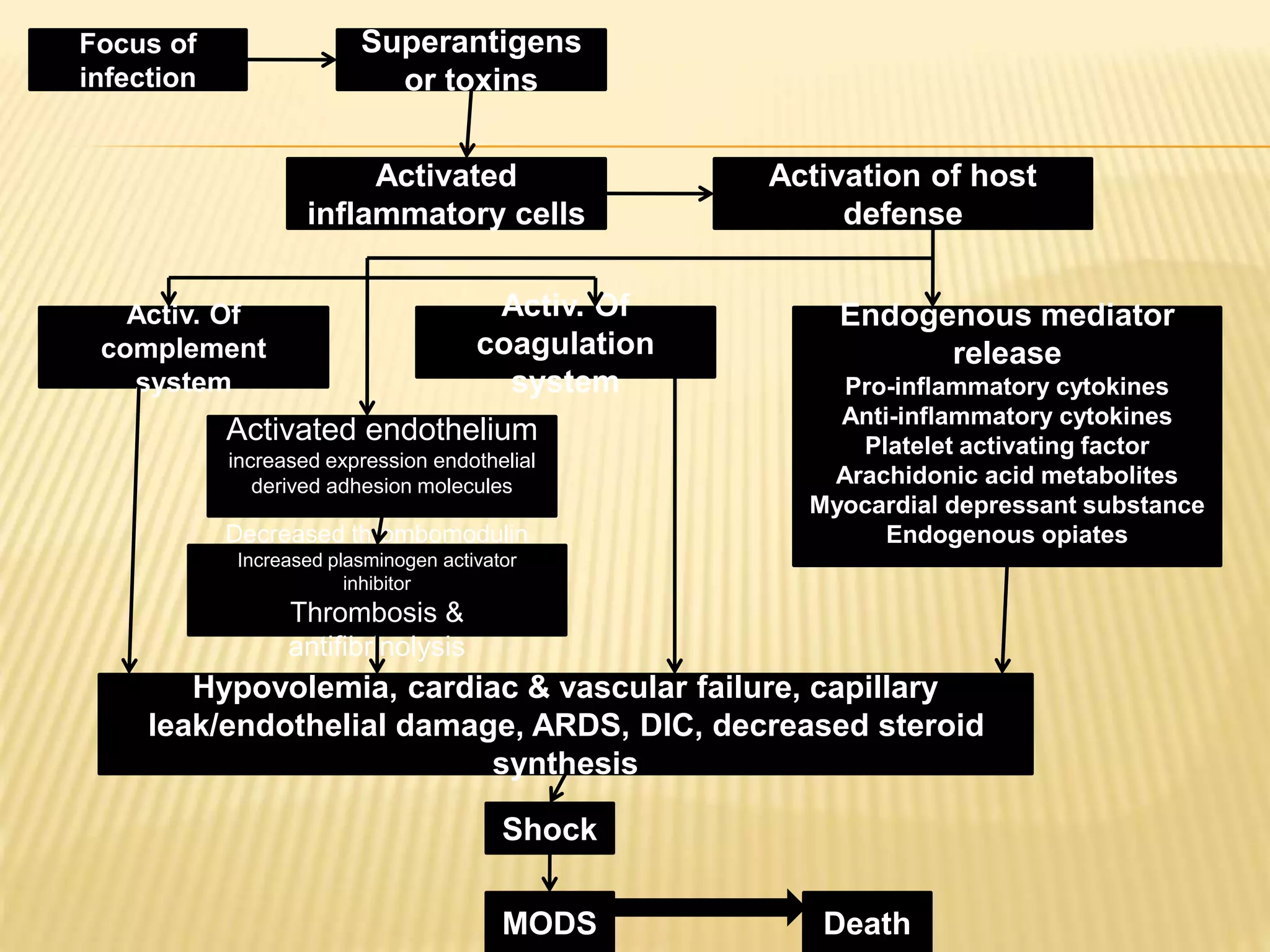
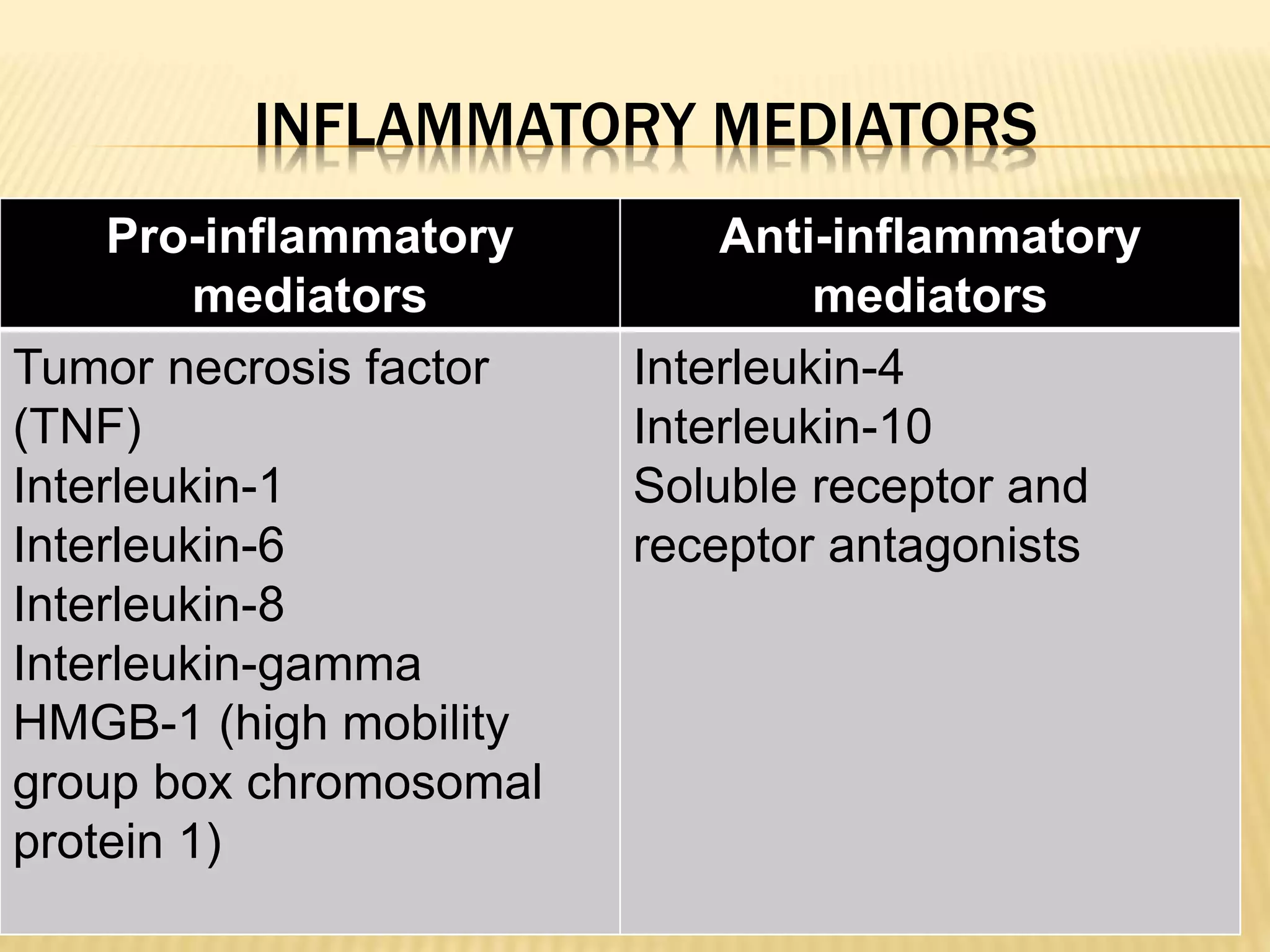
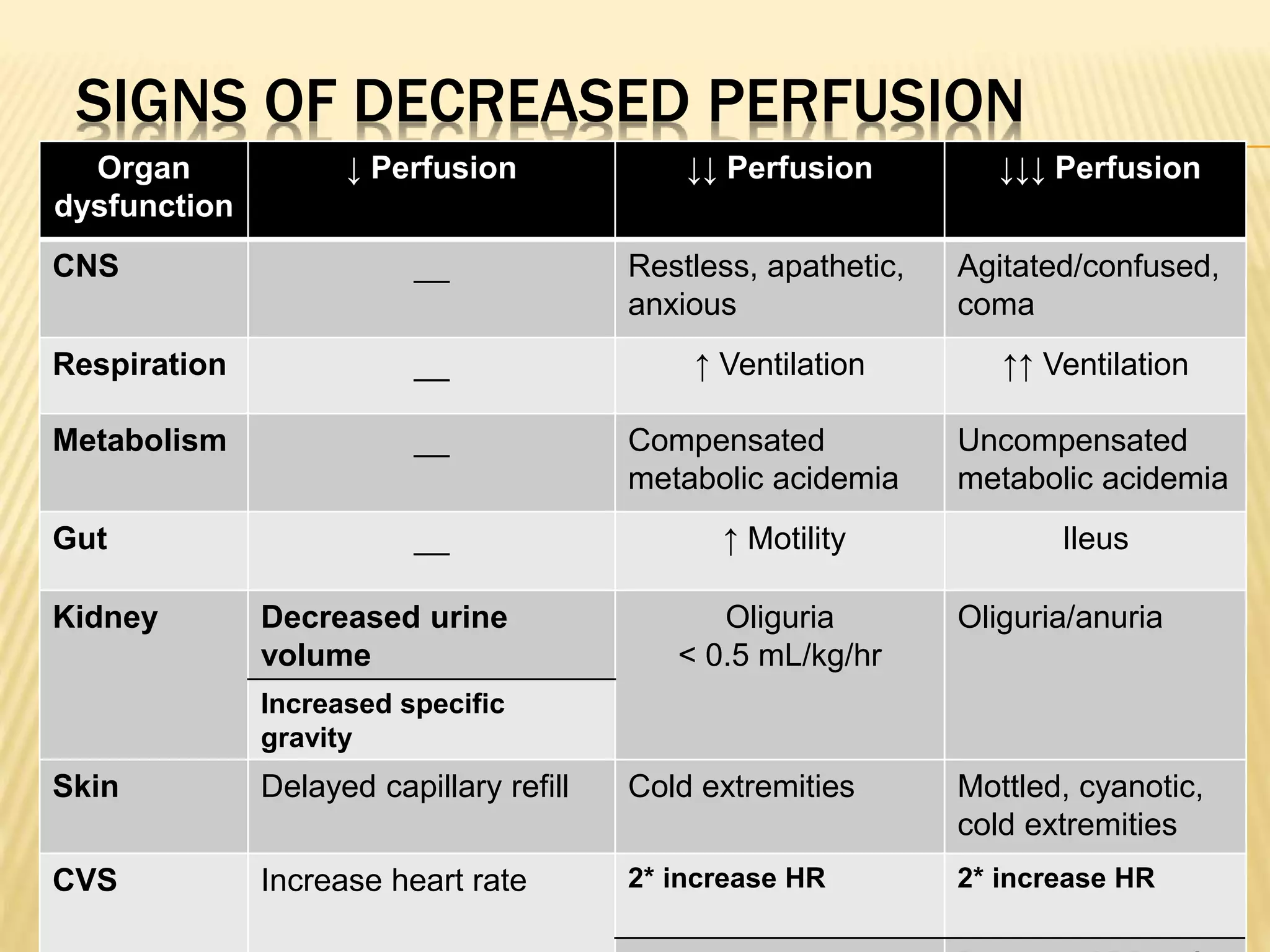
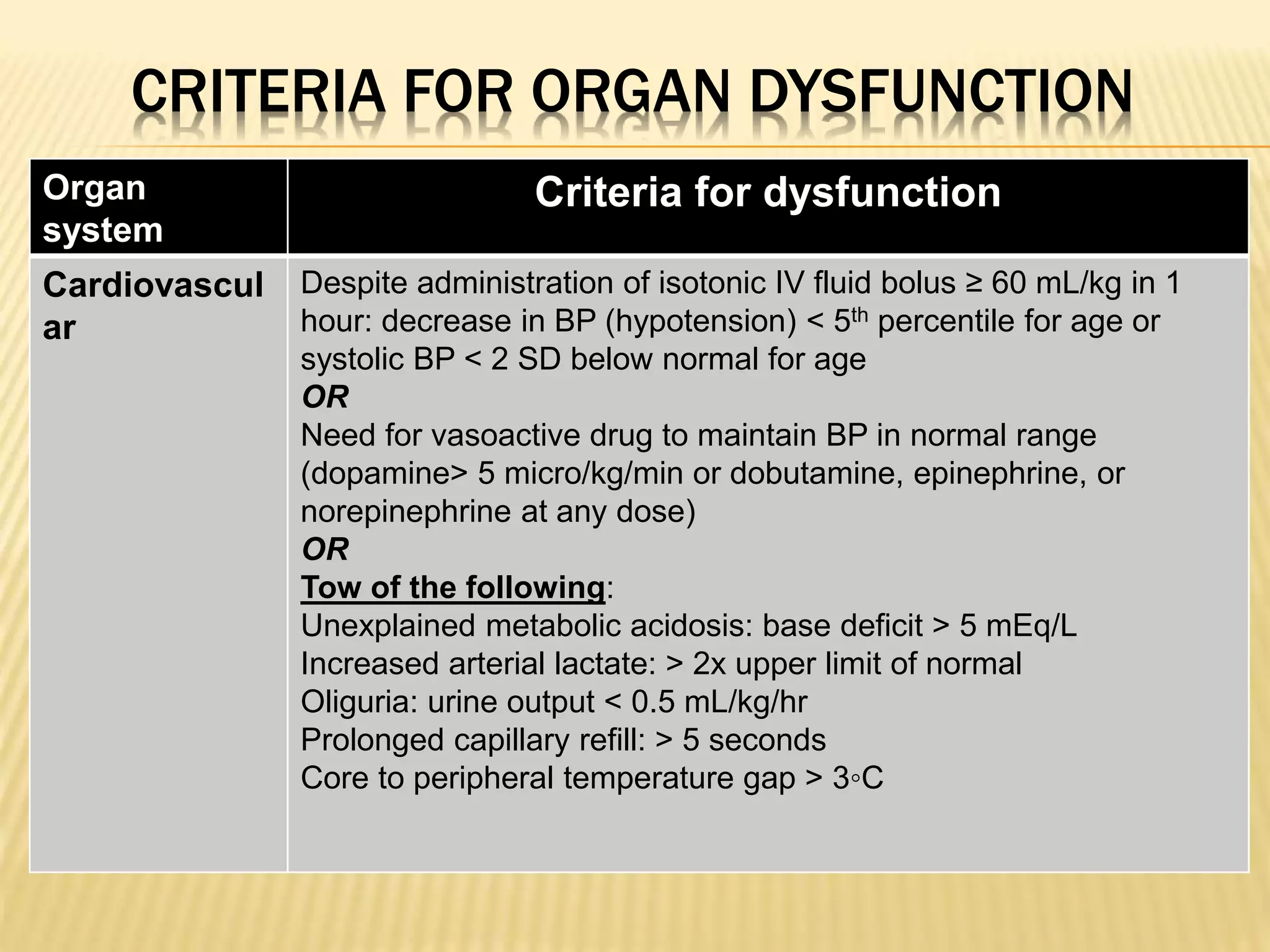
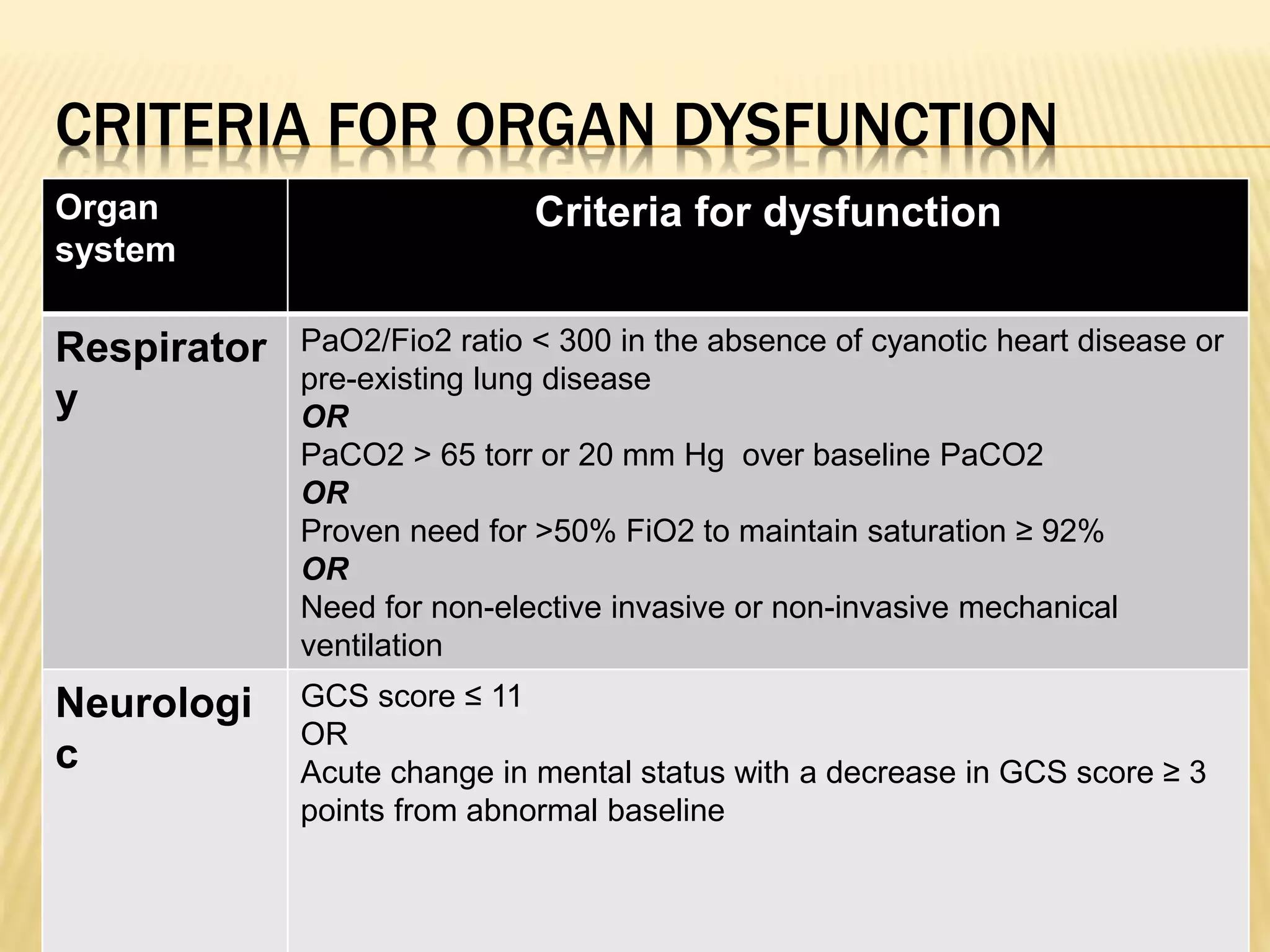
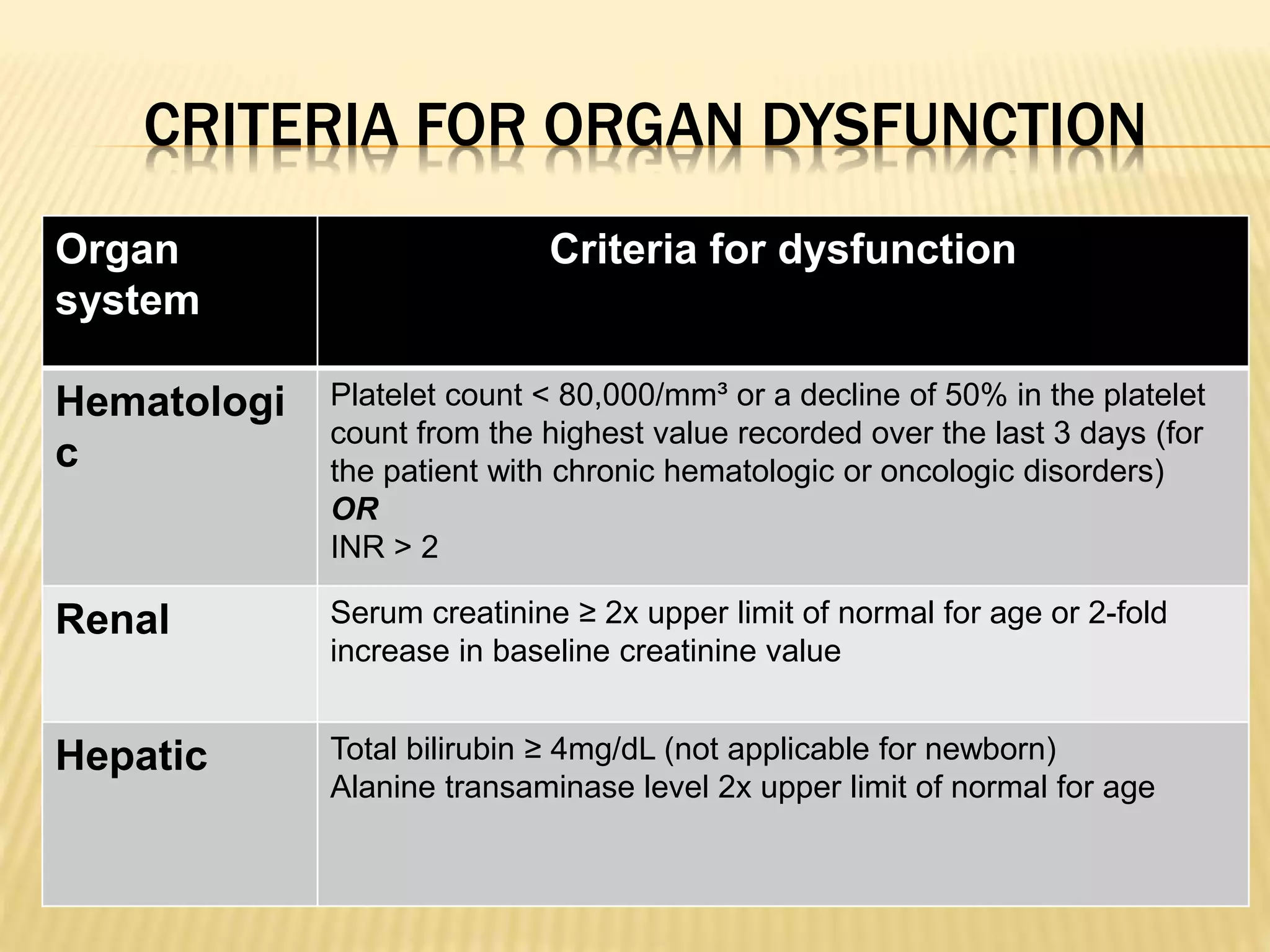
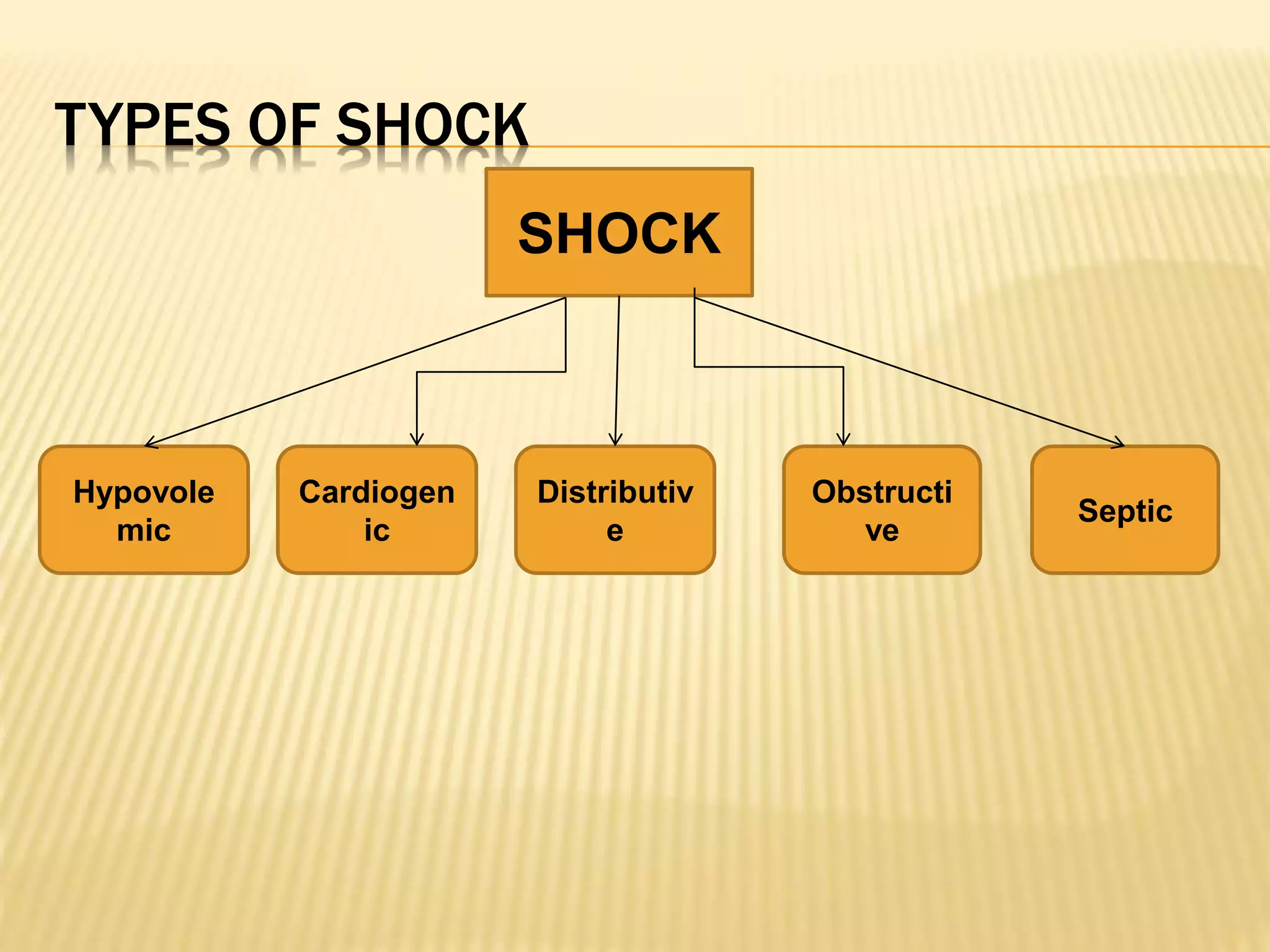
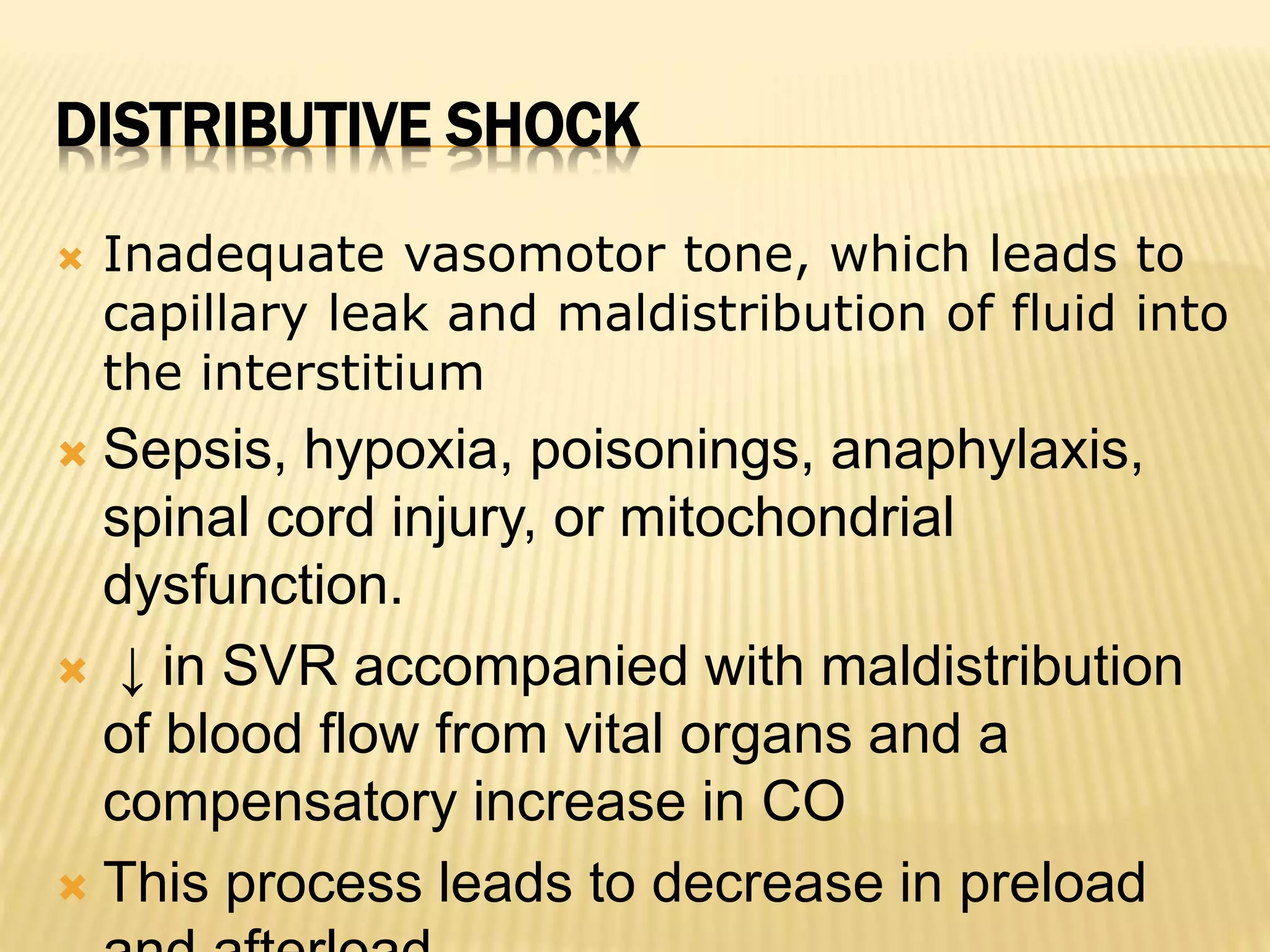
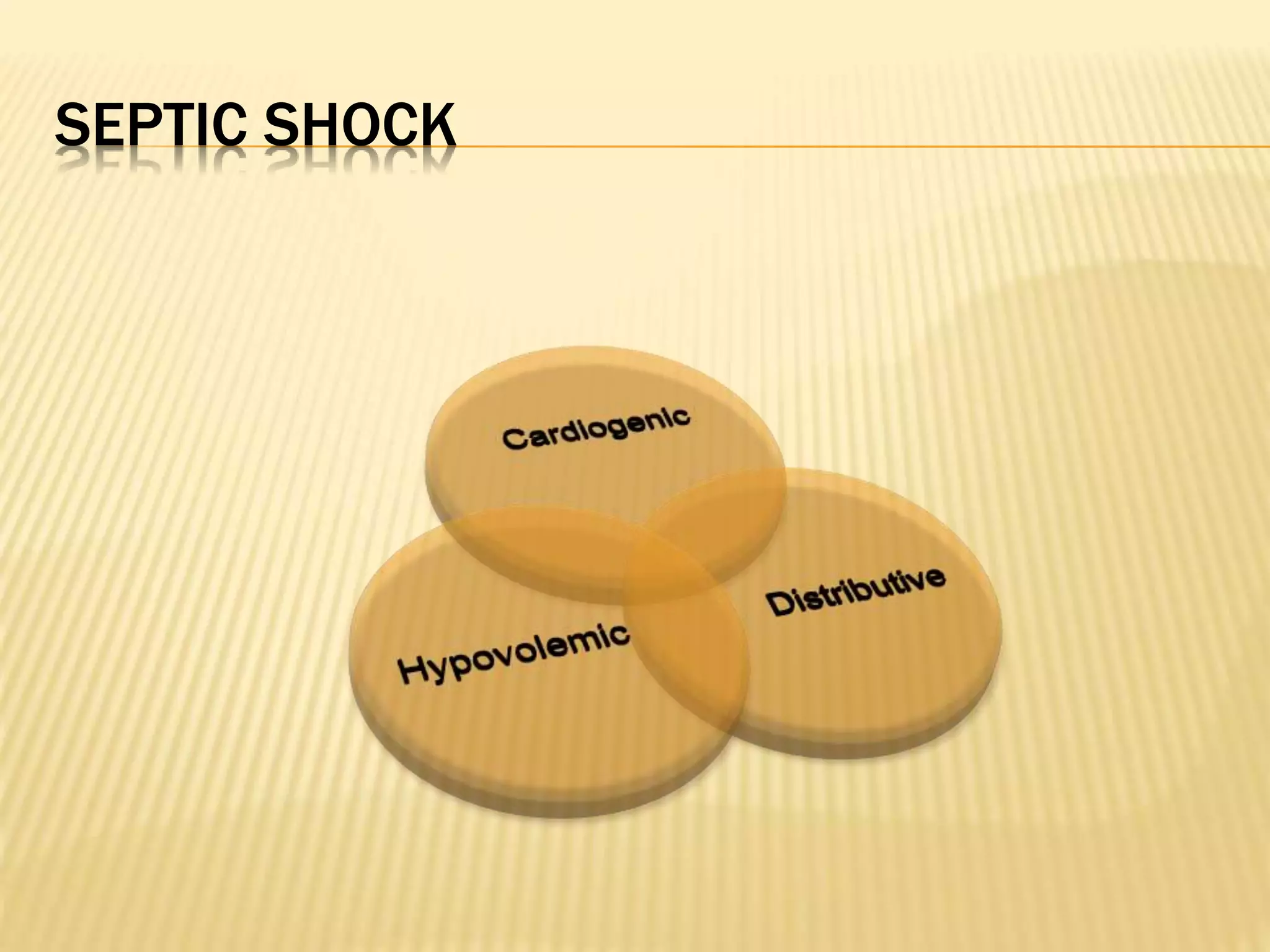
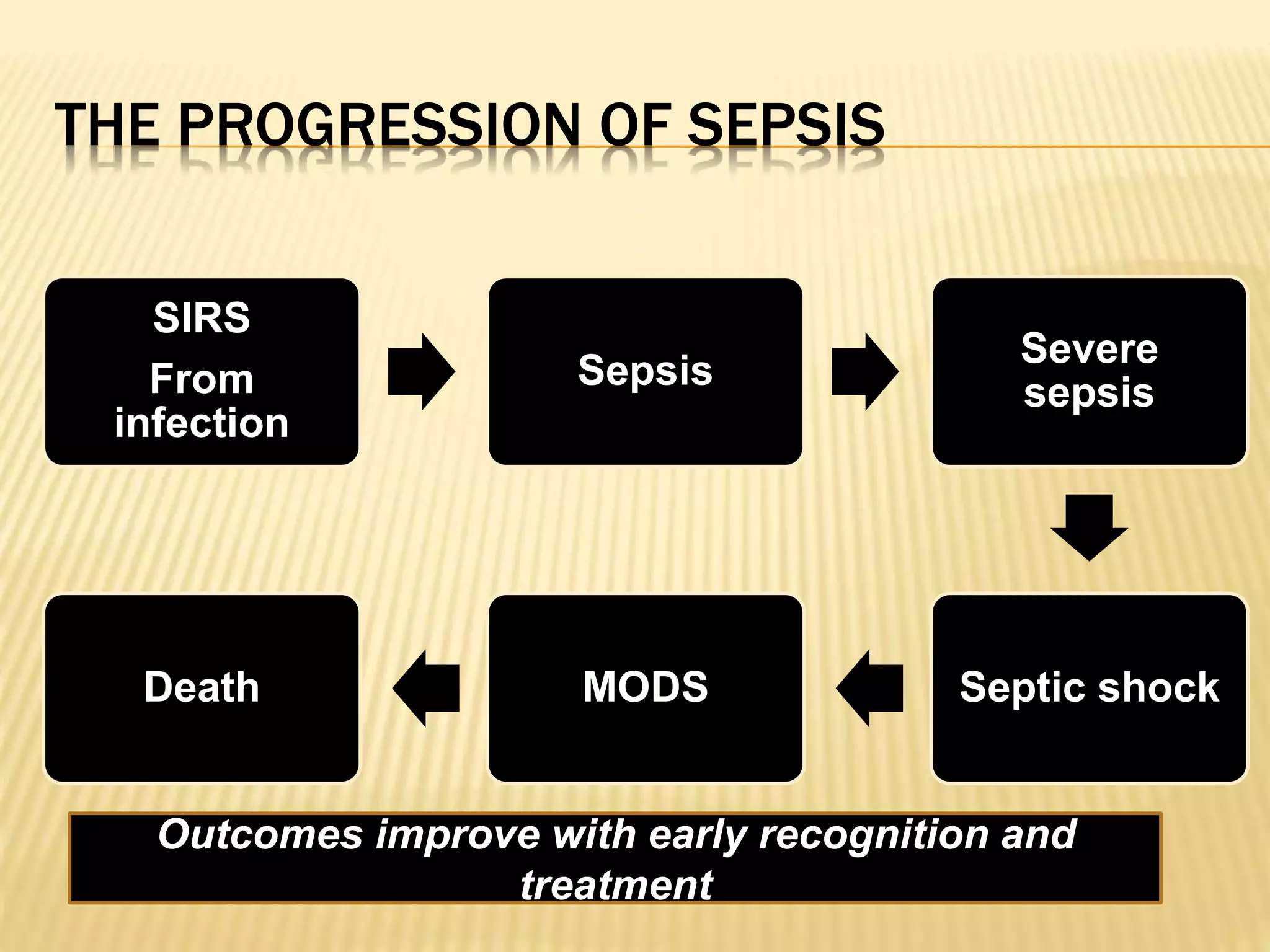
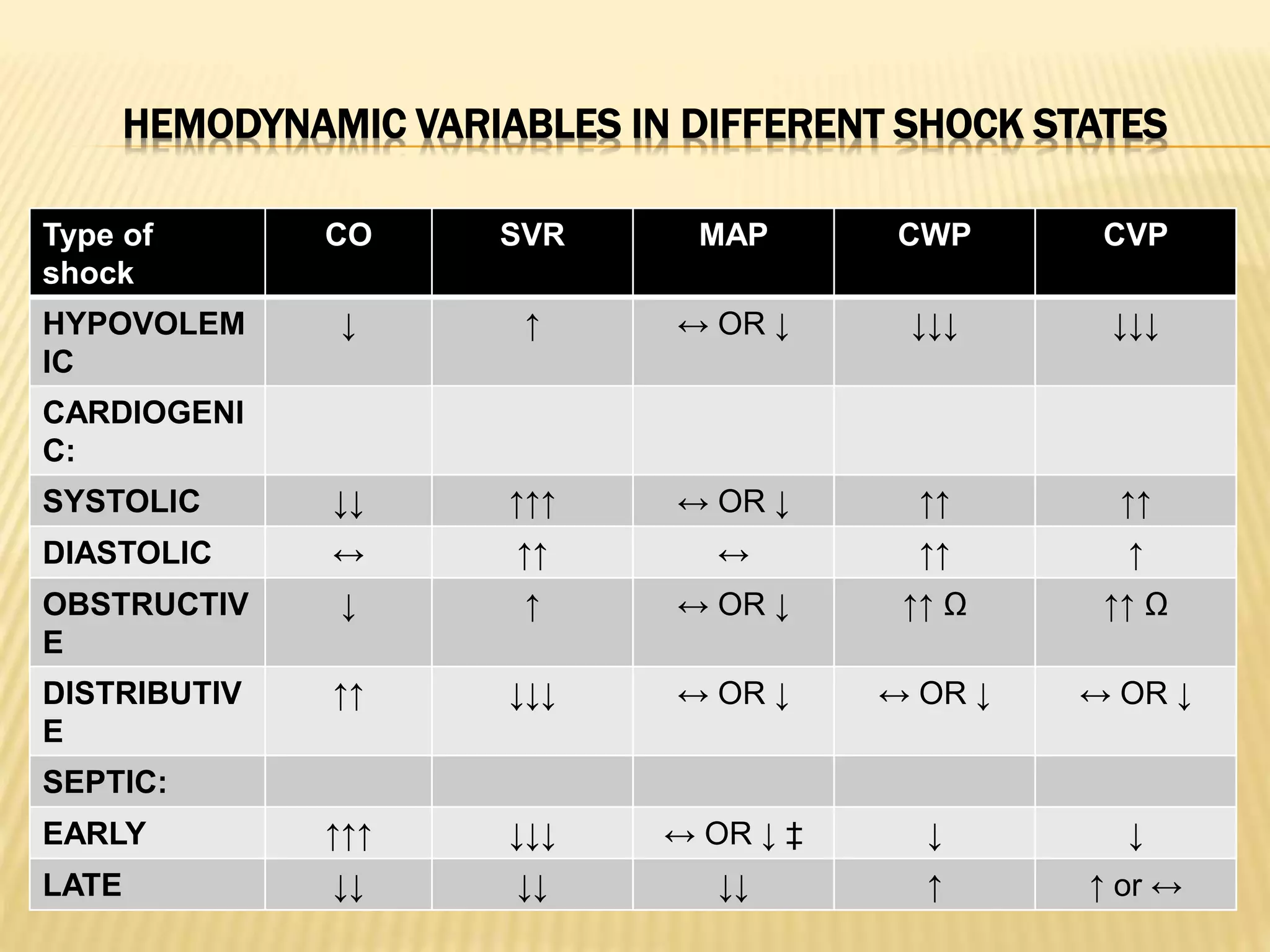
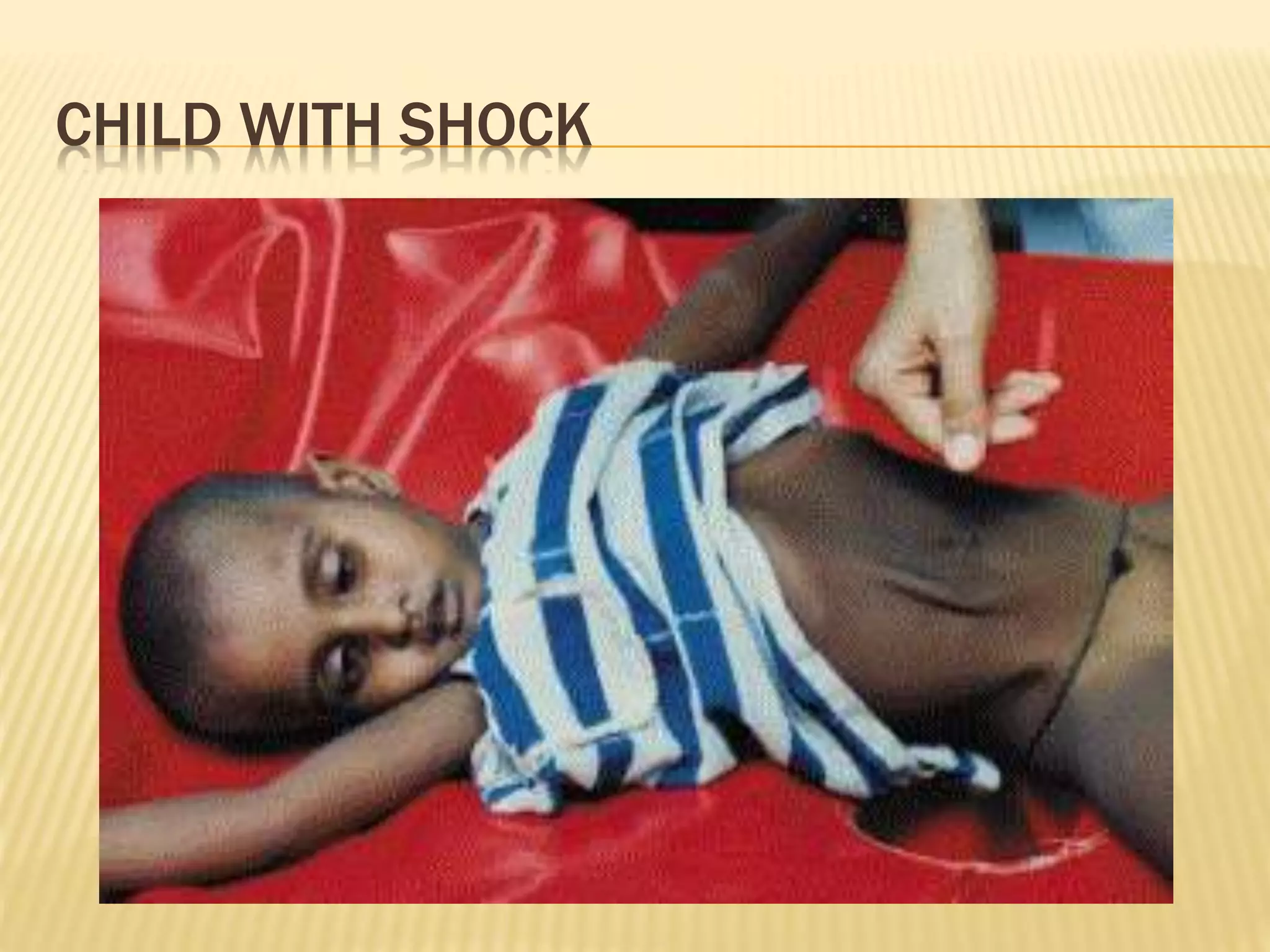
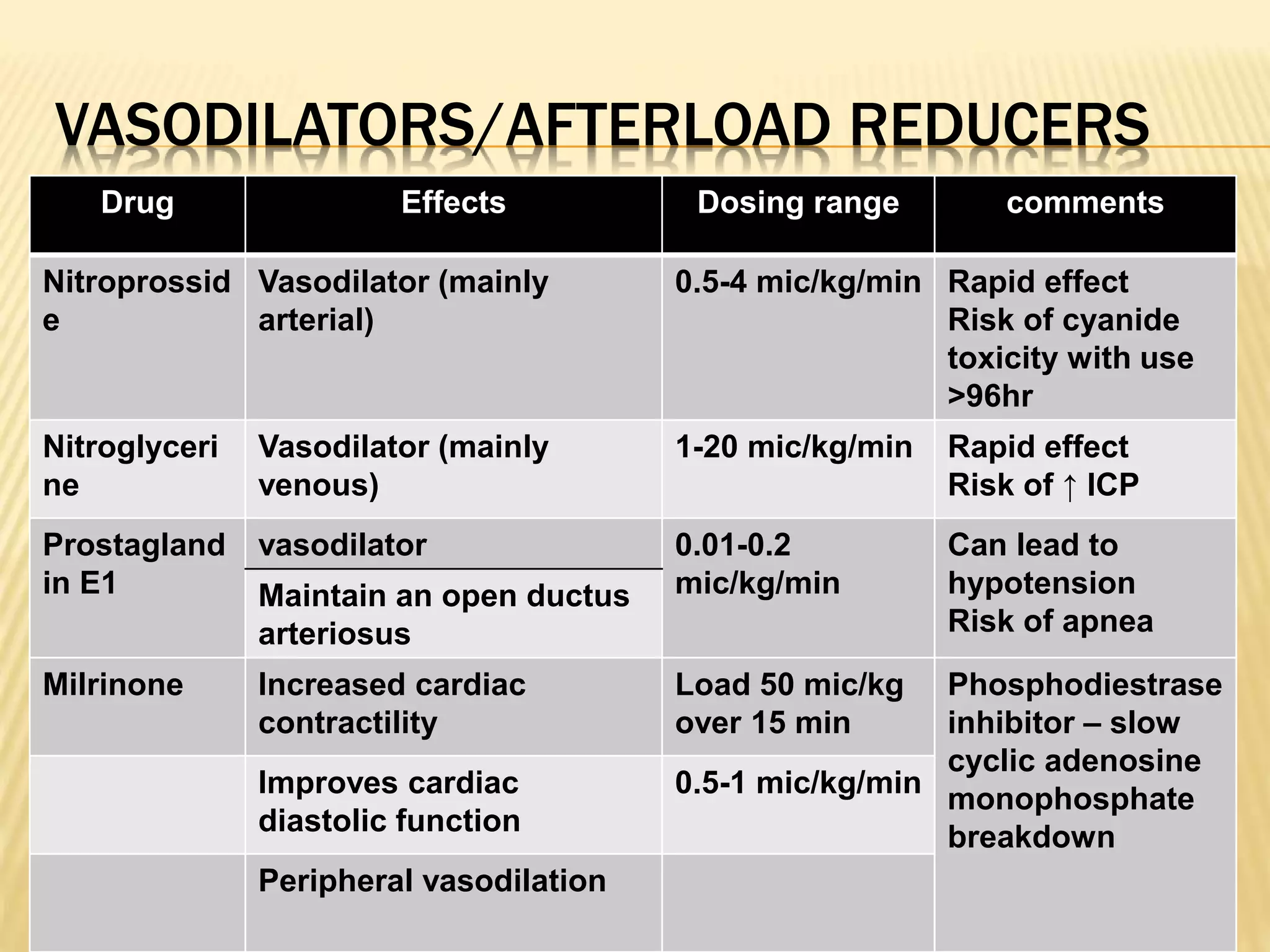
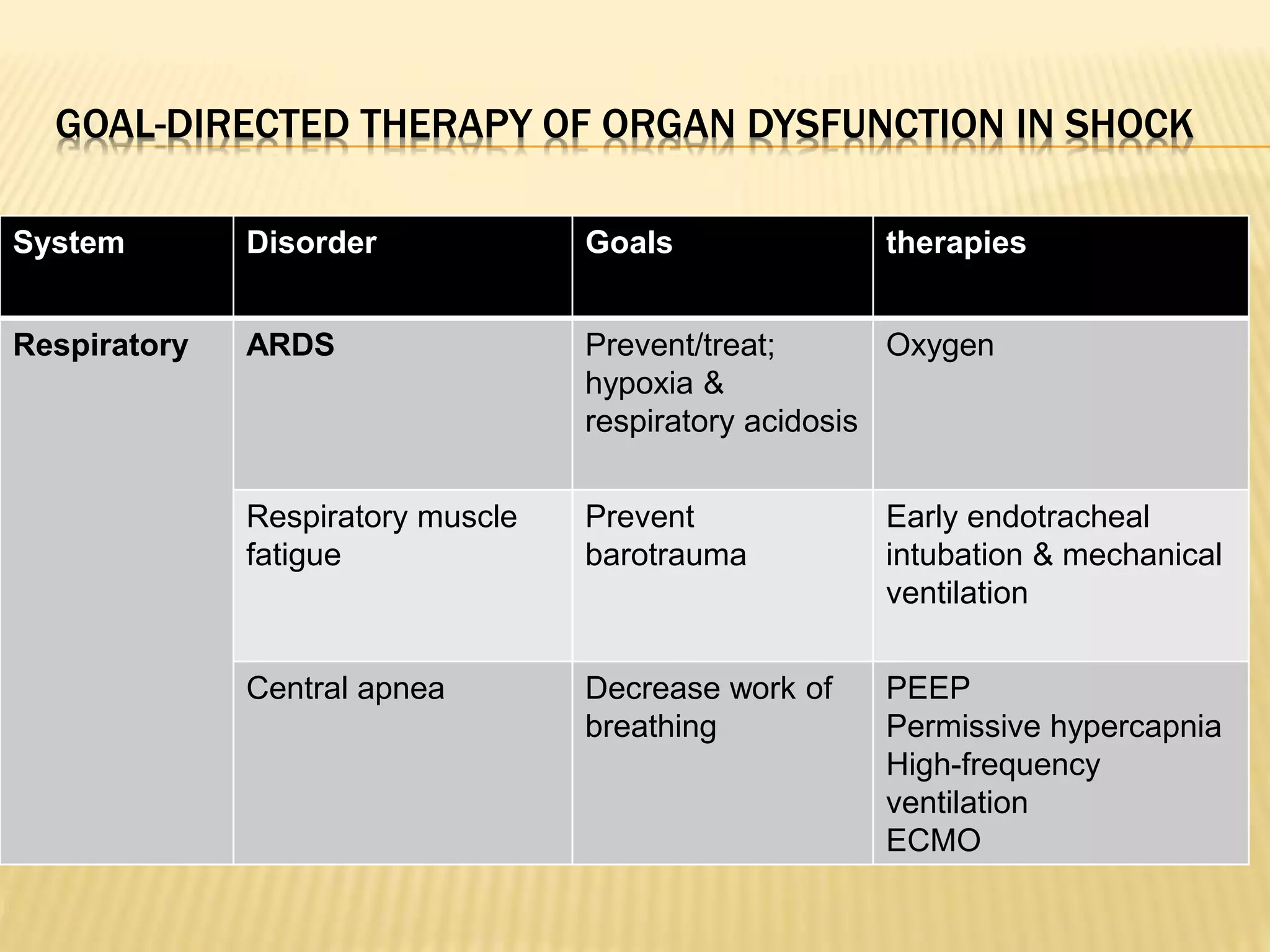
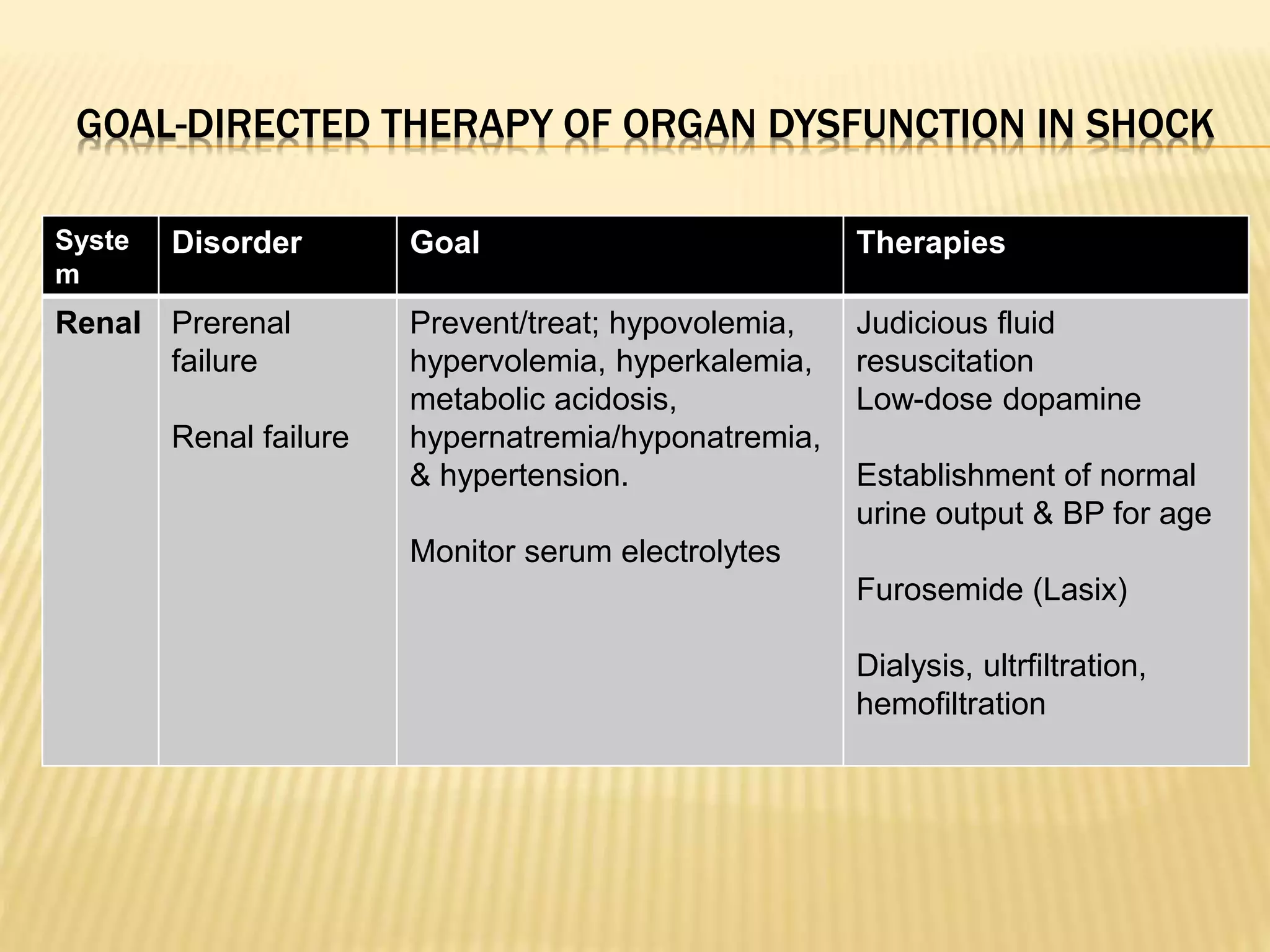
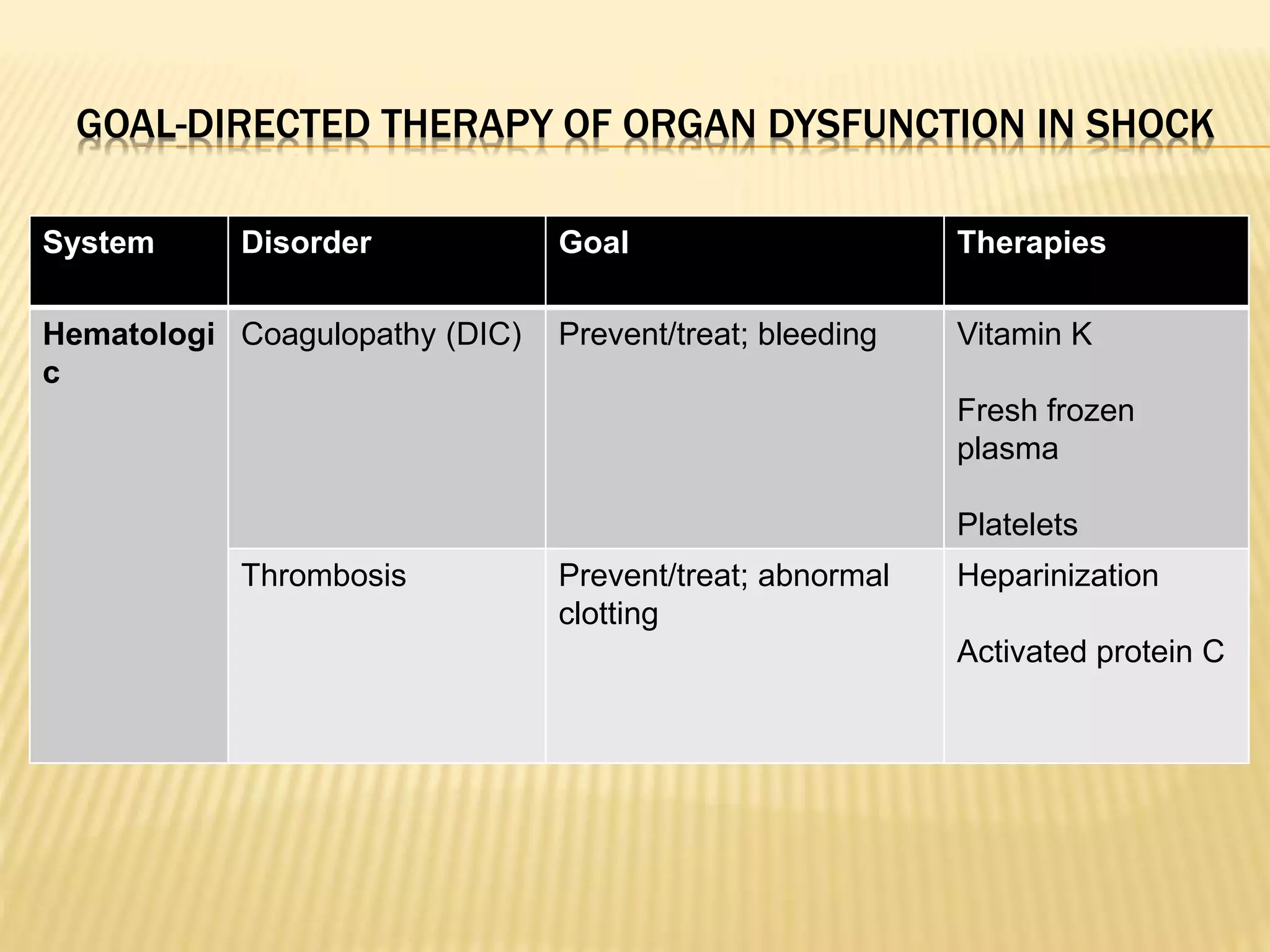
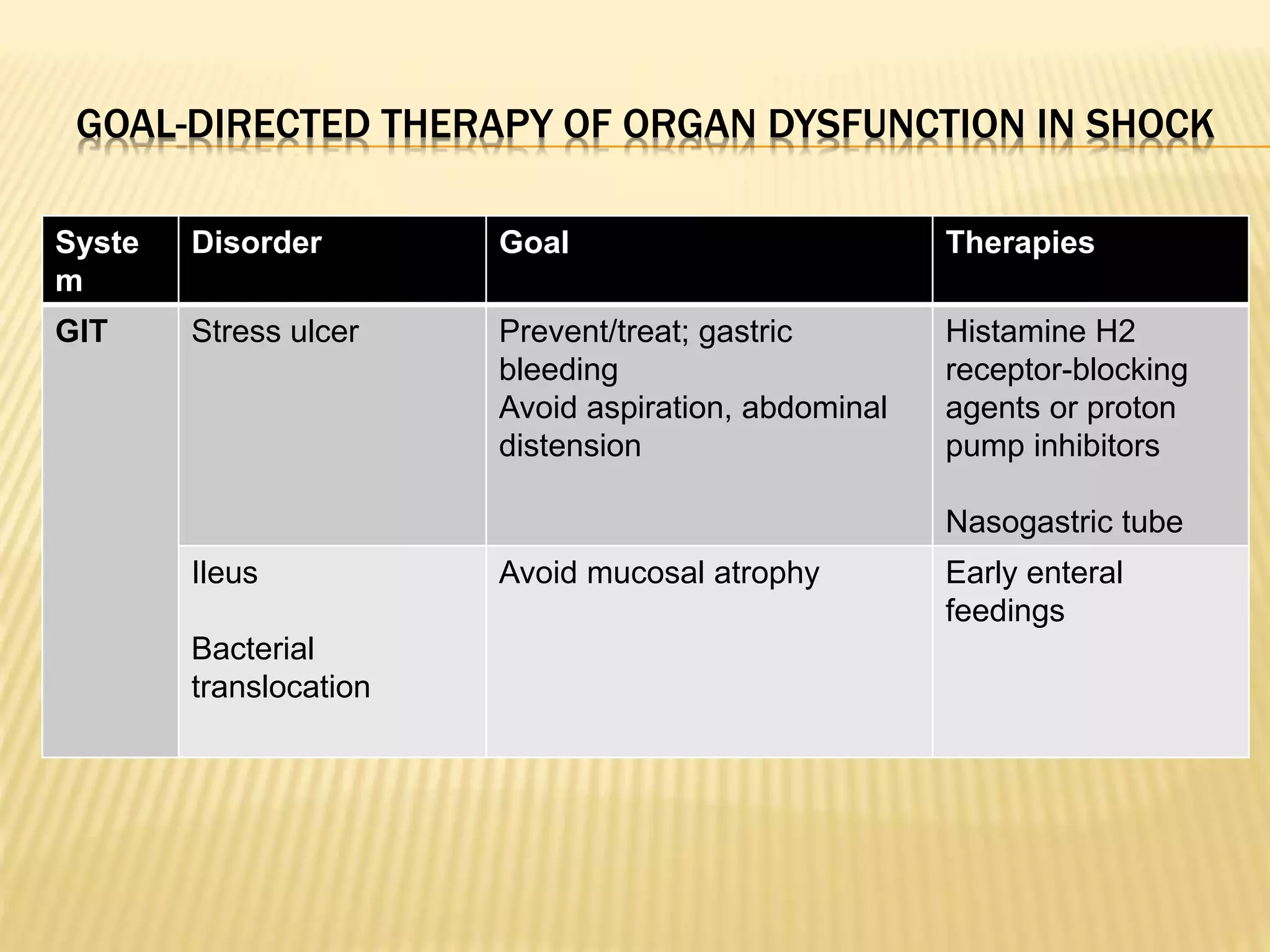
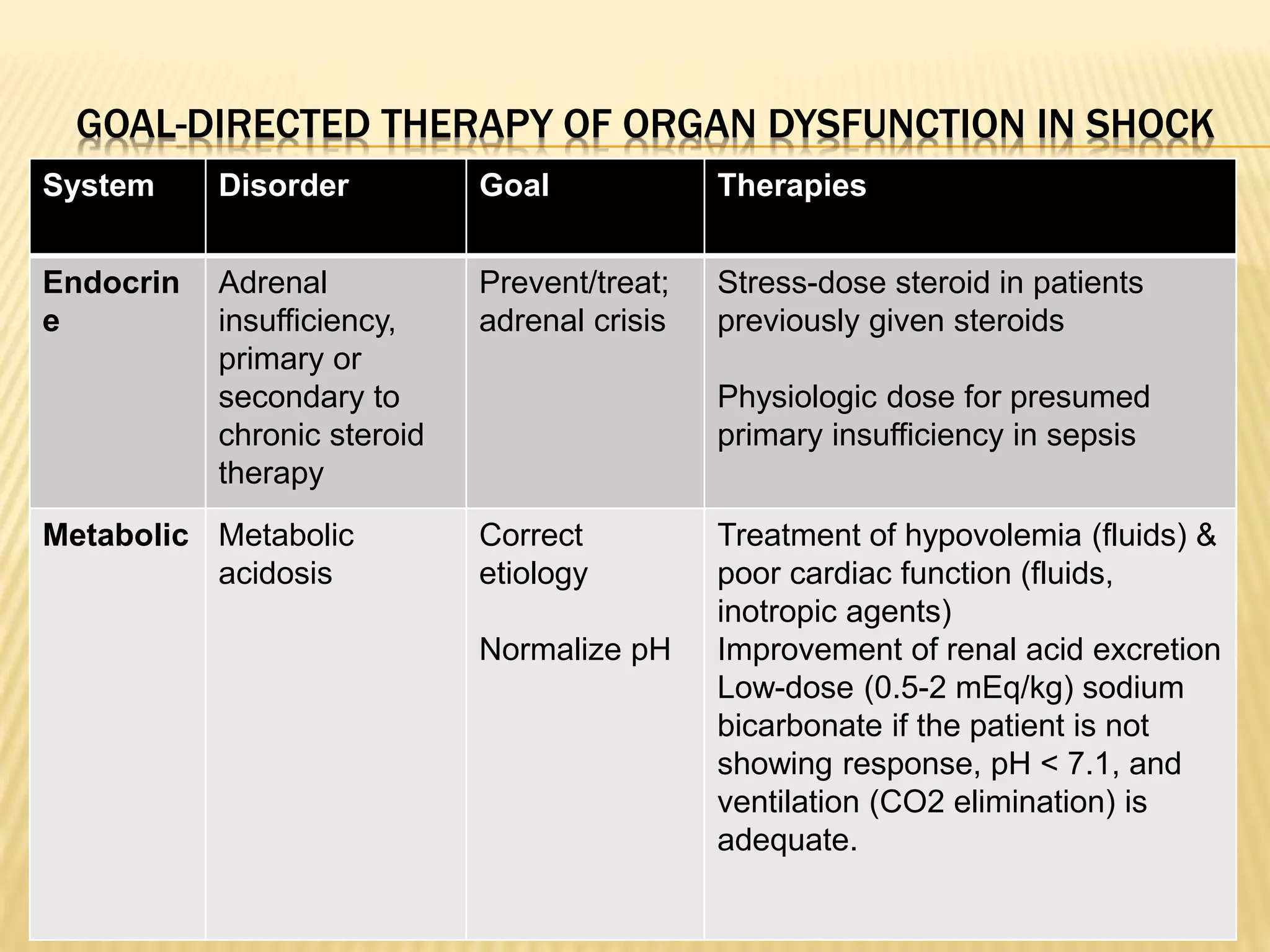
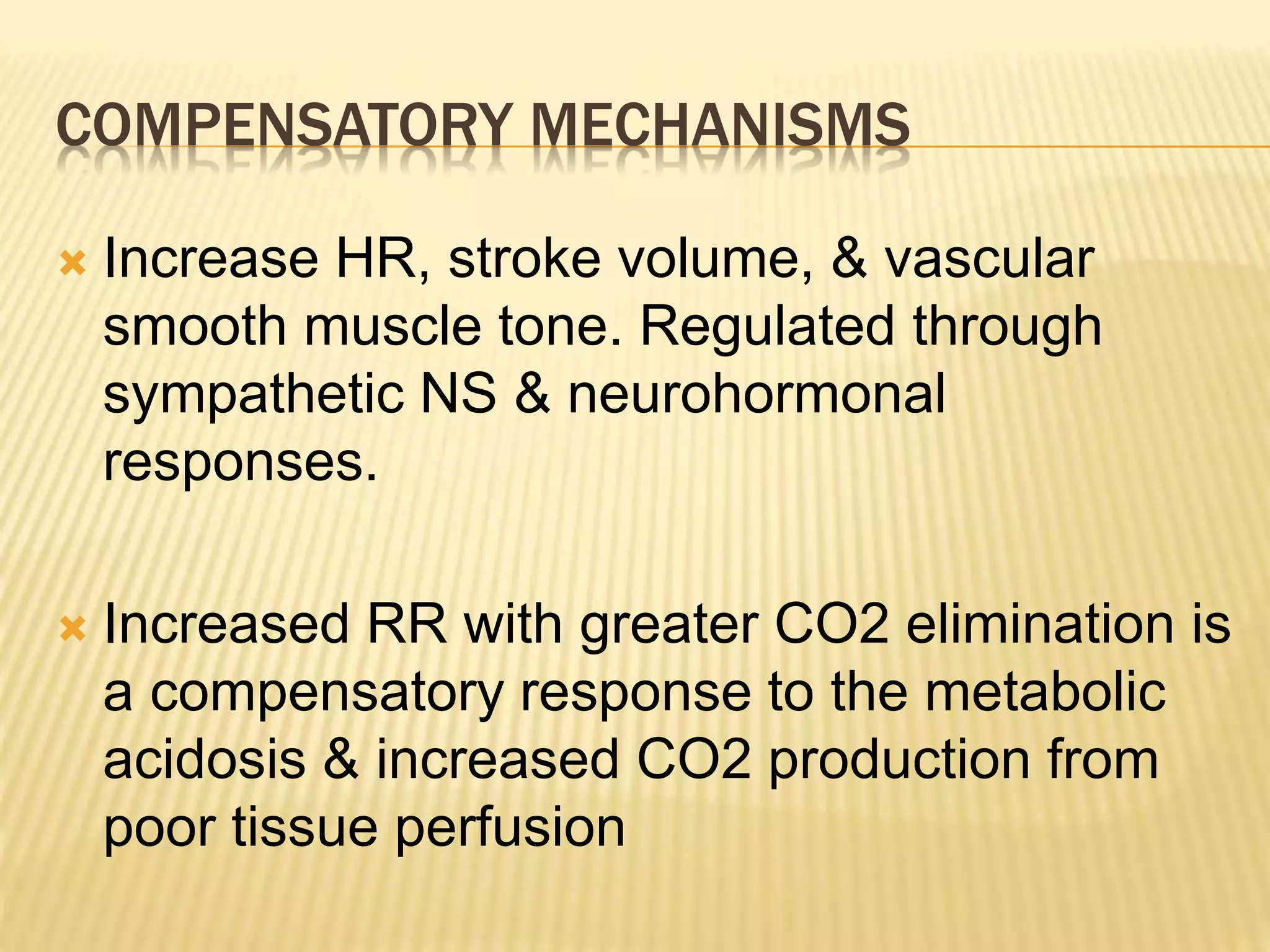
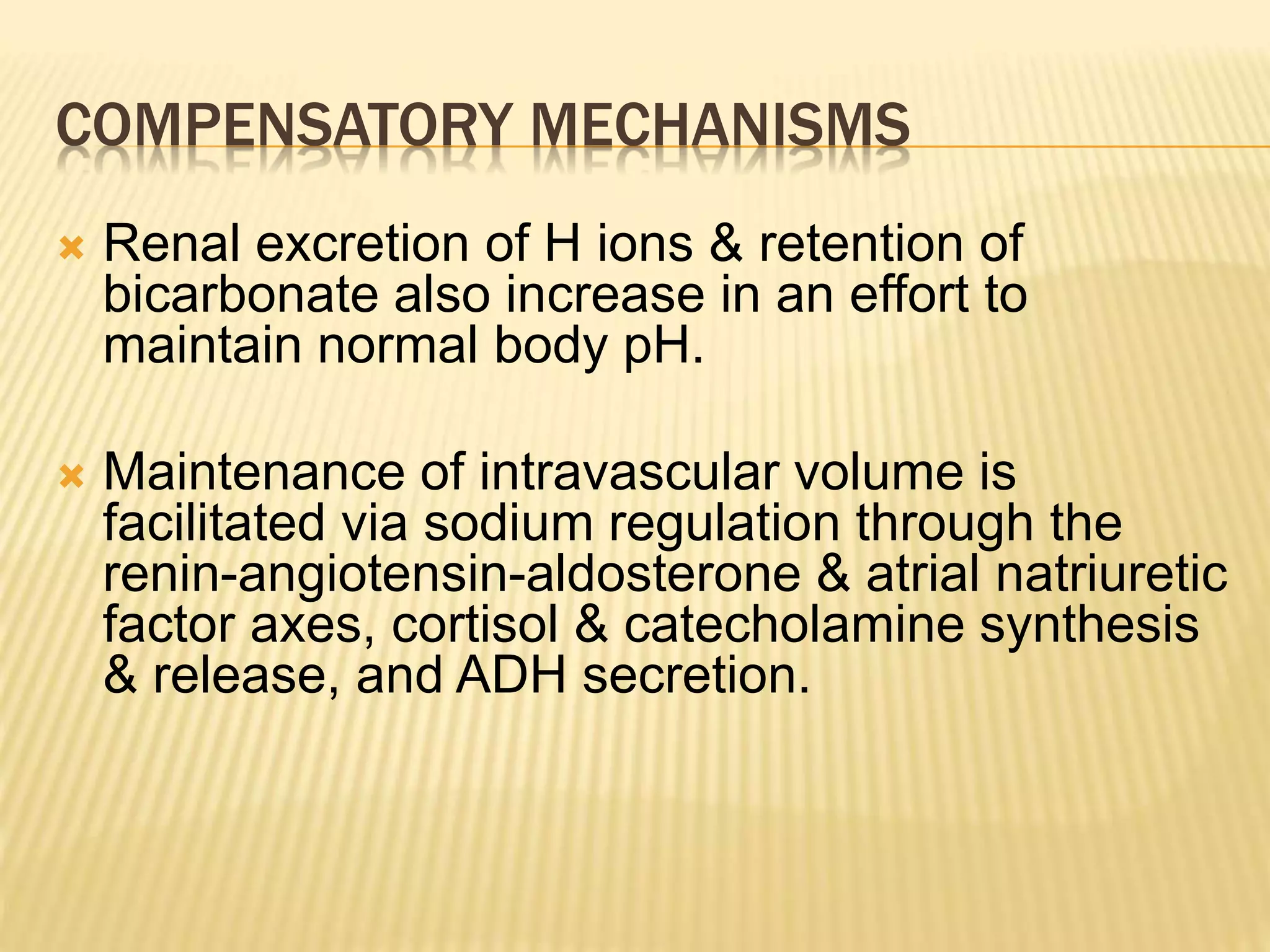
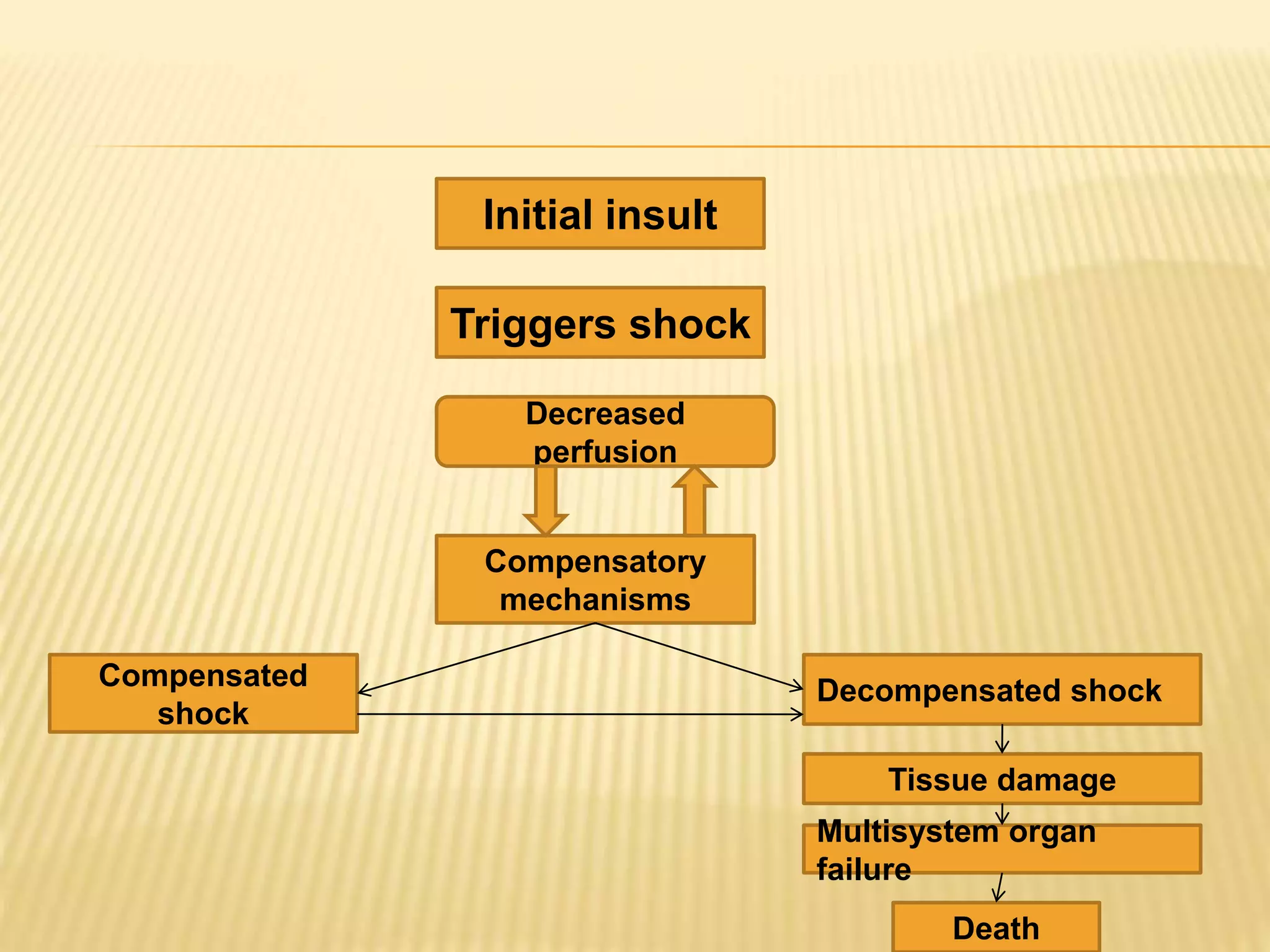
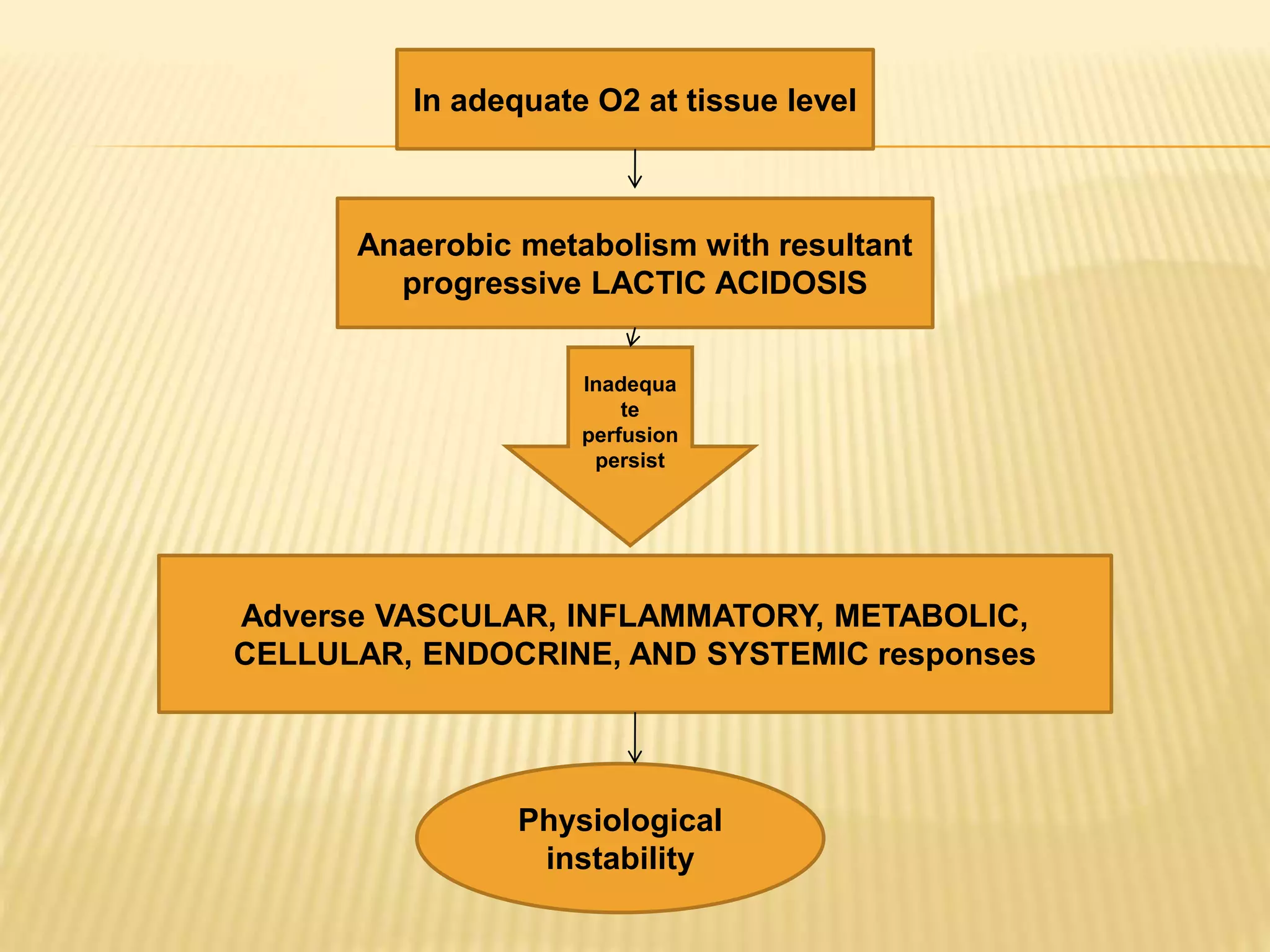
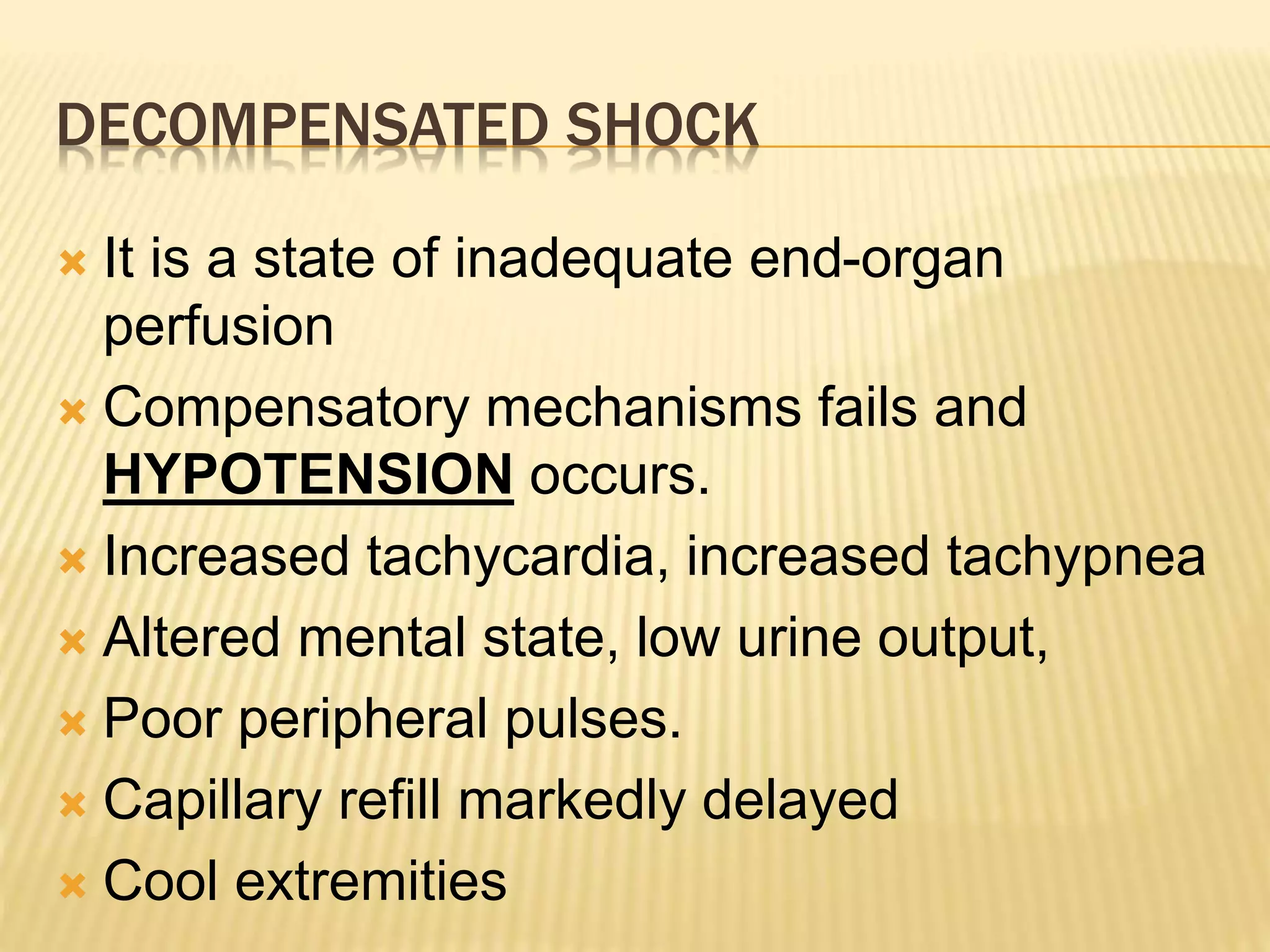
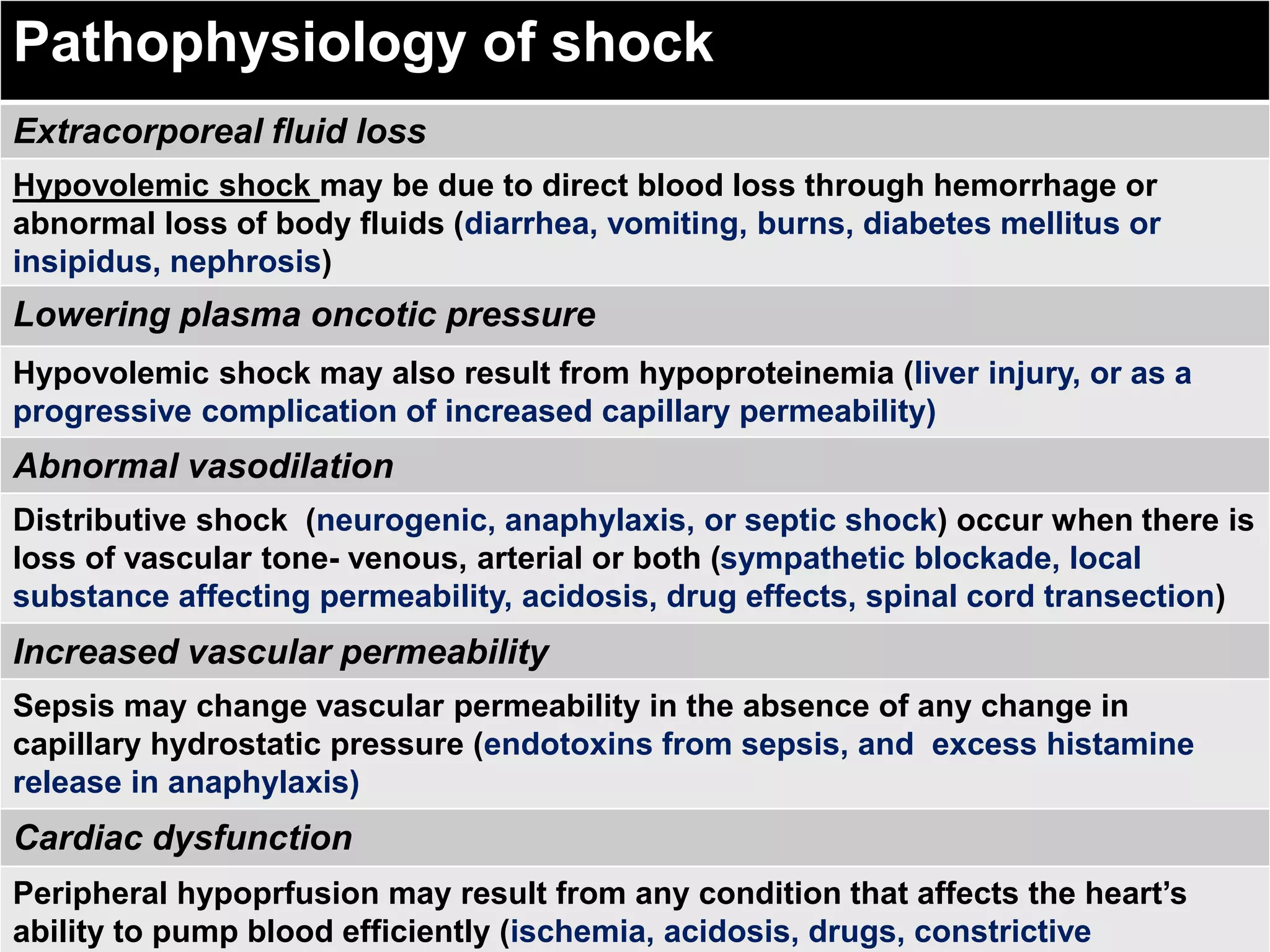
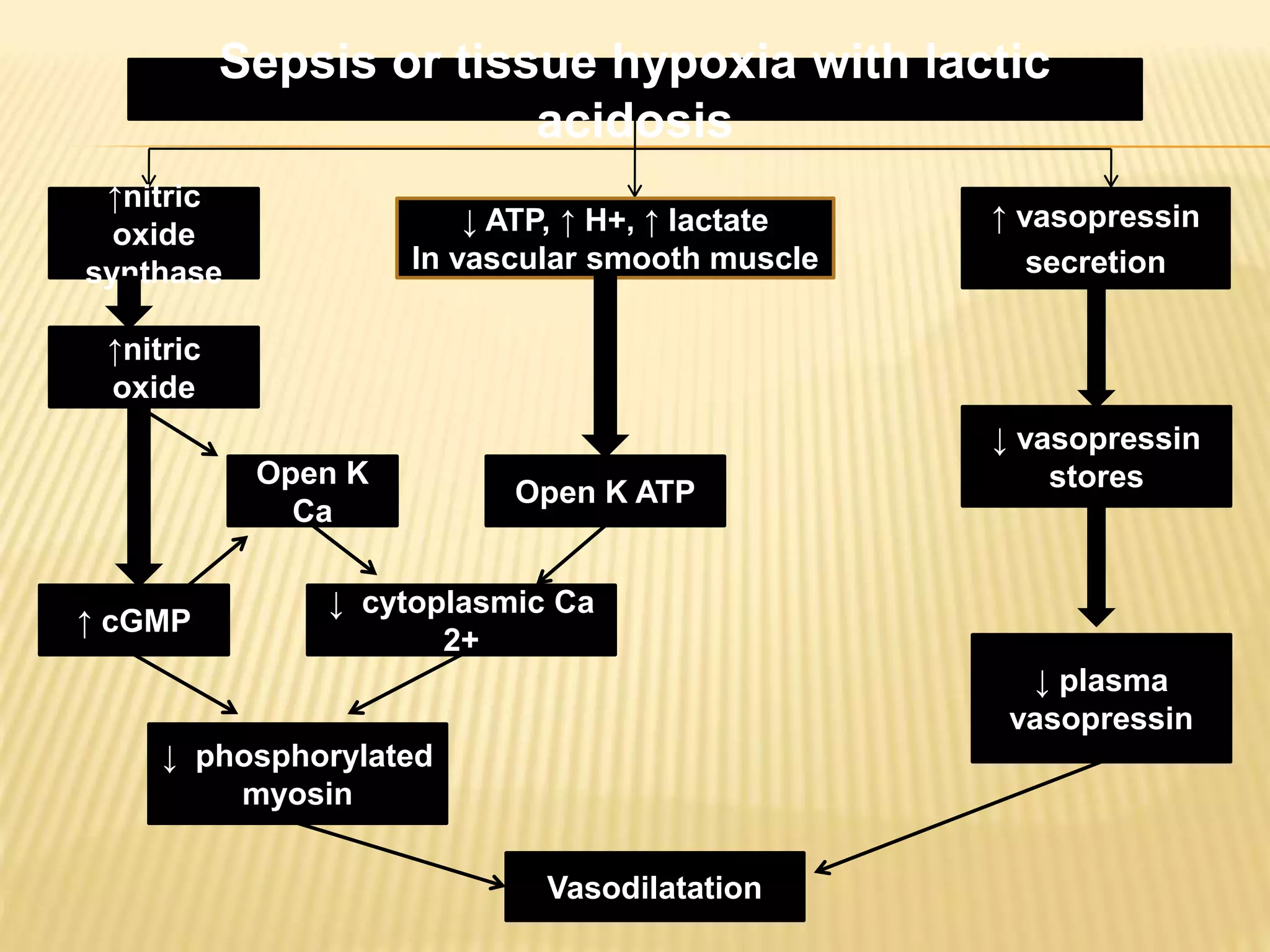
This document discusses approaches to hypovolemic and septic shock in children. It defines shock and describes the pathophysiology, stages, and management. Shock results from inadequate oxygen delivery to tissues. Initially, compensatory mechanisms attempt to maintain blood pressure, but the condition can progress to decompensated then irreversible shock without treatment. Sepsis causes an inflammatory response that can lead to organ dysfunction if uncontrolled. Early intervention is important to improve outcomes from shock.













![Global tissue hypoxia
SIRS
Endothelial activation
Disruption of:
Coagulation
Vascular permeability
Vascular tone
Microcirculatory failure
Precipitated by:
Cytokines
[Over]production
of nitric
oxide
Results in:
Loss of vasomotor
control
Under‐perfusion of
tissues
Hypotension
Ait‐Oufella H, et al. Intensive Care Med 2010;26:1286‐1298.
Rivers E, et al. NEJM 2001;345:1368‐1377.
Organ dysfunction
Heart
Lungs
Brain
Kidneys
Liver](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtohypovolemicandsepticshock-140911101035-phpapp01/75/Approach-to-hypovolemic-and-septic-shock-21-2048.jpg)