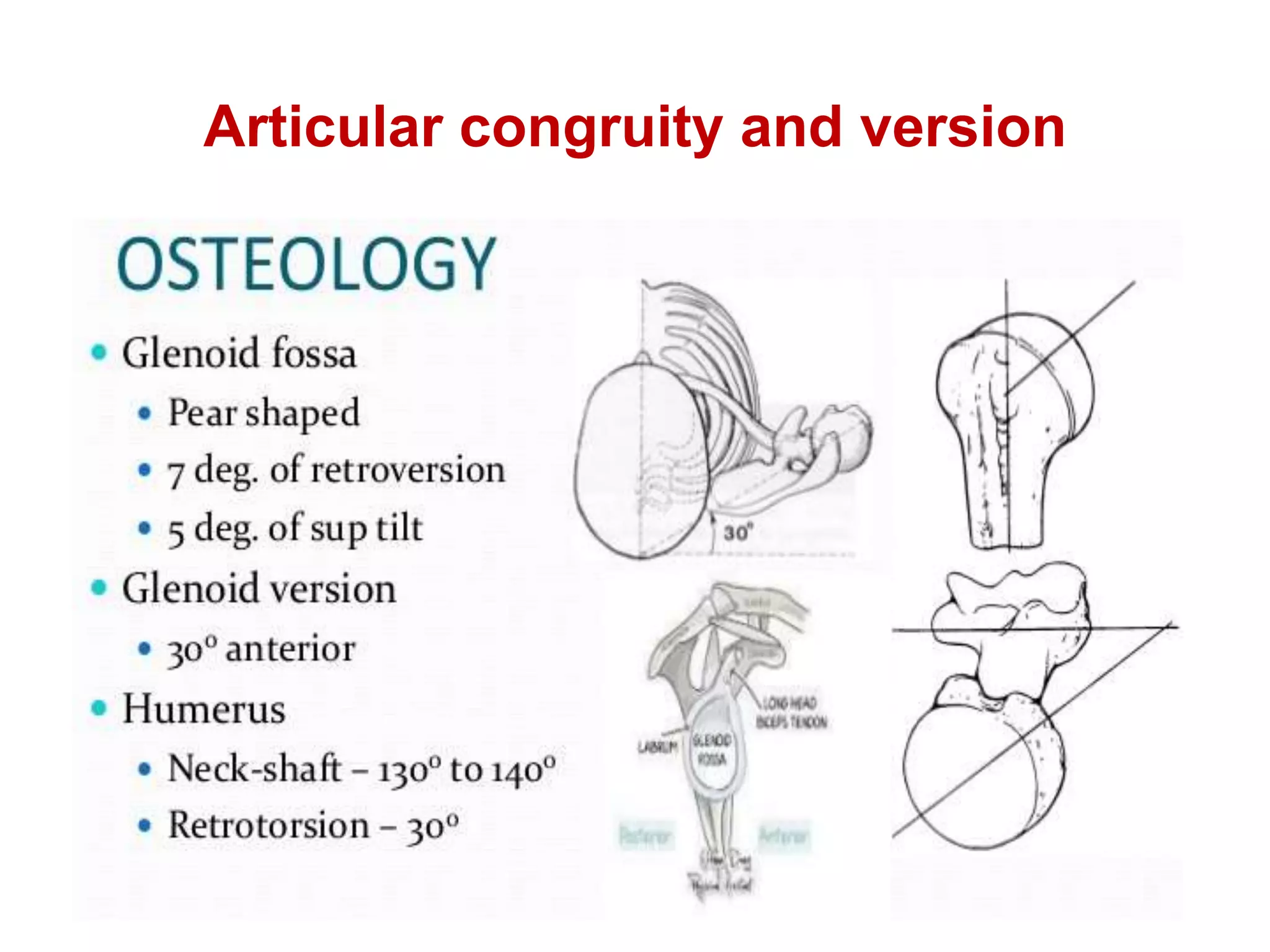
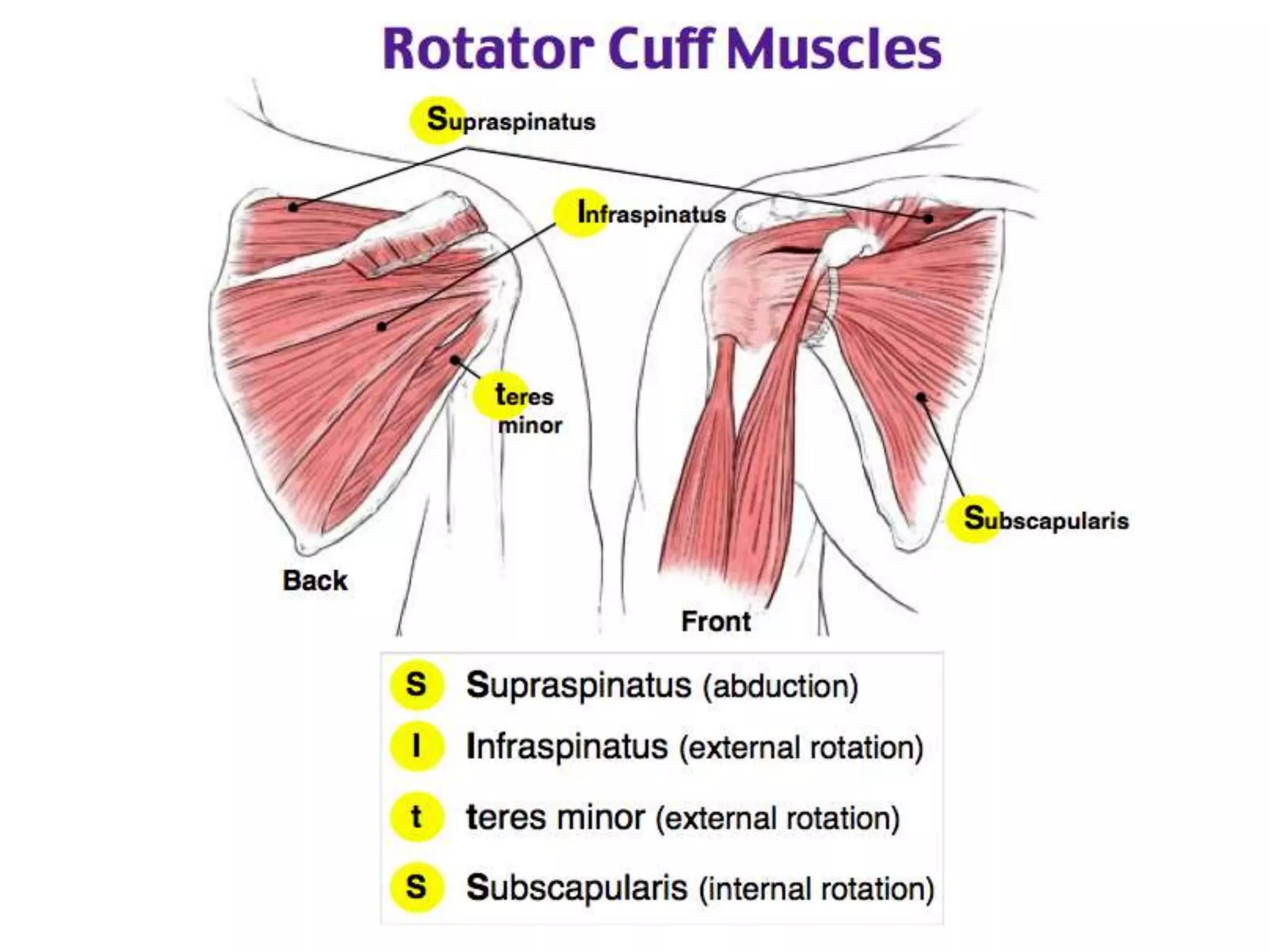
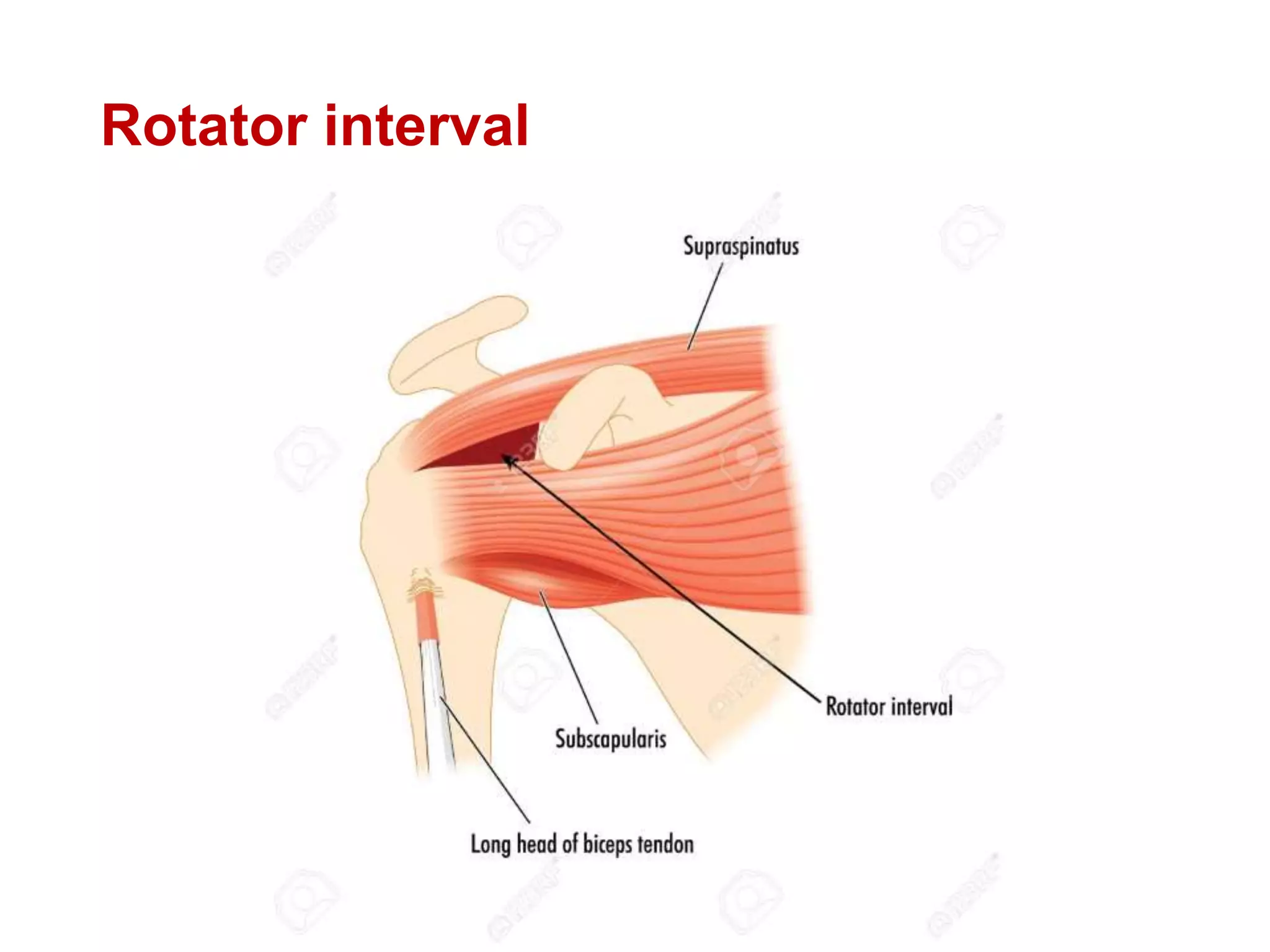
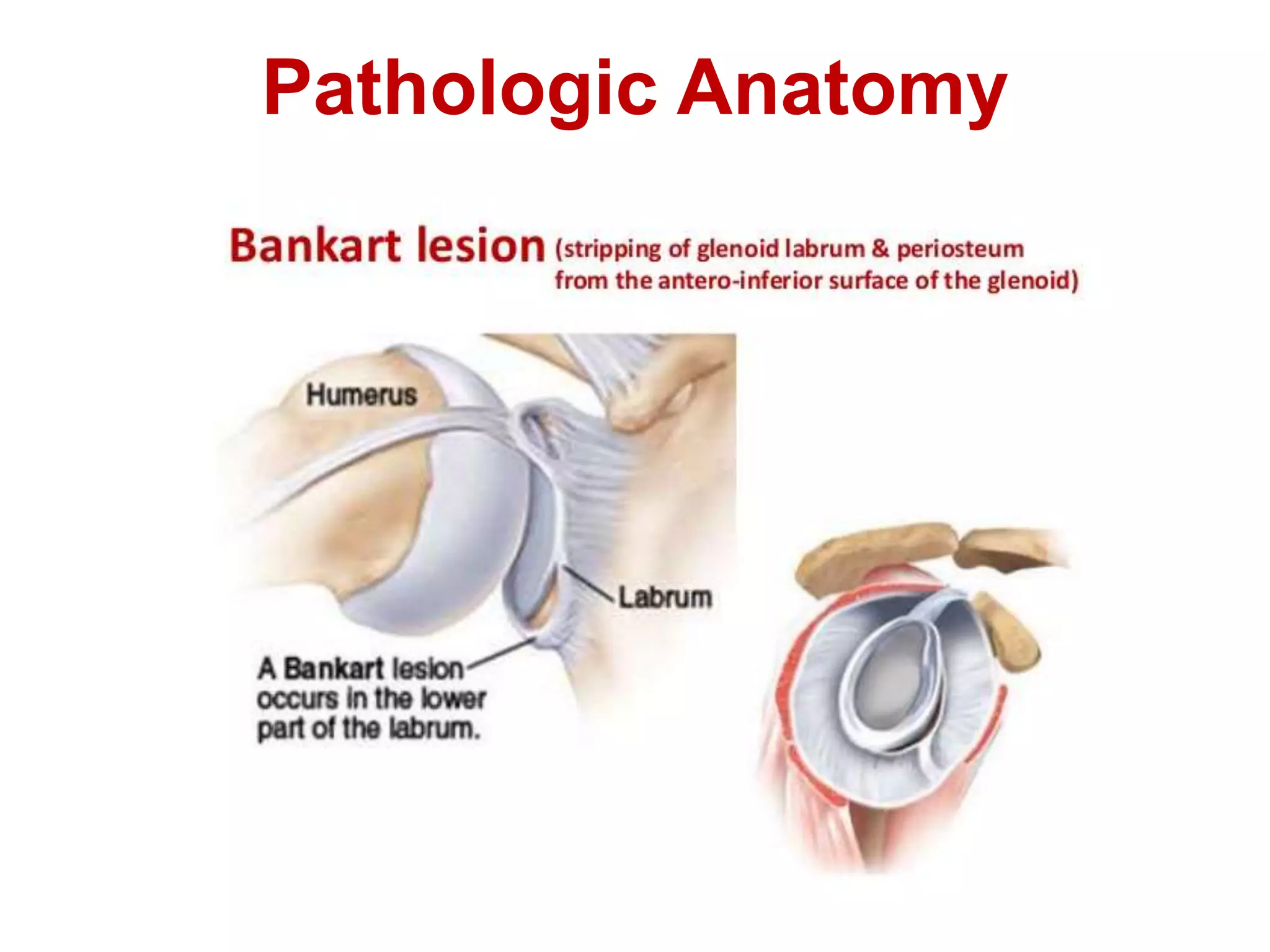
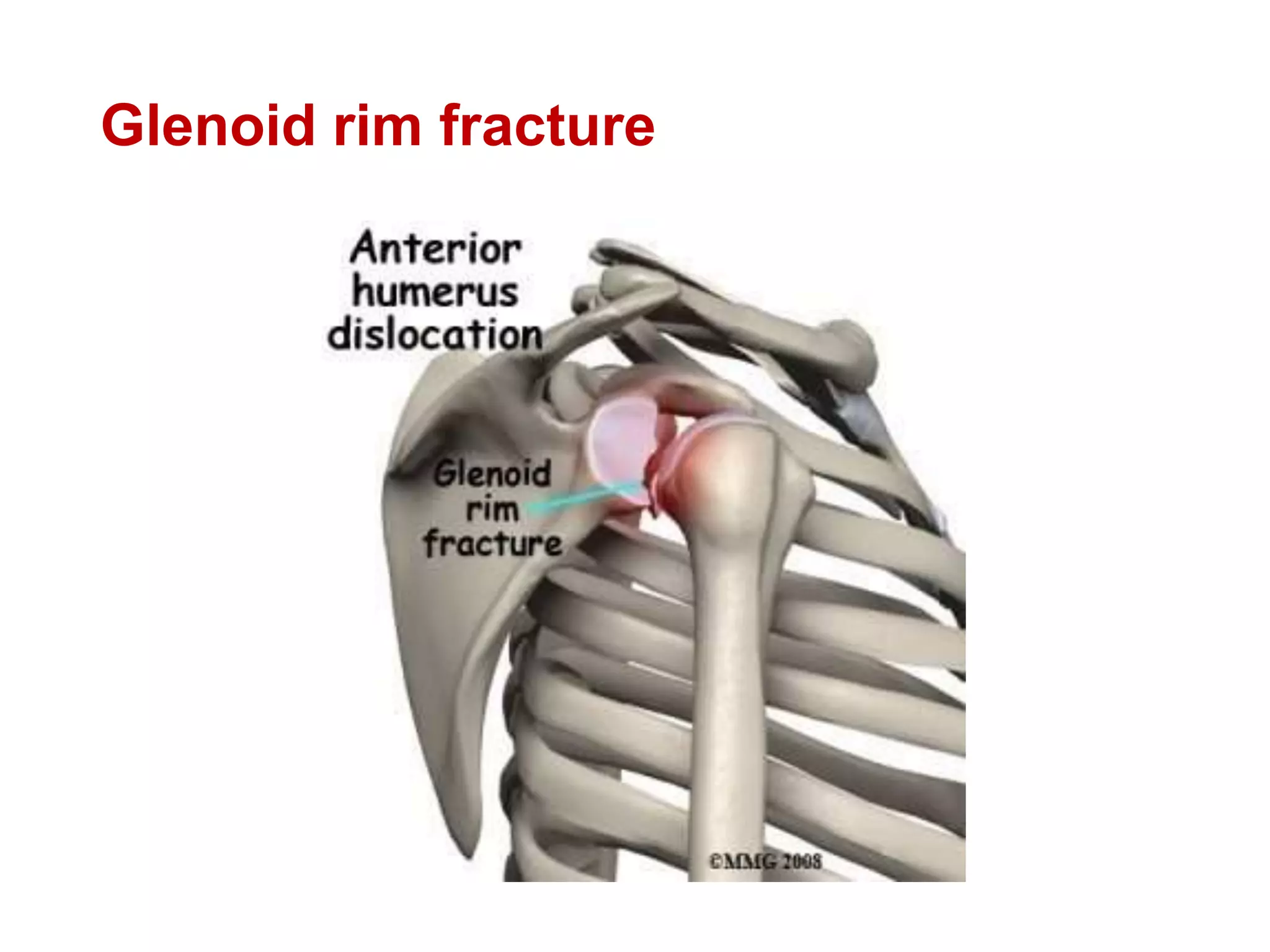
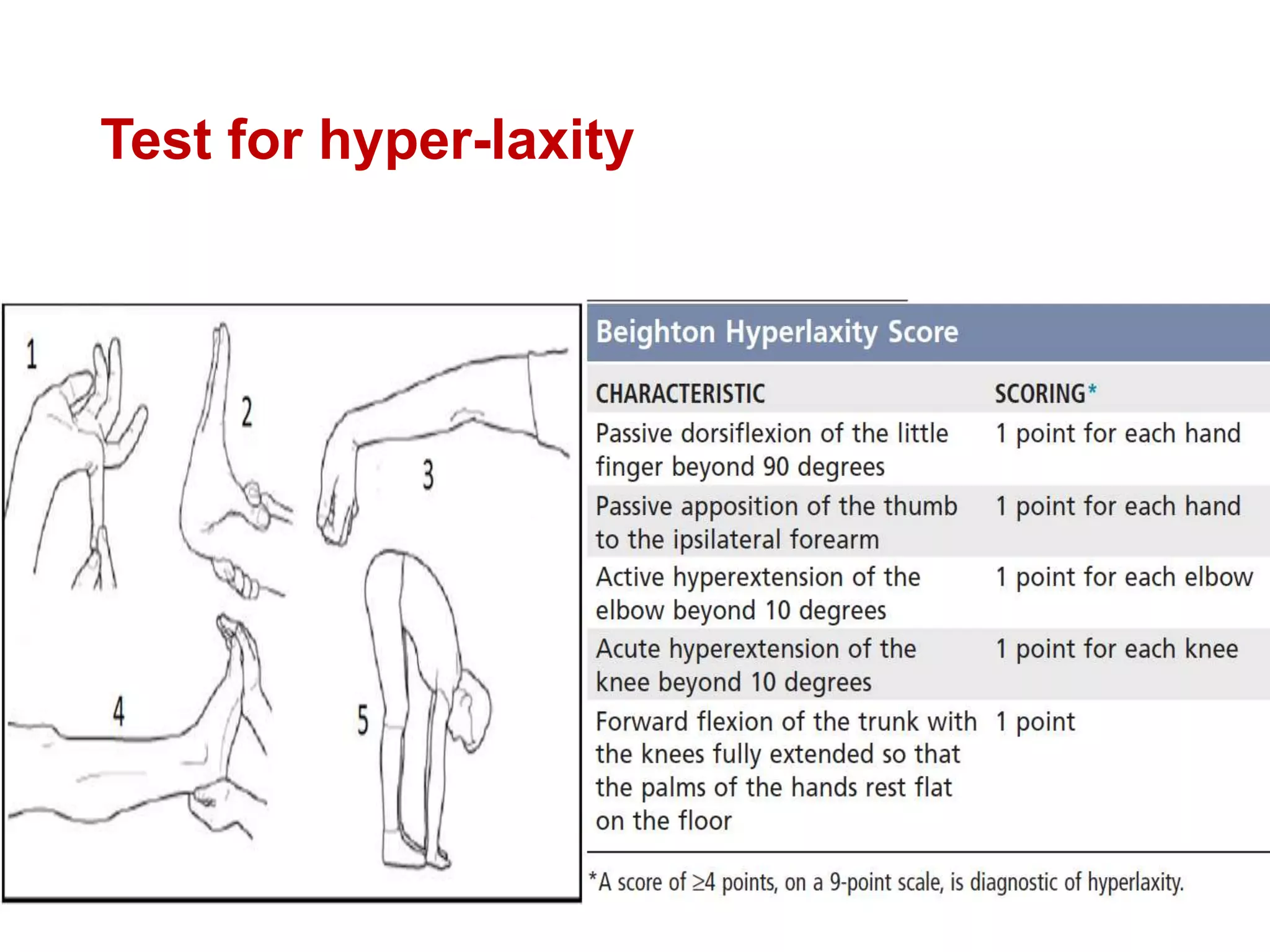
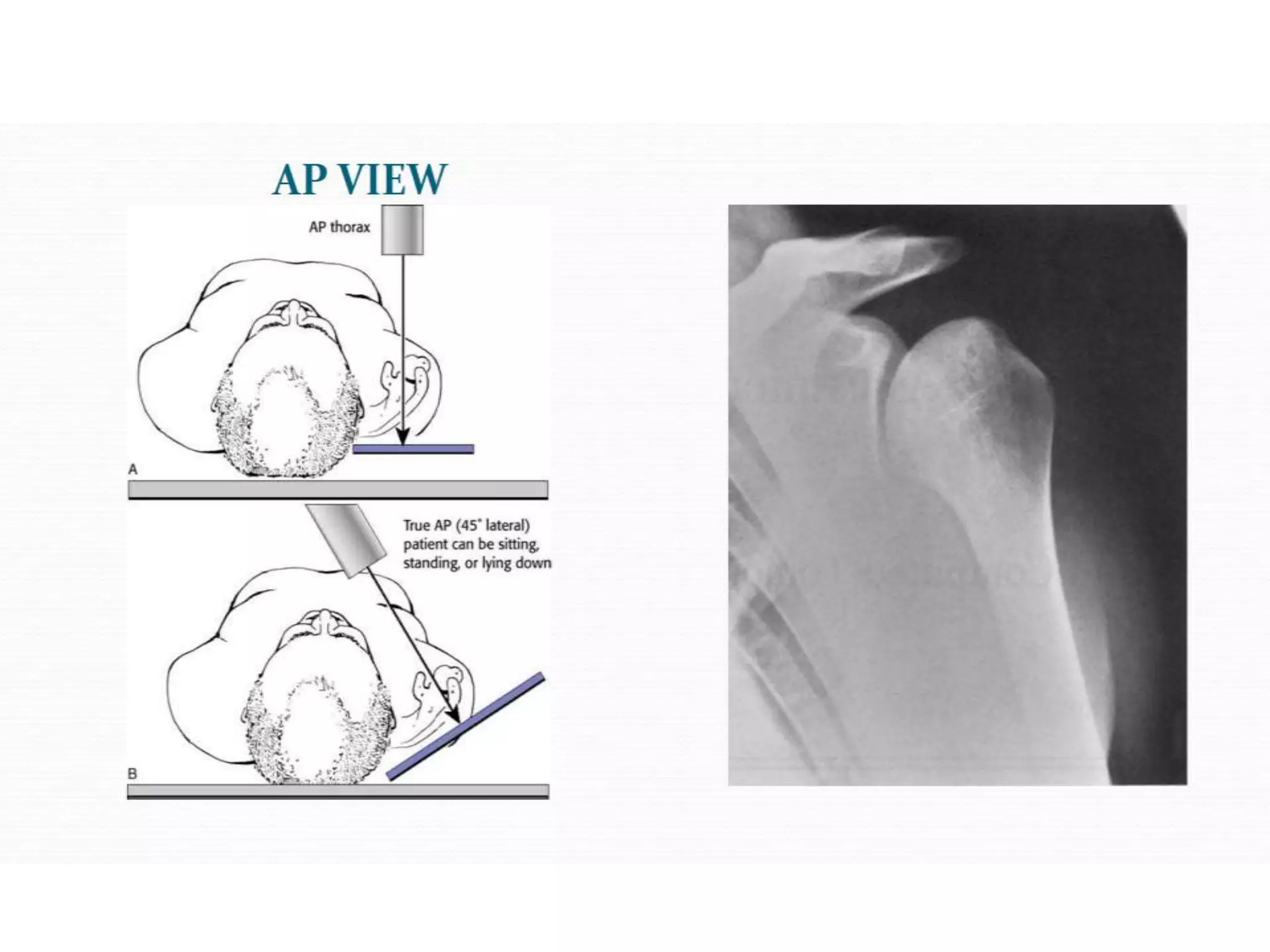
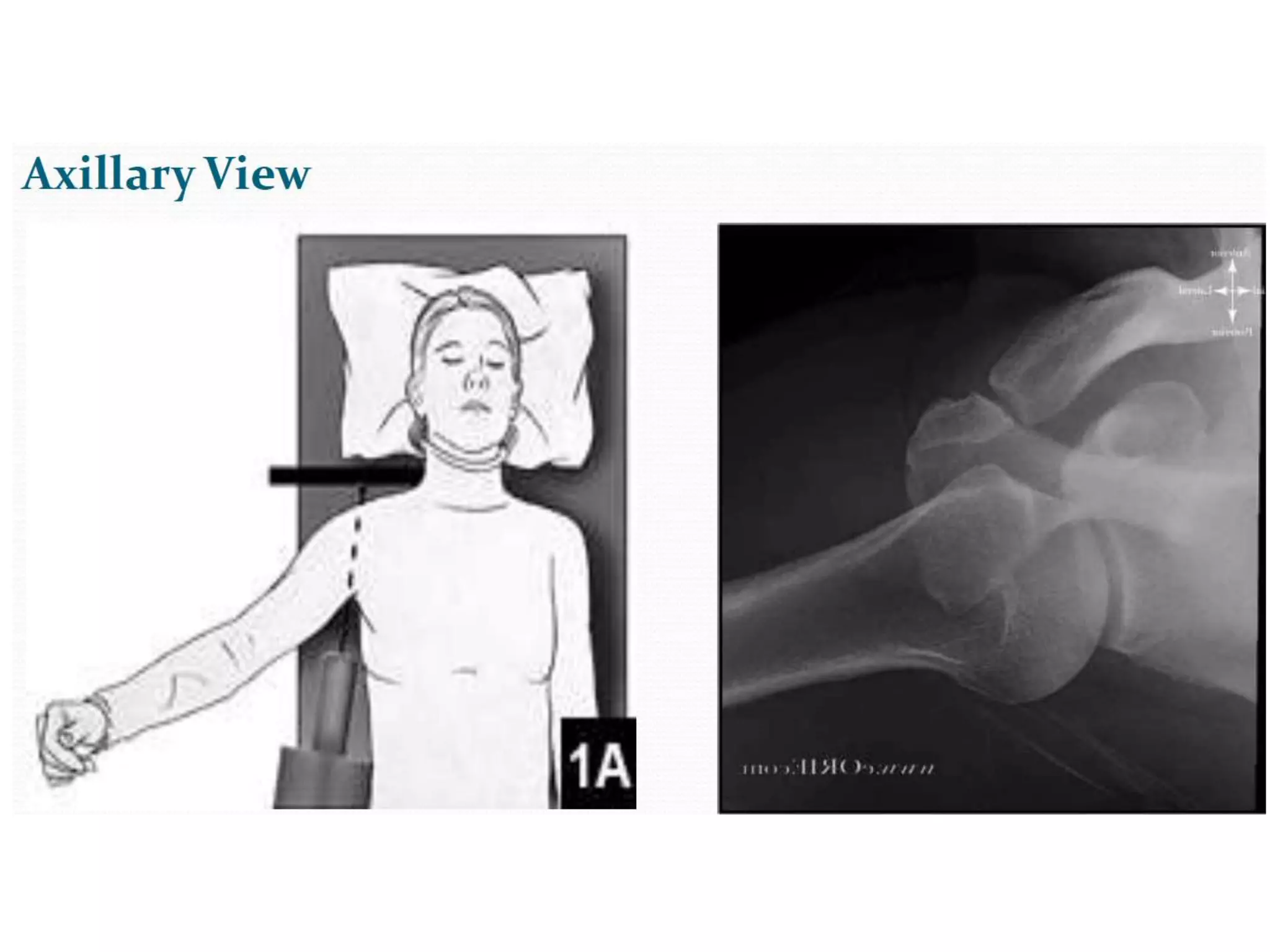
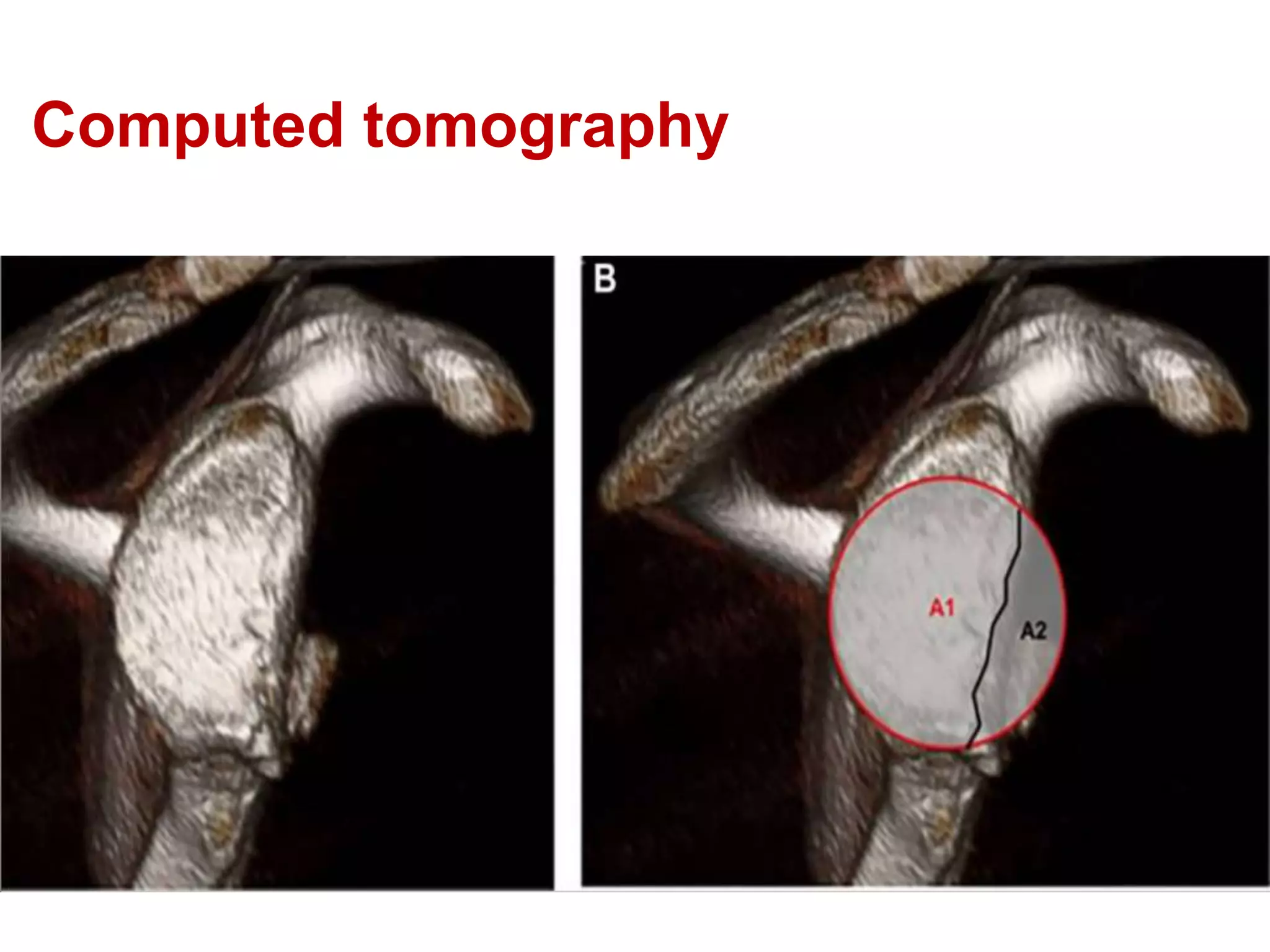
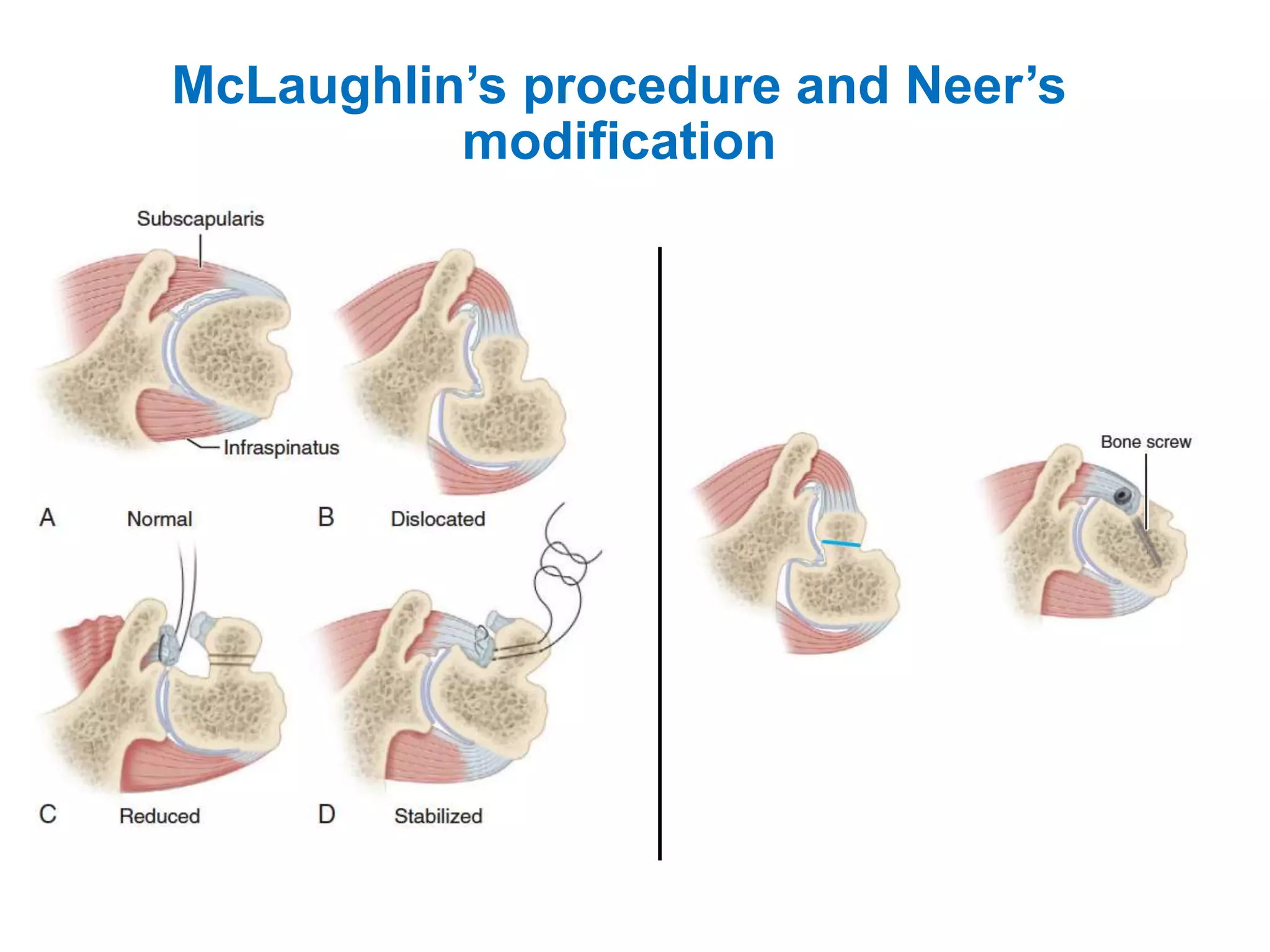
This document discusses shoulder instability, including the normal anatomy, causes of instability, classifications, clinical evaluation, radiographic evaluation, and treatment options. The glenohumeral joint has the highest mobility of any joint but lacks stability. Instability can be caused by excessive ligament laxity, bone defects, or trauma. Clinical exams include special tests like the apprehension and relocation tests. Treatment may involve arthroscopic or open stabilization surgery like Bankart repair, with post-op rehabilitation progressing from immobilization to strengthening and return to activity.