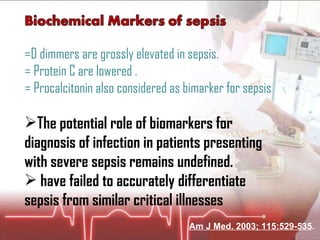
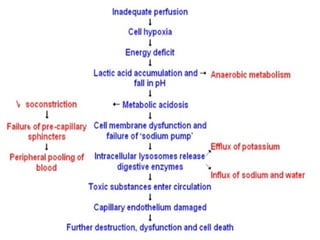
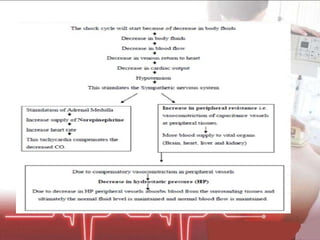
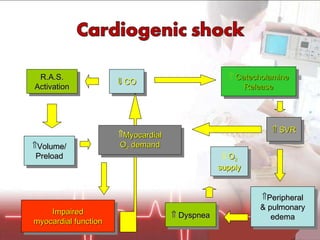
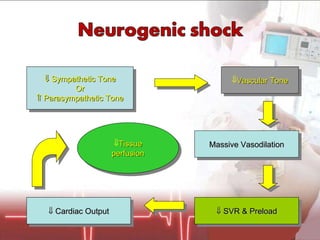
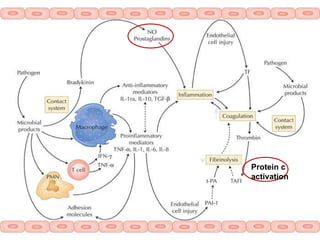
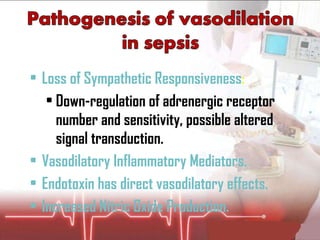
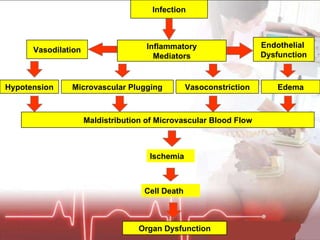
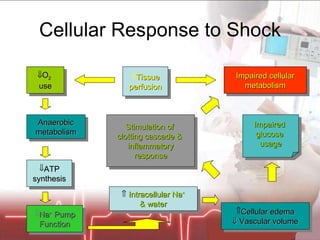
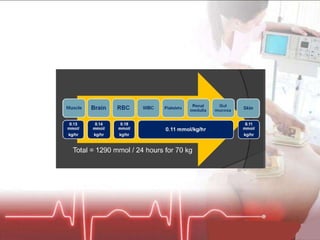
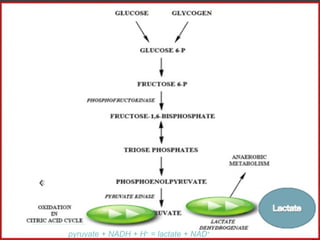
The document discusses cellular response and biochemical markers of shock. It summarizes that cellular response to shock is reflected in clinical manifestations and lactate is the most important biochemical marker of shock, supported by evidence. However, other markers like procalcitonin, D-dimers, and protein C have conflicting evidence and need further validation to diagnose infection in patients with sepsis or septic shock. Nitrite/nitrate concentration and procalcitonin level may be the most suitable tests for defining patients with septic shock.




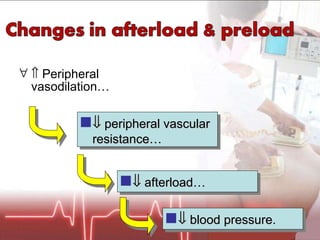
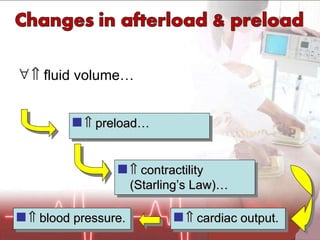
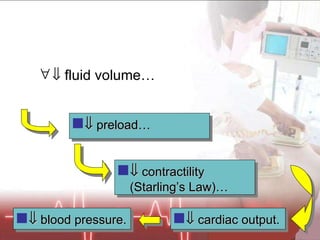



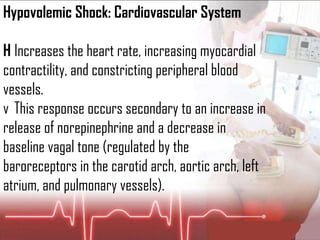


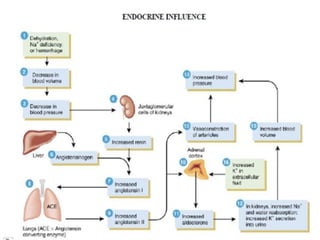
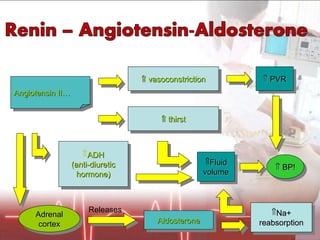
![Plasma volume [Na+] &/Or Kidney (juxtaglomerular apparatus) Detected by Releases Renin Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I… Converts Via ACE (A ngiotensin C onverting E nzyme) Angiotensin II…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newpre-100514034607-phpapp01/85/shock-marker-17-320.jpg)

























![Procalcitonin ] Procalcitonin (PCT) has been proposed as a more specific [and better prognostic marker than CRP, although its value has also been challenged . It remains difficult to differentiate sepsis from other non-infectious causes of systemic inflammatory response syndrome , and there is a continuous search for better biomarkers of sepsis. J Crit Care 2004, 19:152-157 Lancet Infect Dis 2007](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newpre-100514034607-phpapp01/85/shock-marker-53-320.jpg)