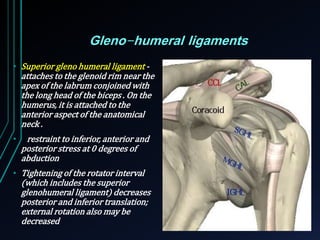
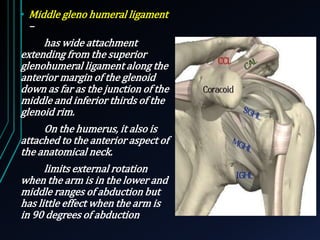
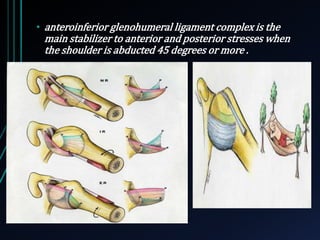
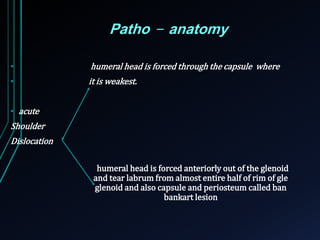
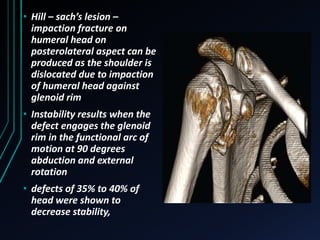
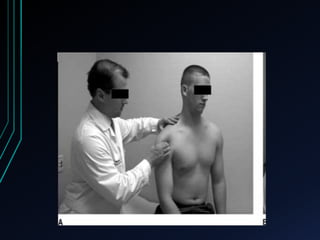
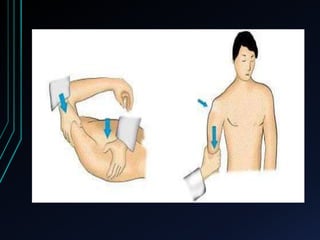
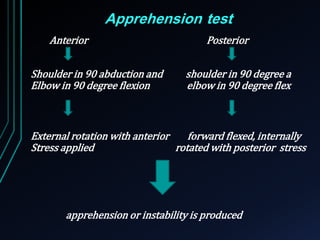
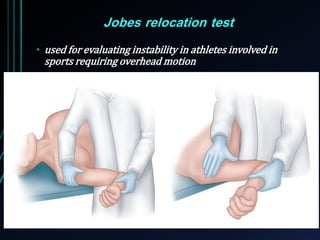
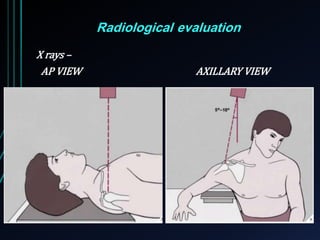
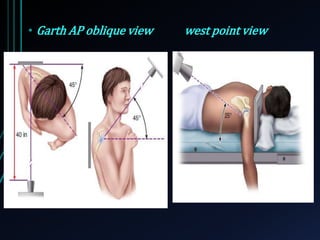
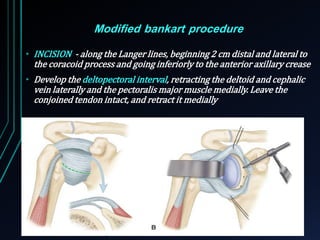
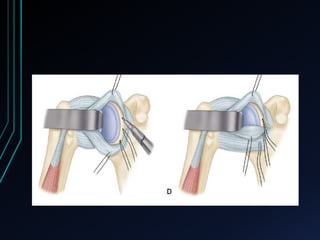
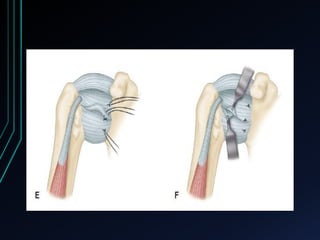
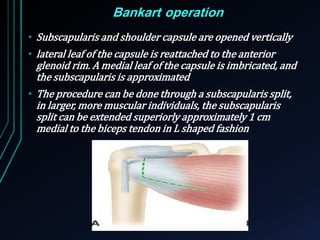
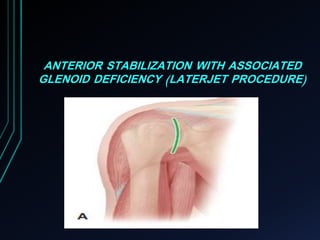
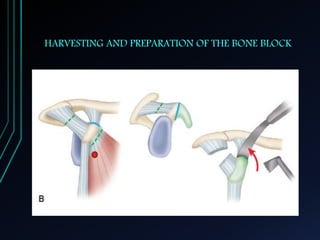
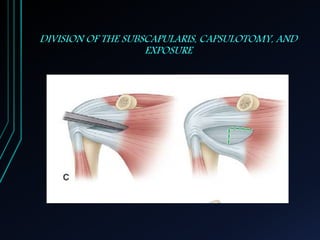
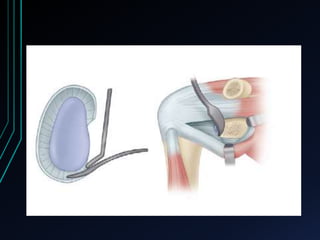
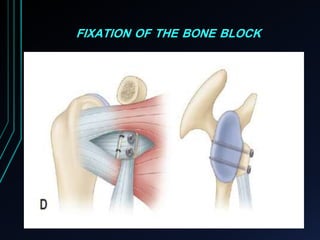
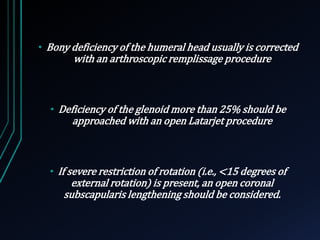
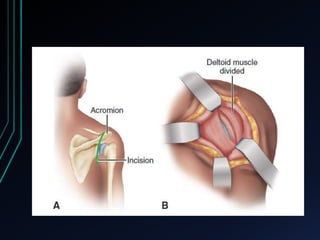
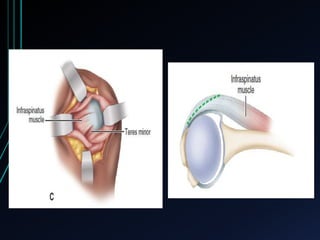
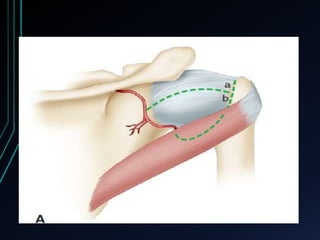
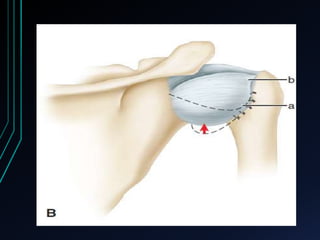
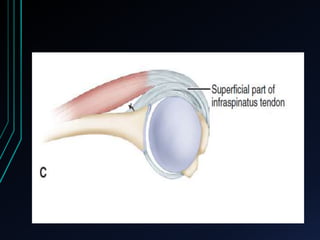
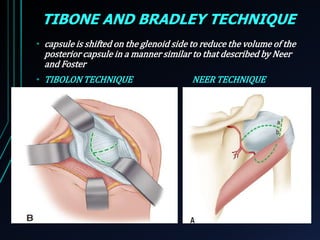
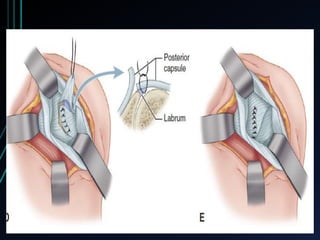
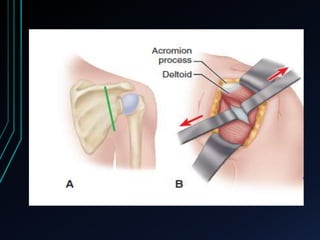
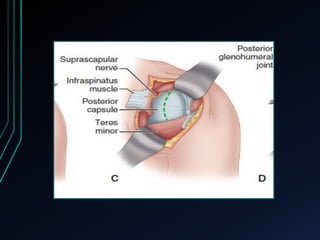
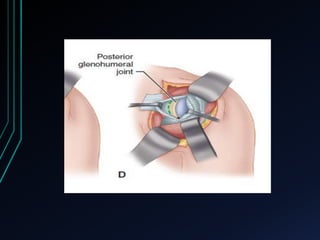
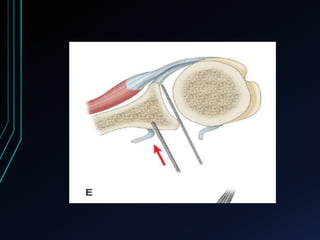
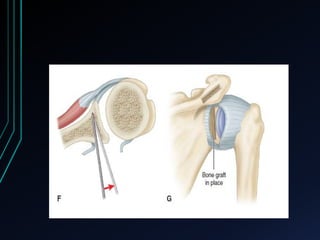
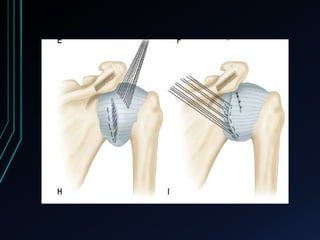
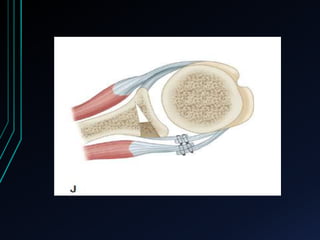
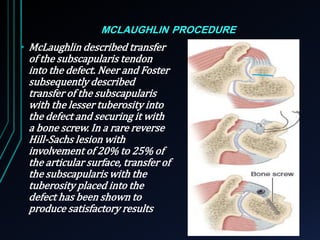
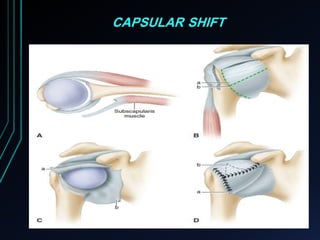
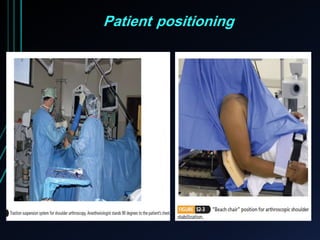
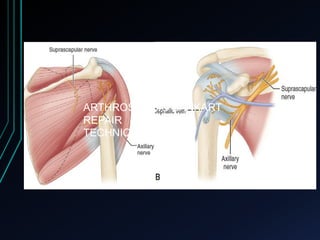
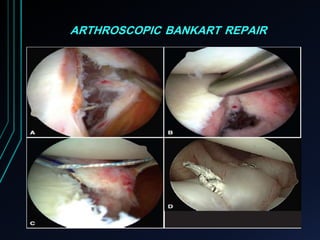
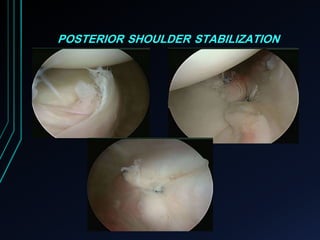
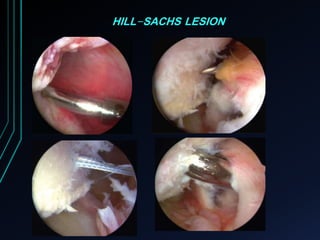
This document discusses recurrent shoulder dislocations. It provides information on the anatomy and stabilizing structures of the shoulder joint. Recurrent dislocations are most common in younger patients and those with underlying bone defects or ligament laxity. Evaluation involves assessing the direction, degree, and chronicity of instability through patient history and physical exam maneuvers like the shift test and sulcus test. Classification systems aim to characterize the type and cause of instability to guide treatment.