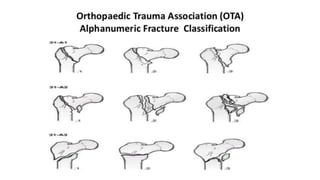
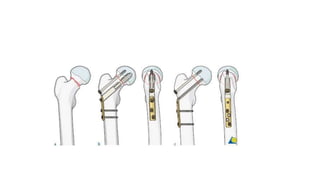
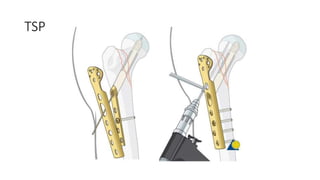
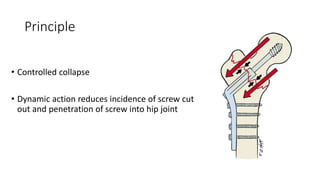
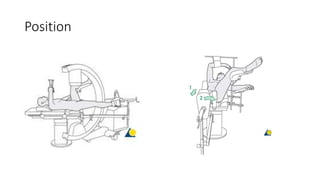
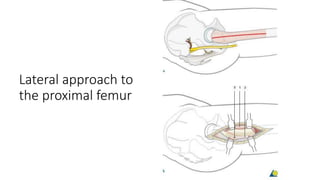
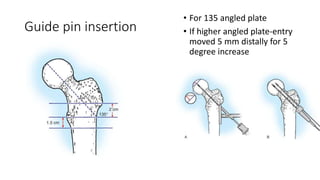
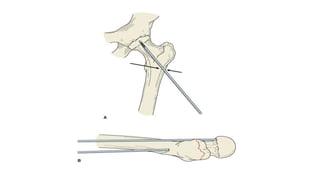
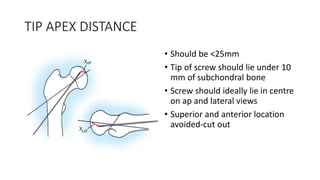
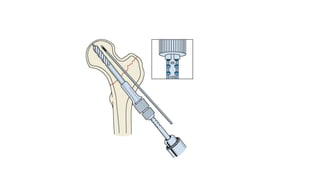
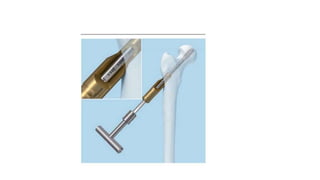
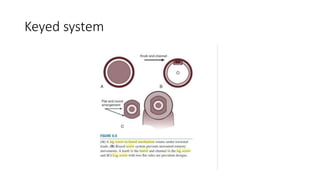
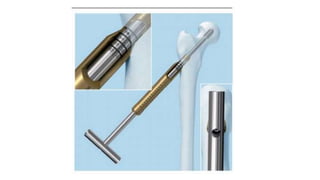
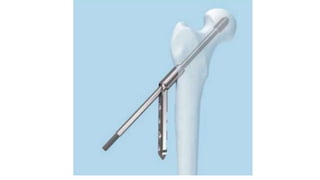
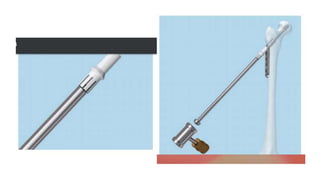
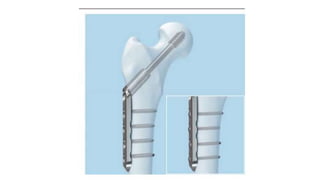
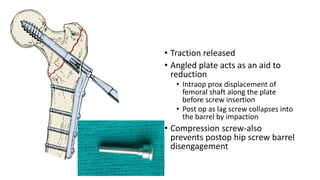
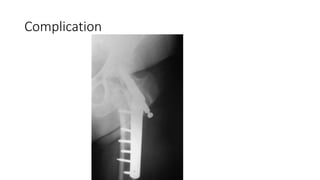
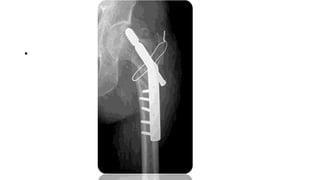
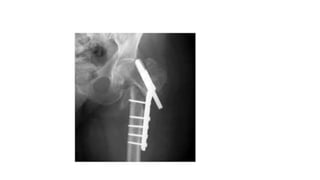
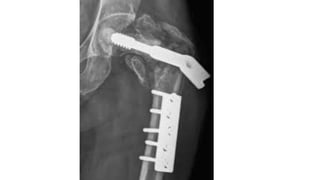
This document discusses the dynamic hip screw (DHS), used to treat intertrochanteric hip fractures. The DHS provides controlled collapse and dynamic action to reduce complications like screw cut-out. Key steps of the procedure include closed reduction of the fracture, guide pin and plate insertion at 135 degrees, and measuring screw length. Factors like tip-apex distance and screw position are important to prevent complications. The DHS works by creating compression as the lag screw collapses into the barrel post-operatively.