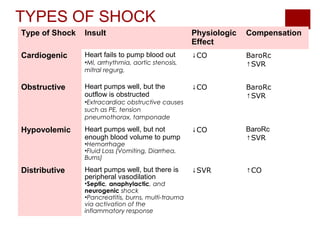
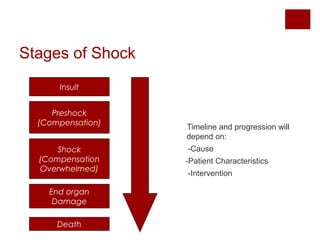
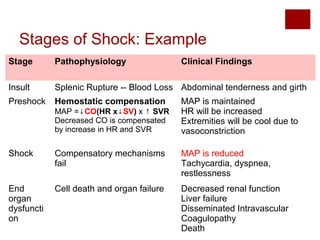
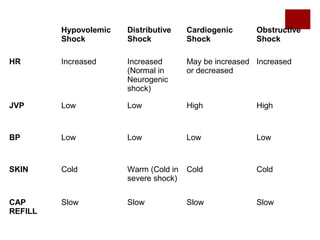
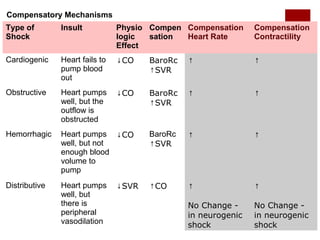
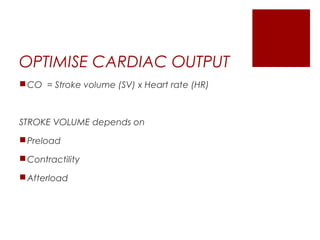
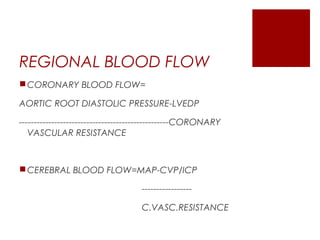
This document discusses shock, including definitions, types, stages, assessment, and management. It defines shock as inadequate perfusion and oxygenation of cells. The main types of shock discussed are cardiogenic, obstructive, hypovolemic, and distributive. Assessment involves the ABCs with consideration of exposure for trauma. Management aims to optimize oxygen content, cardiac output, blood pressure, and regional blood flow. Case examples demonstrate application to patients with hemorrhagic, cardiogenic, septic, neurogenic, and pancreatitis-associated shock.