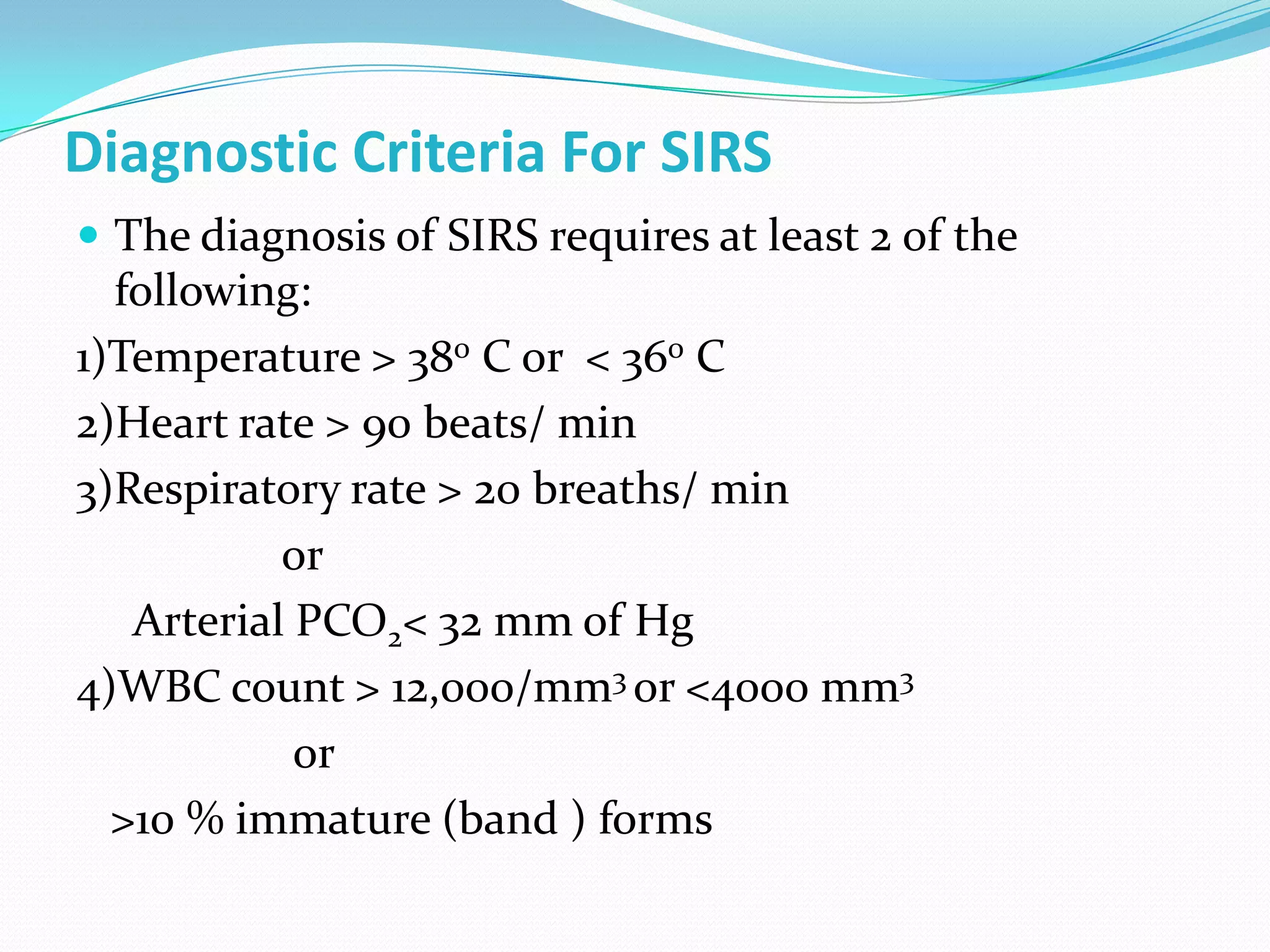
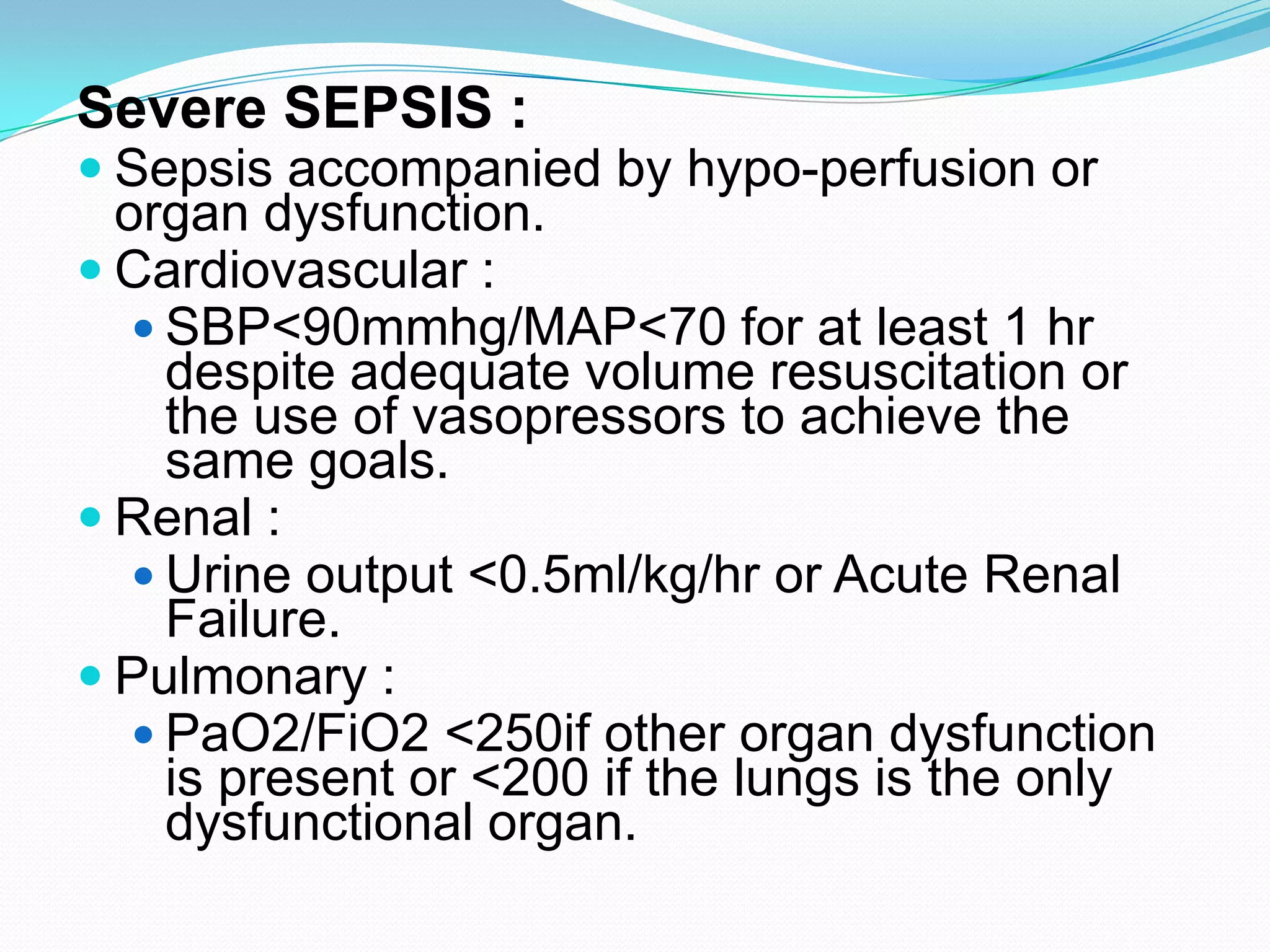
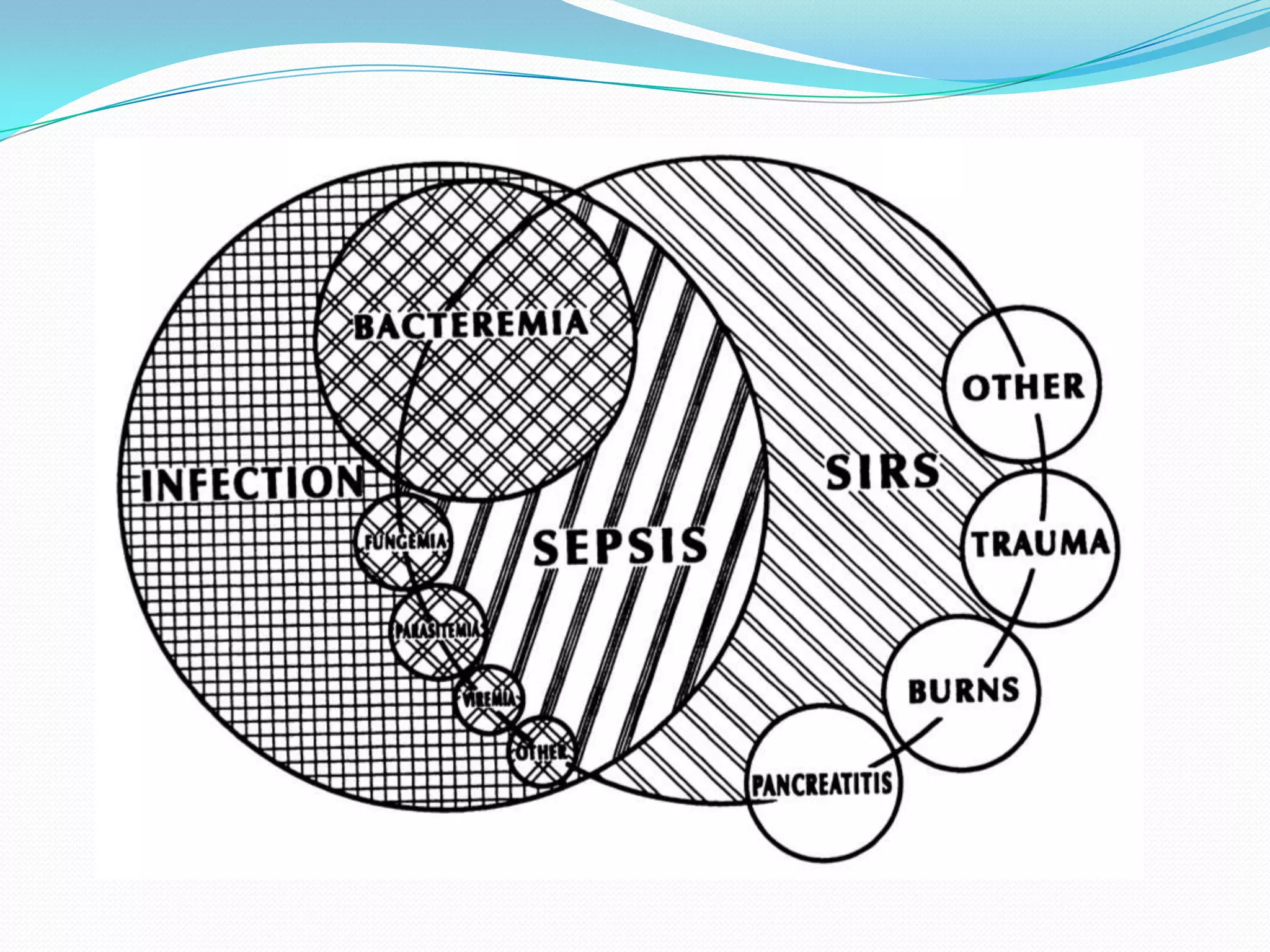
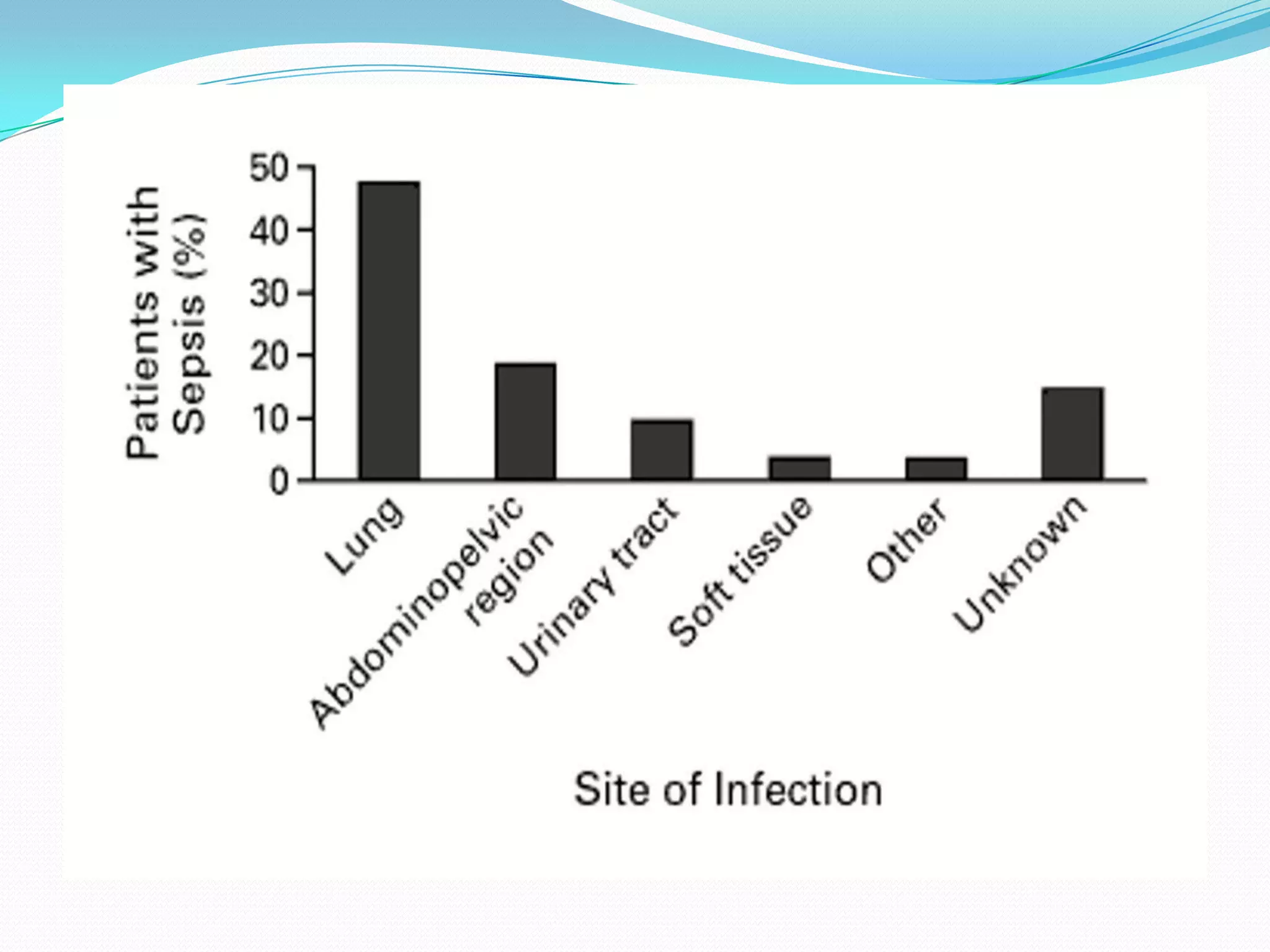
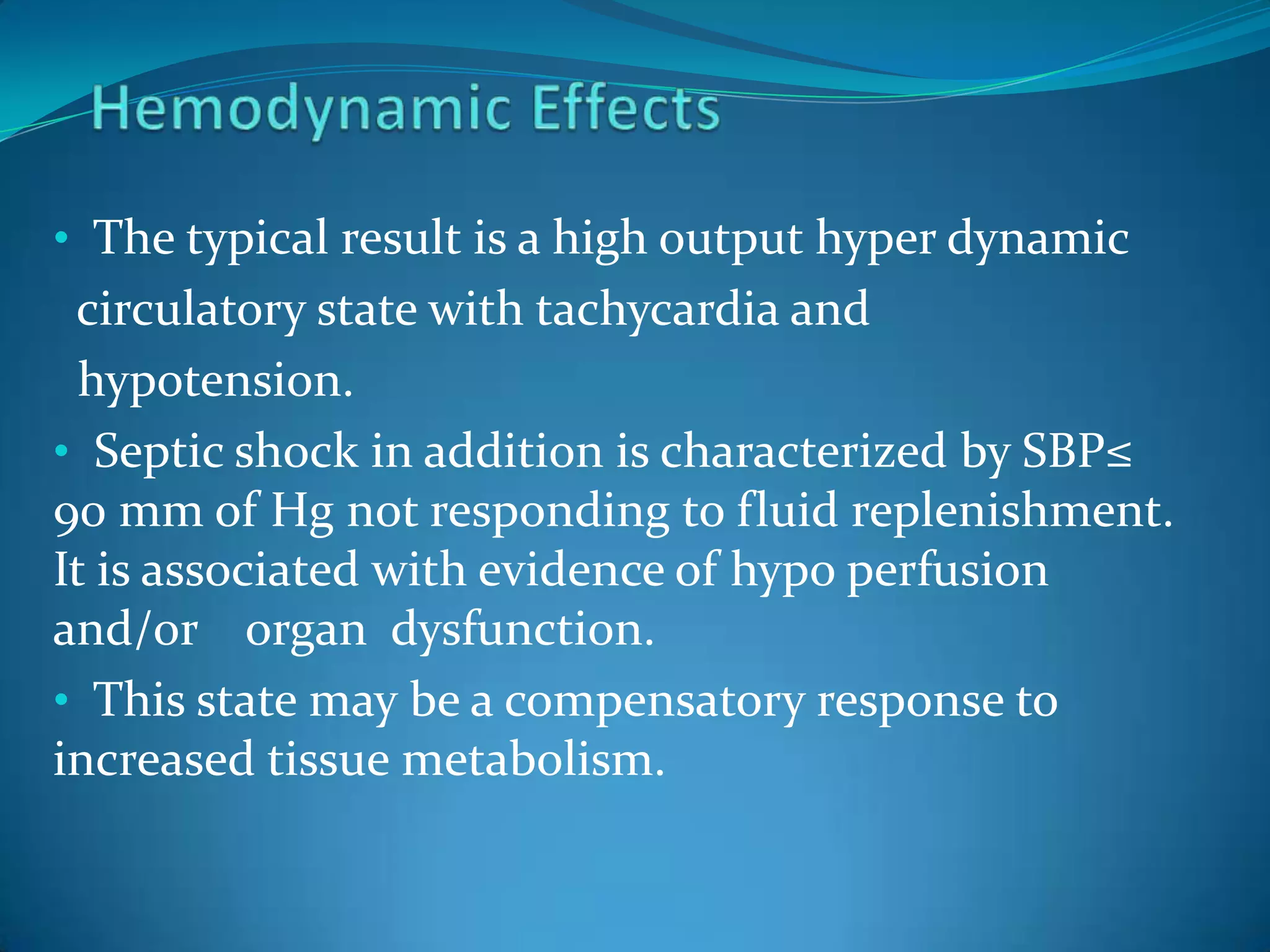
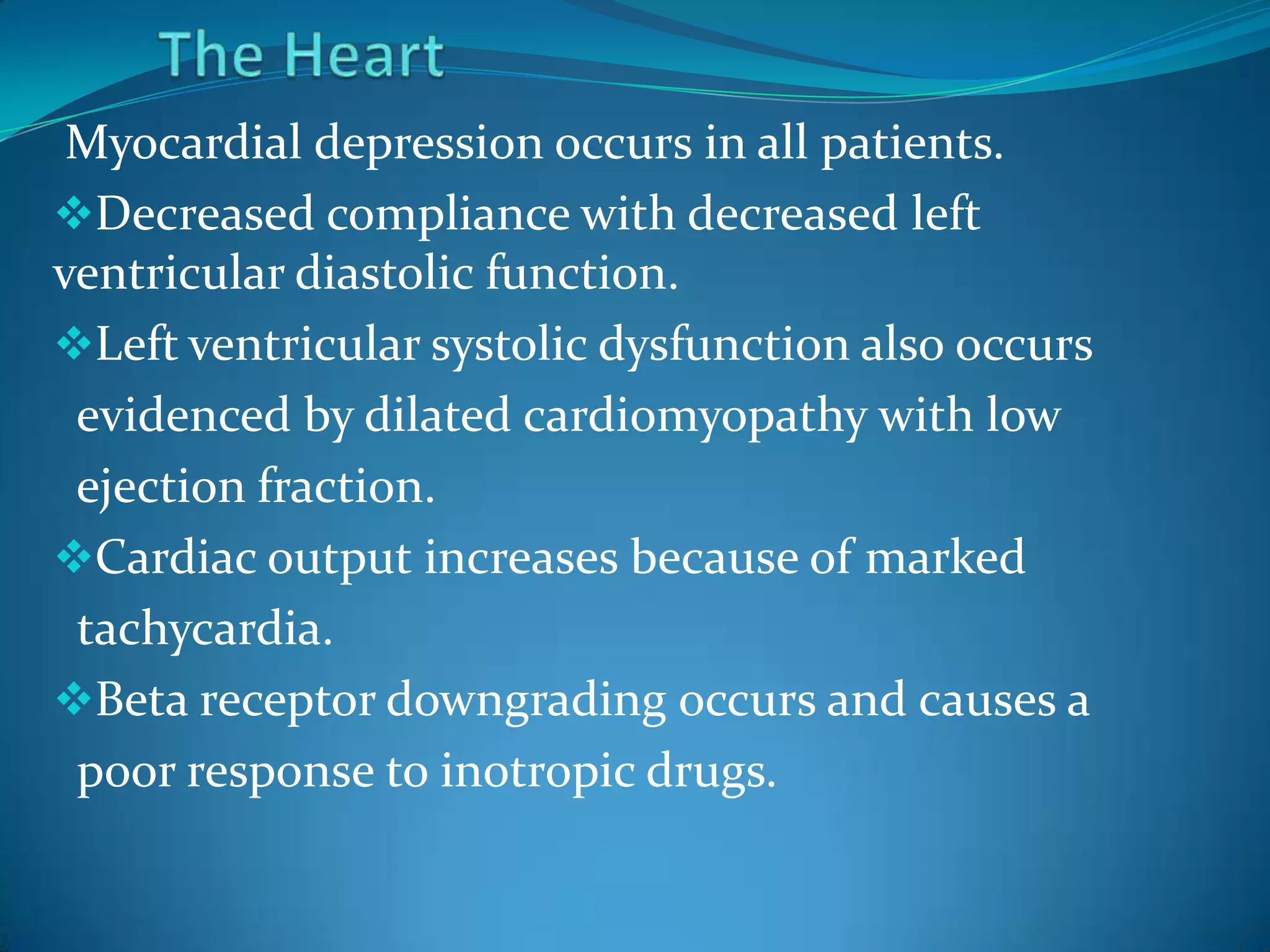
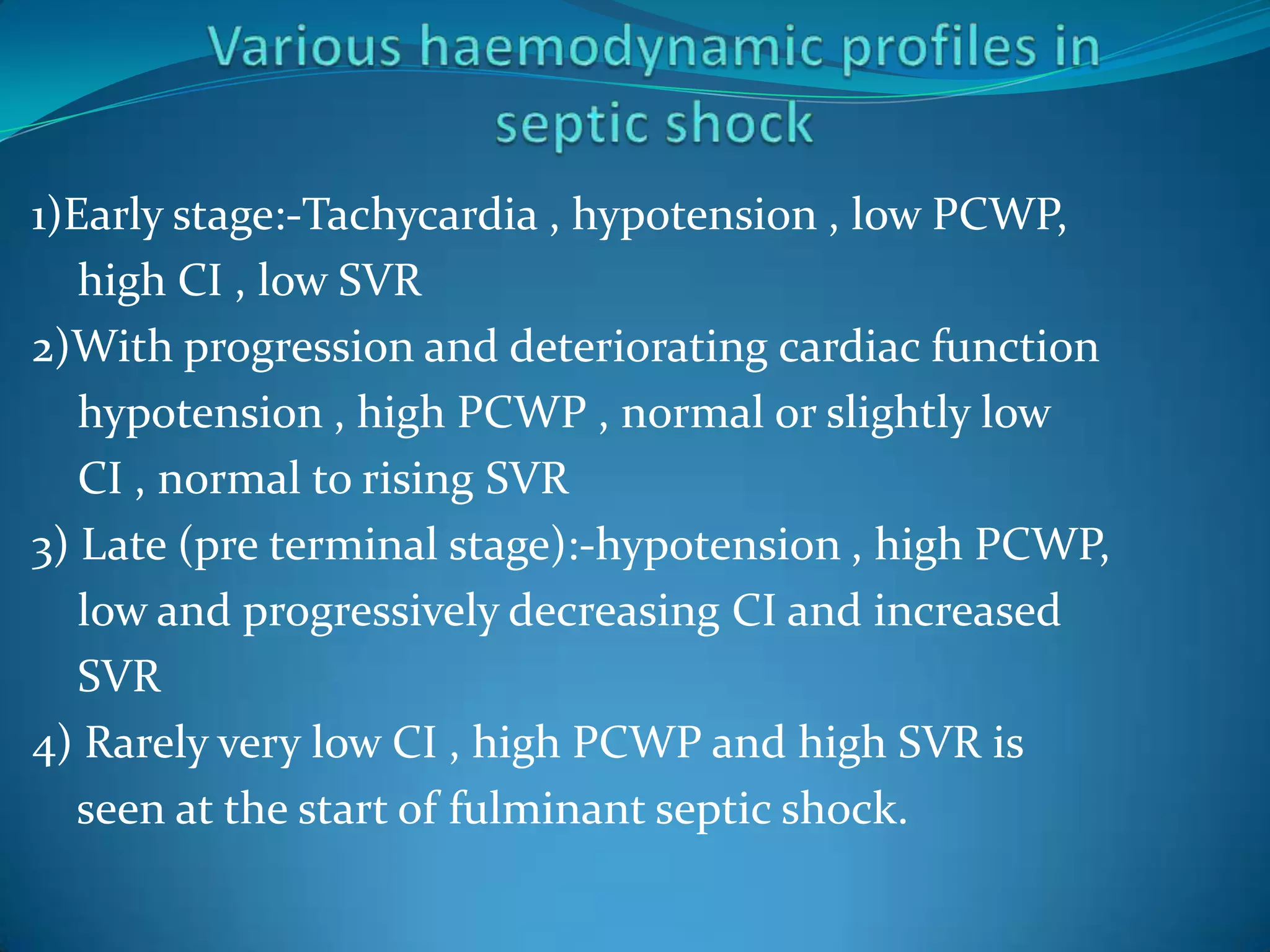
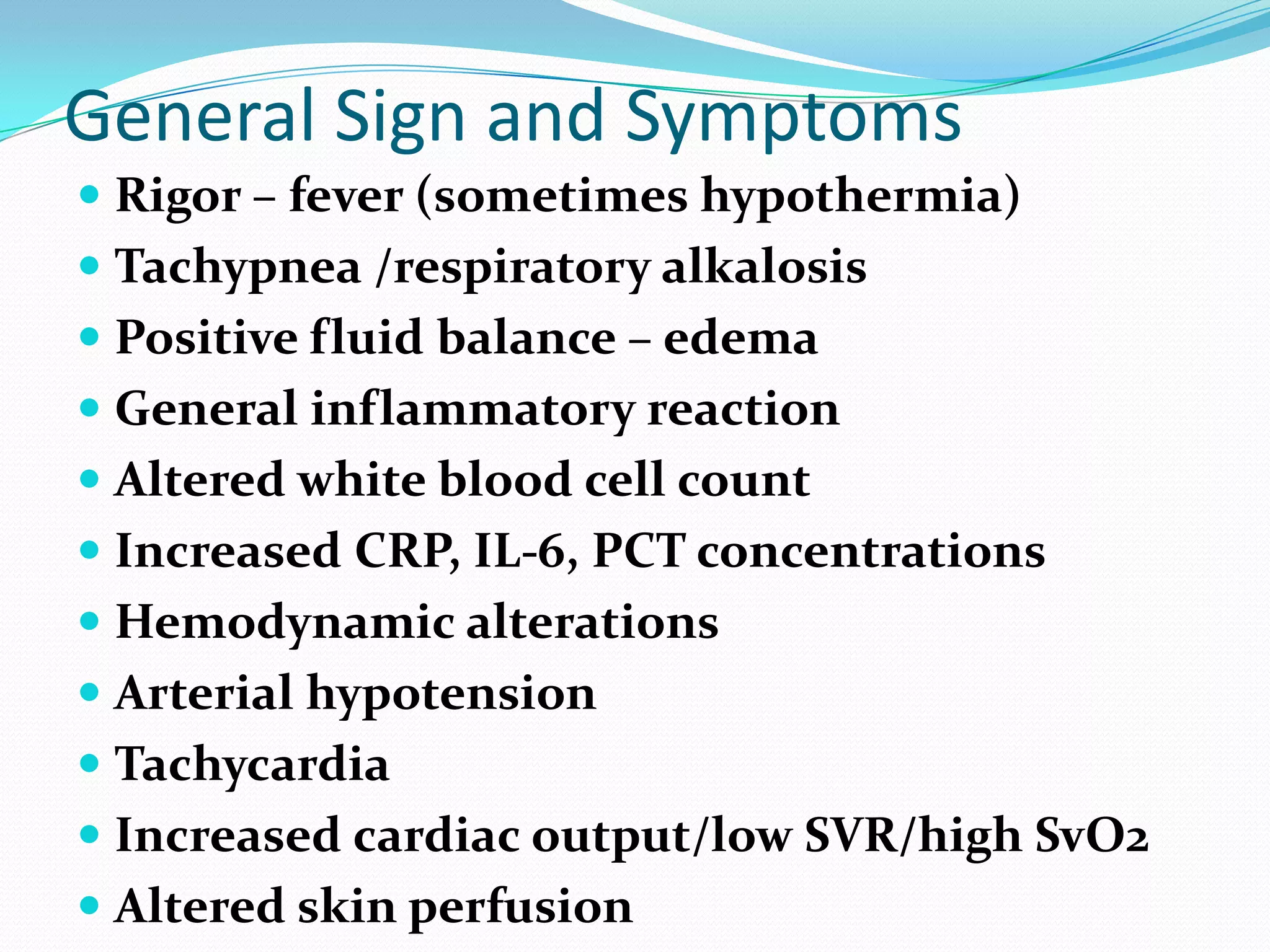
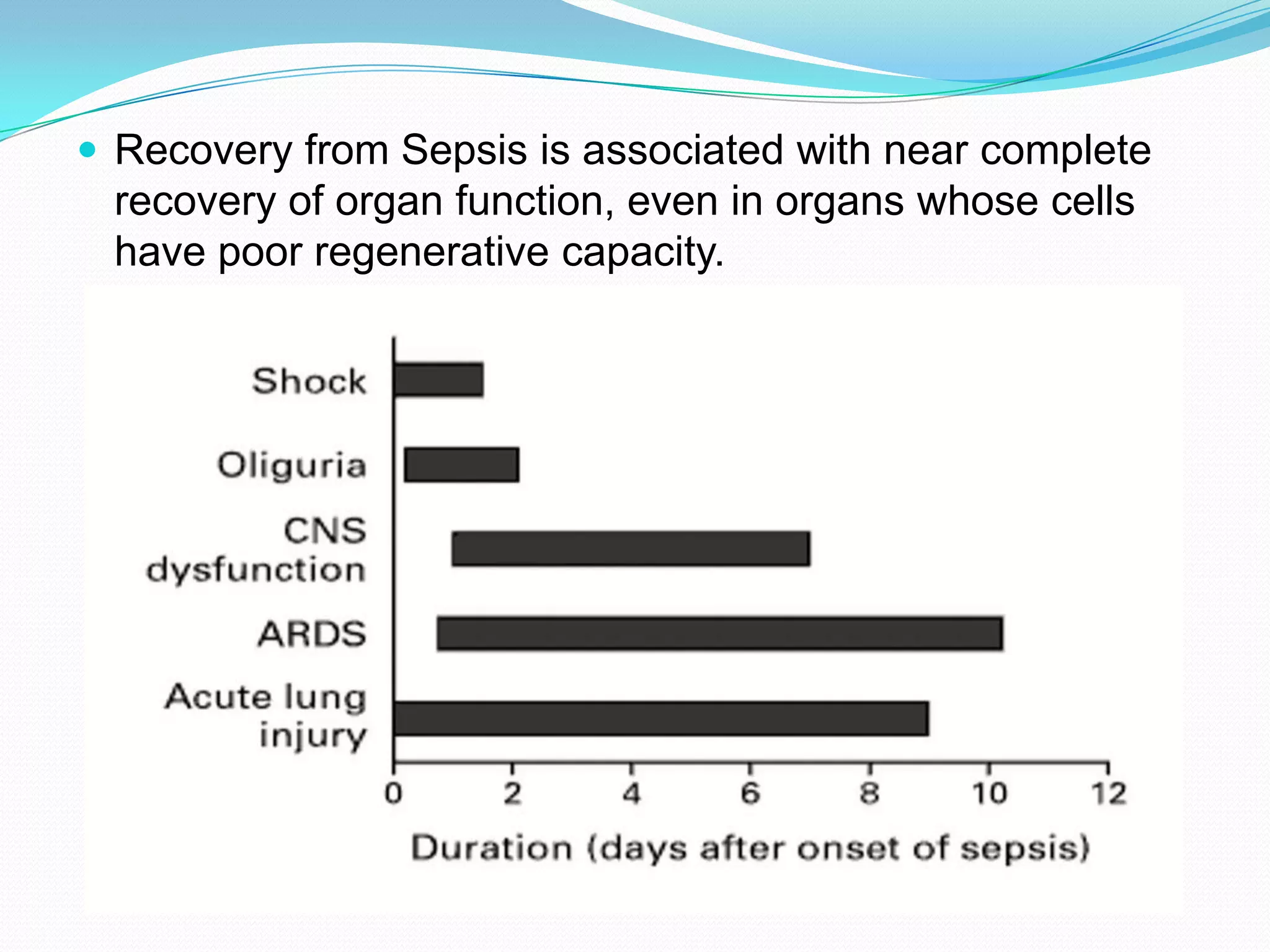
- Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response caused by infection that can progress to severe sepsis and septic shock. Severe sepsis is defined as sepsis with organ dysfunction, while septic shock involves hypotension refractory to fluid resuscitation along with lactate levels over 2 mmol/L despite fluid resuscitation.
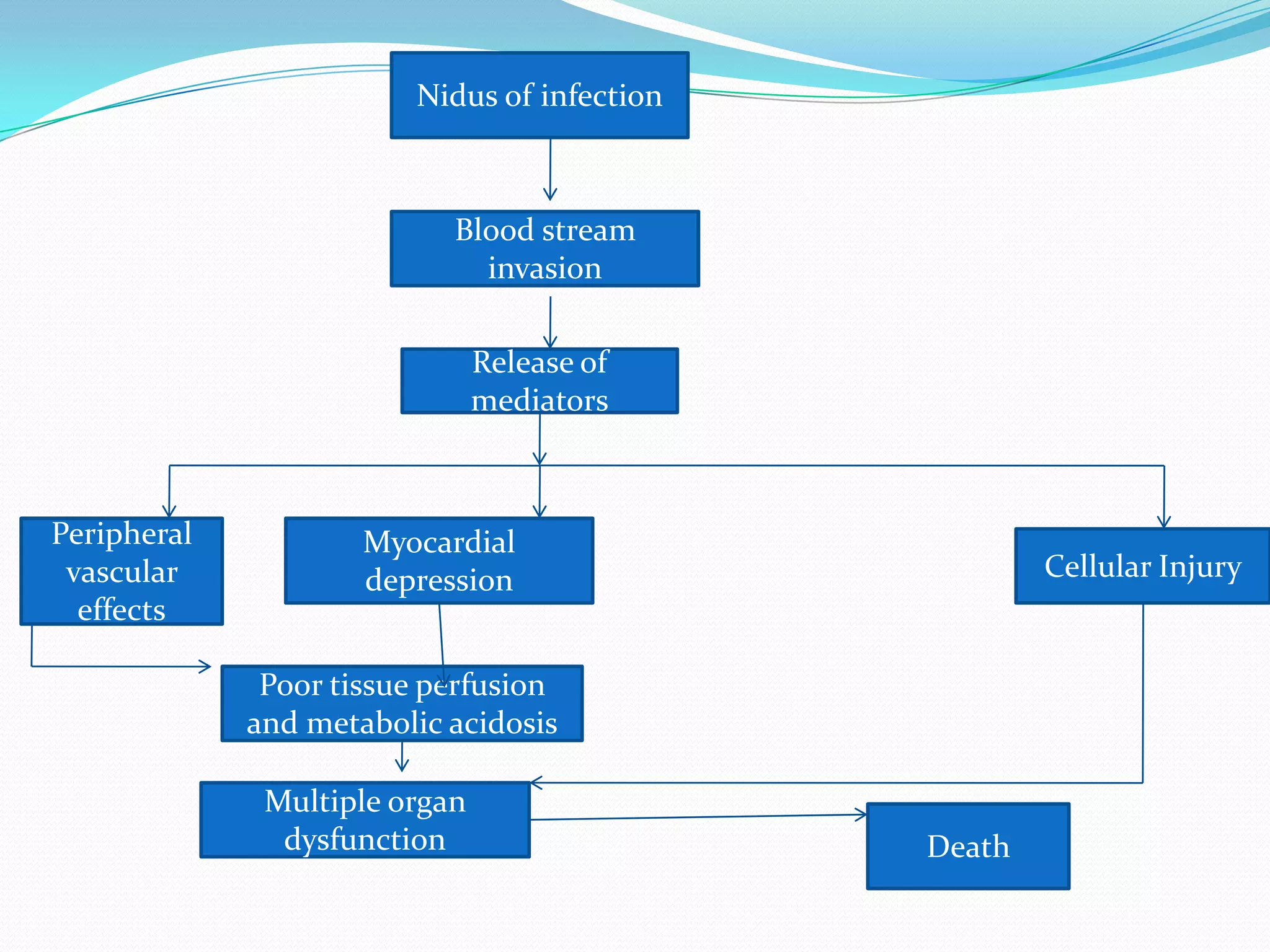
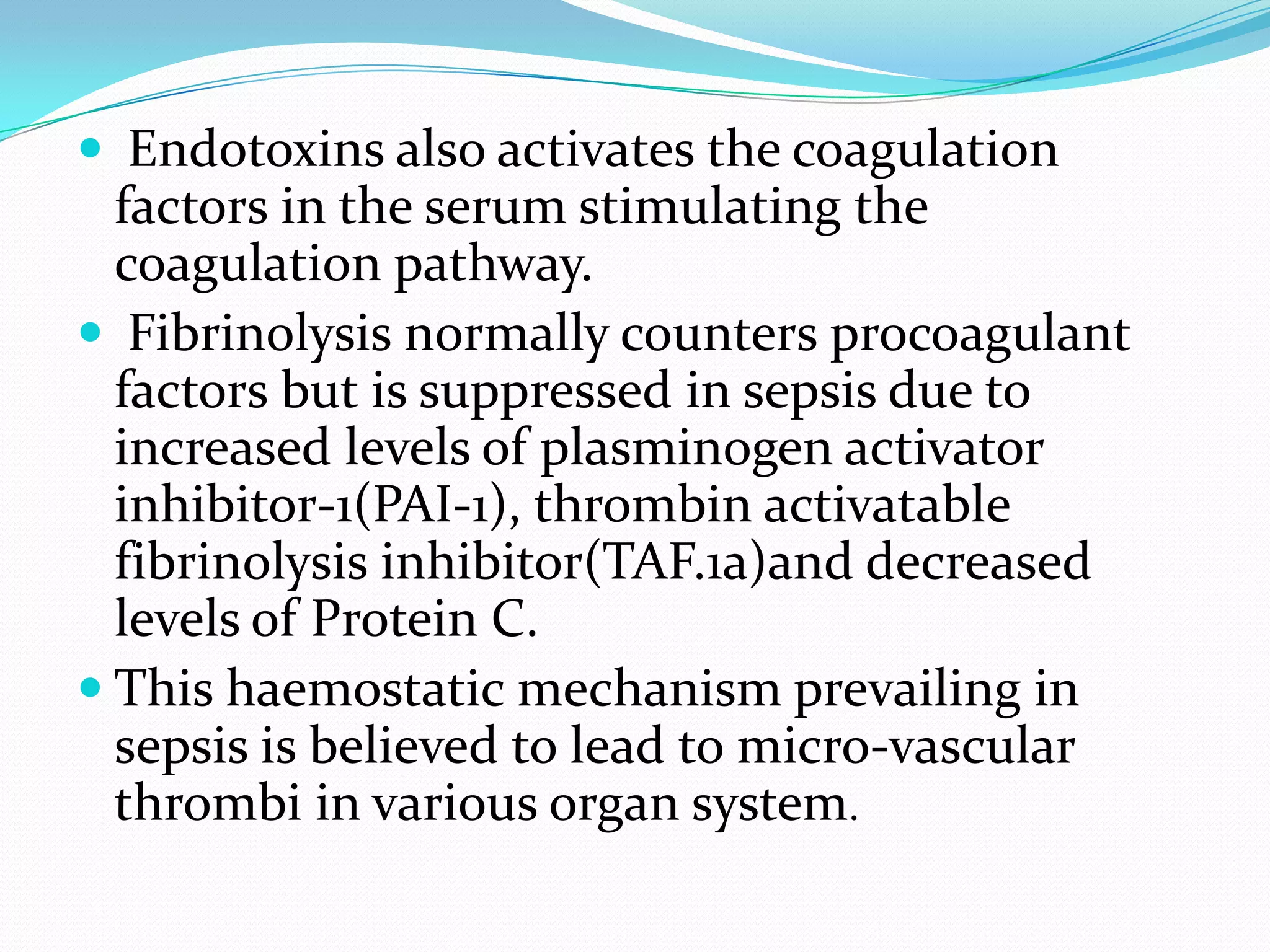
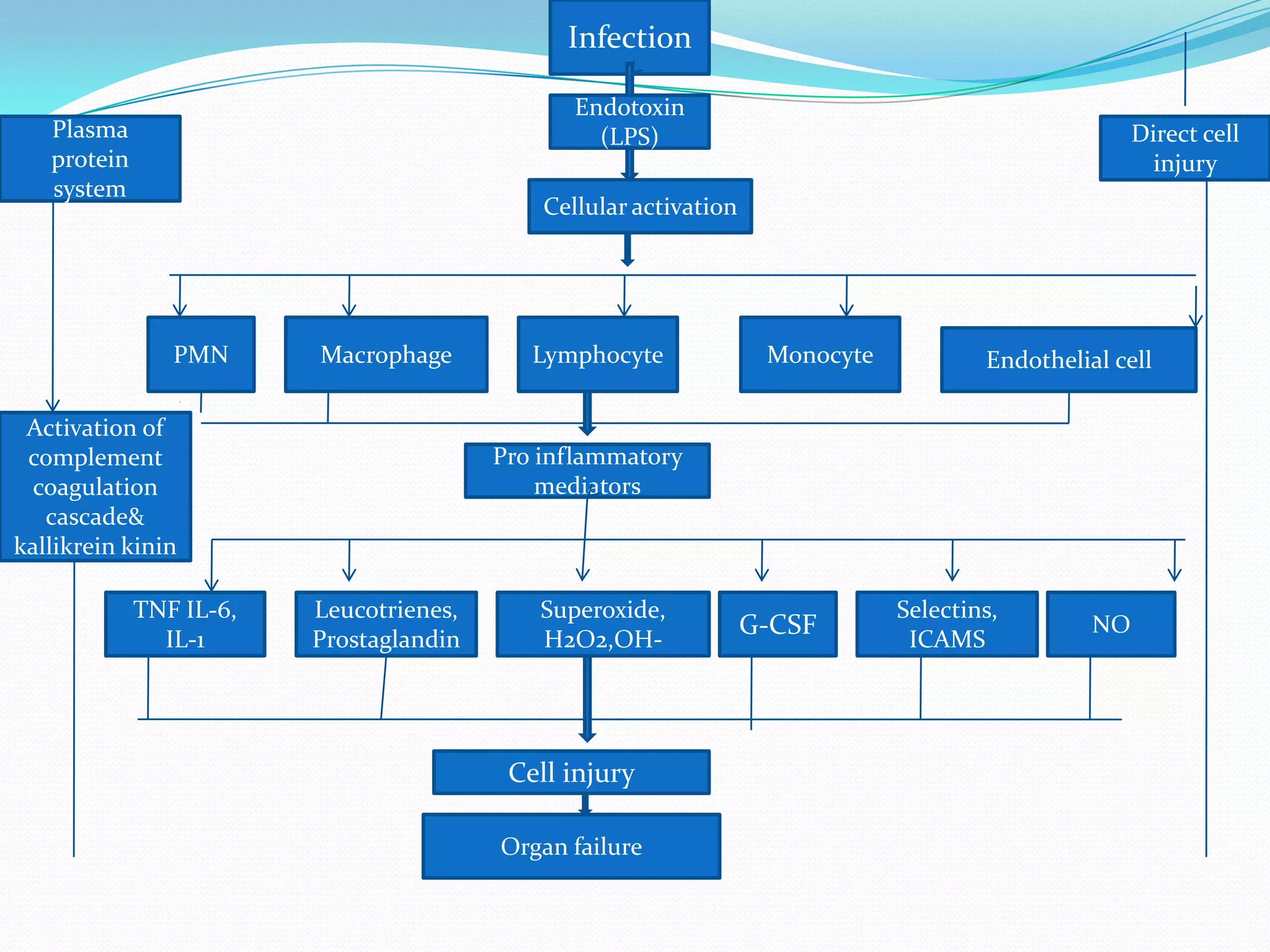
- The pathophysiology involves an initial infection that triggers a systemic inflammatory response and release of cytokines and mediators, leading to endothelial damage, coagulation abnormalities, hypotension, and ultimately multiple organ dysfunction if not treated.
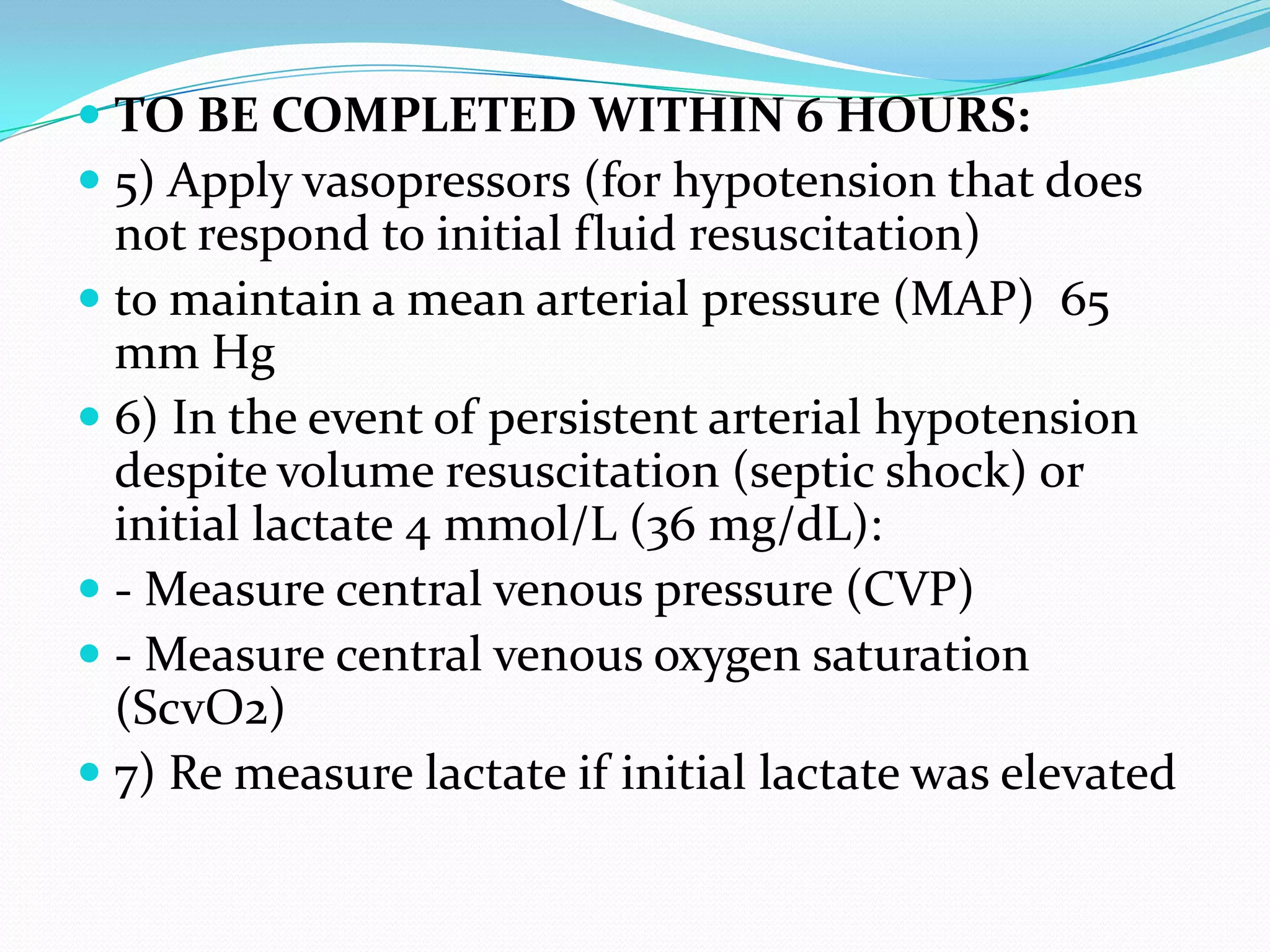
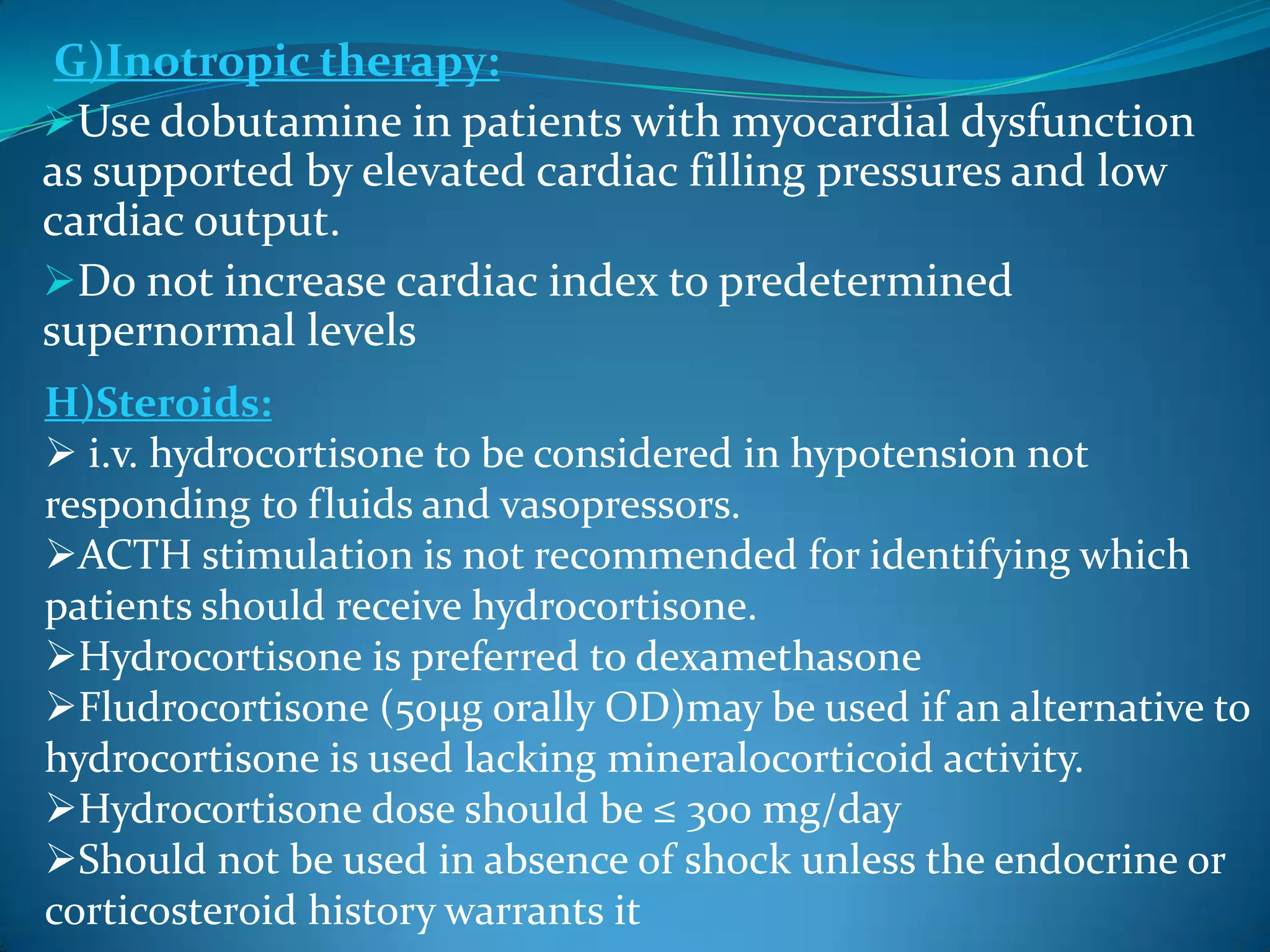
- Treatment involves early goal-directed therapy within 3-6 hours including antibiotics, fluid resuscitation, vasopressors, inotropes, and measures to optimize