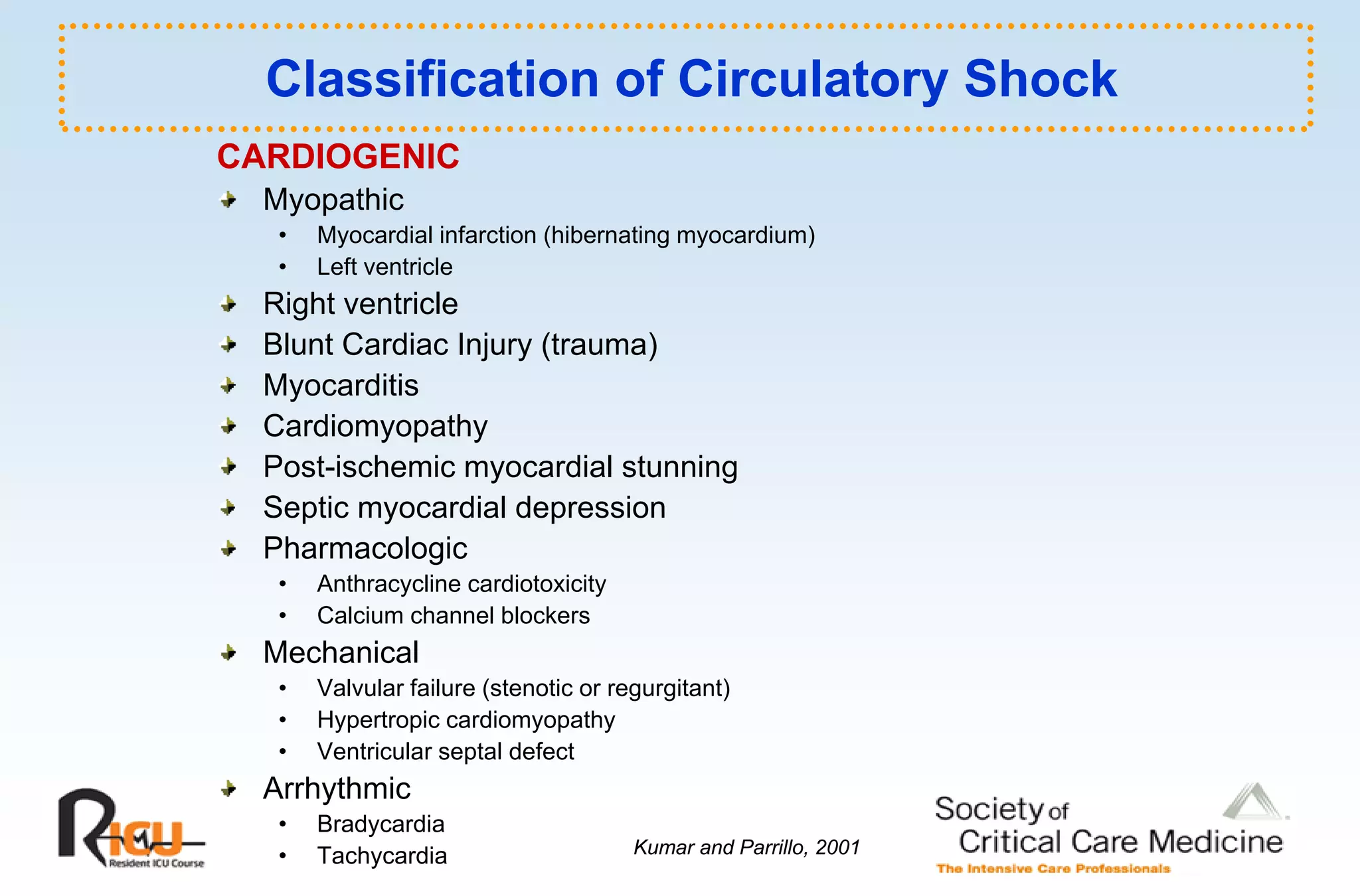
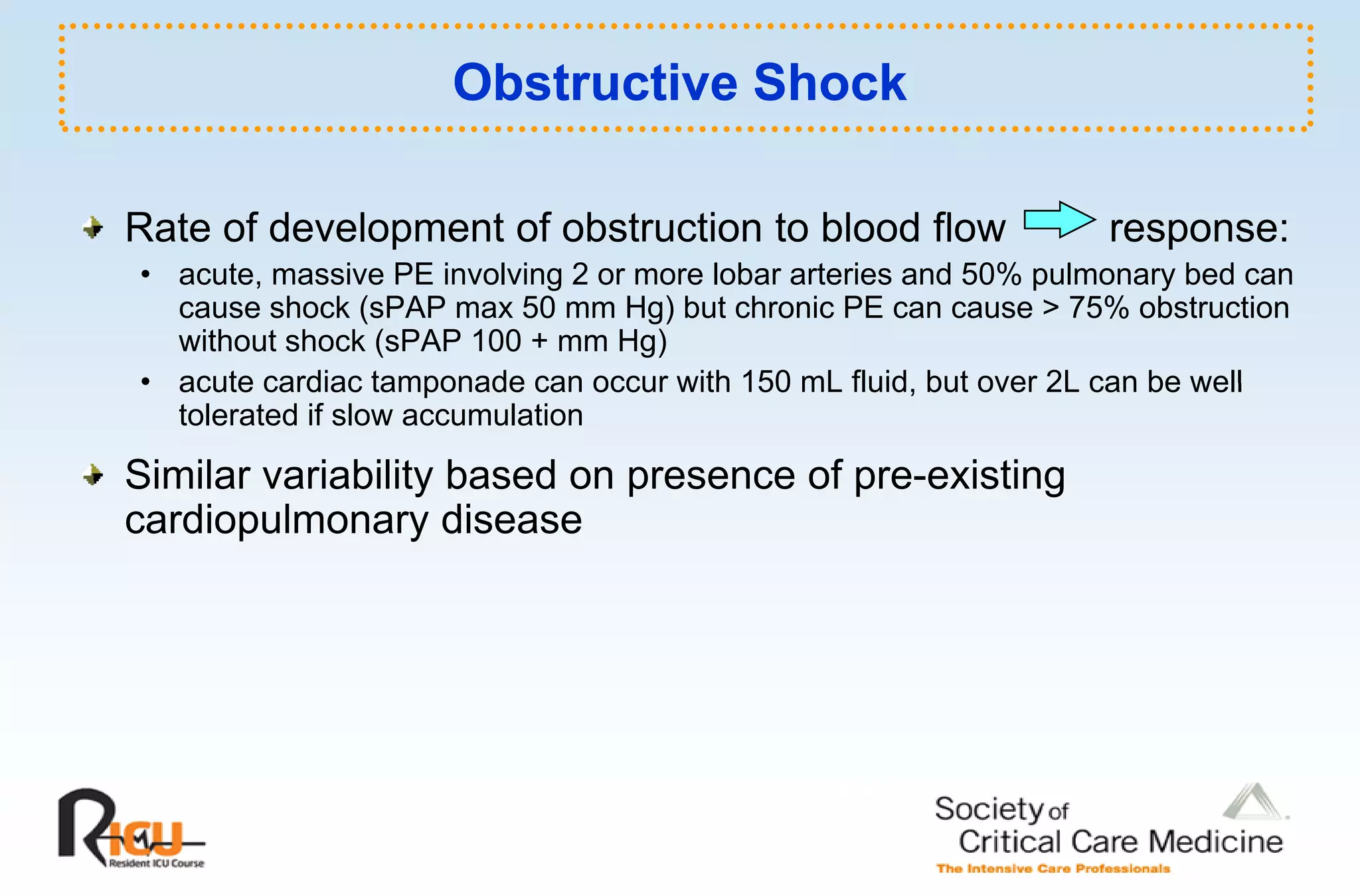
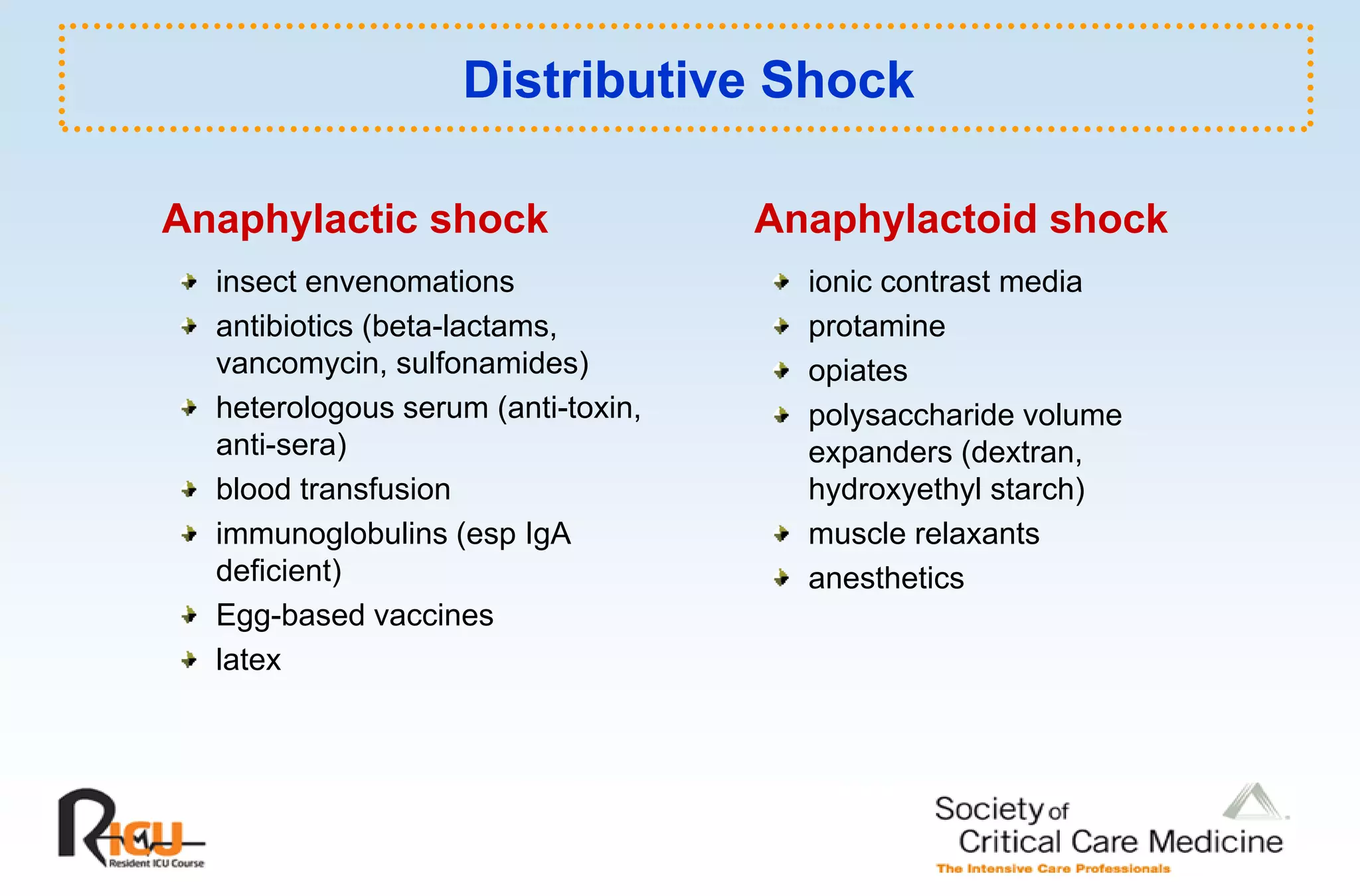
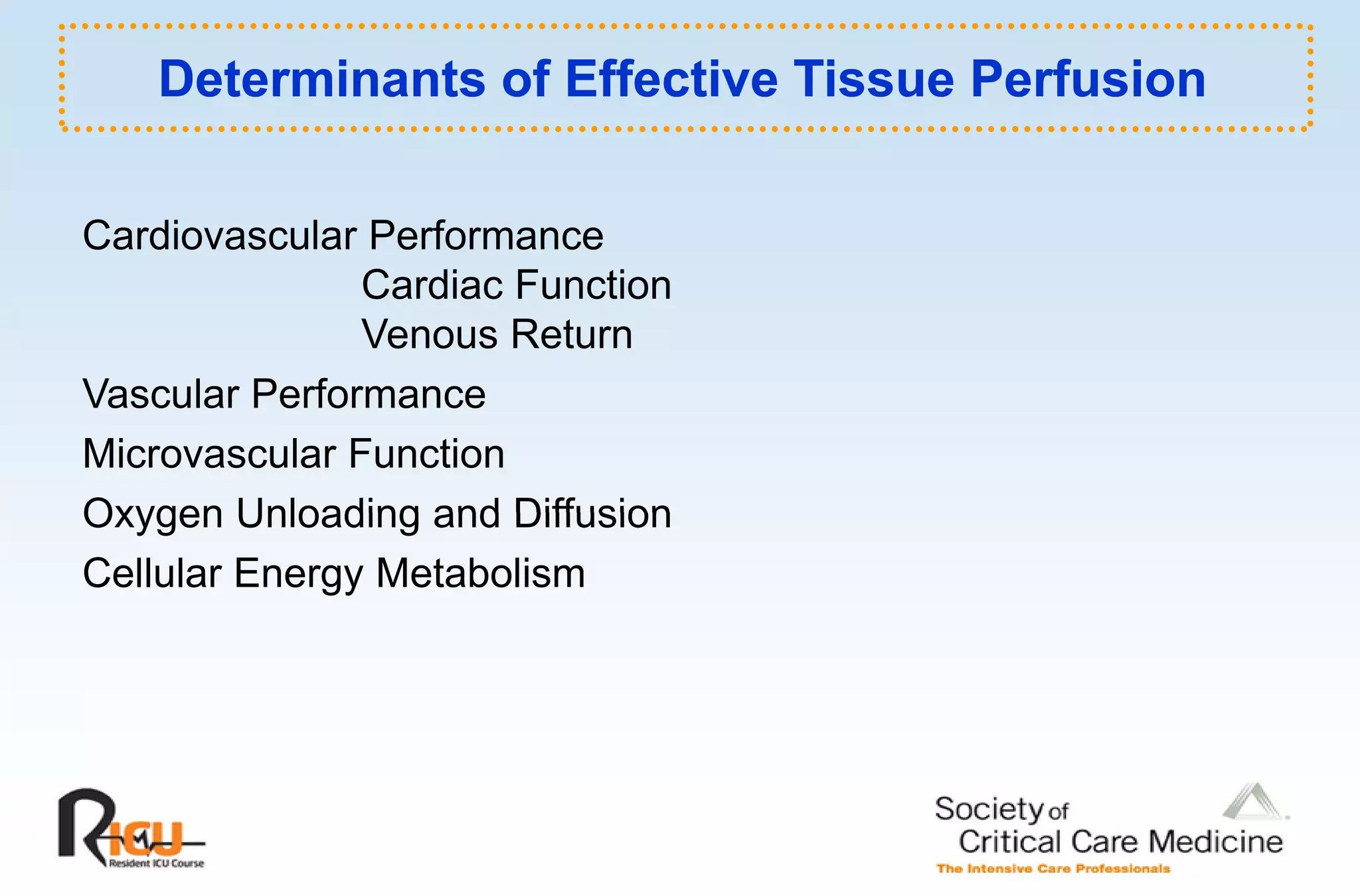
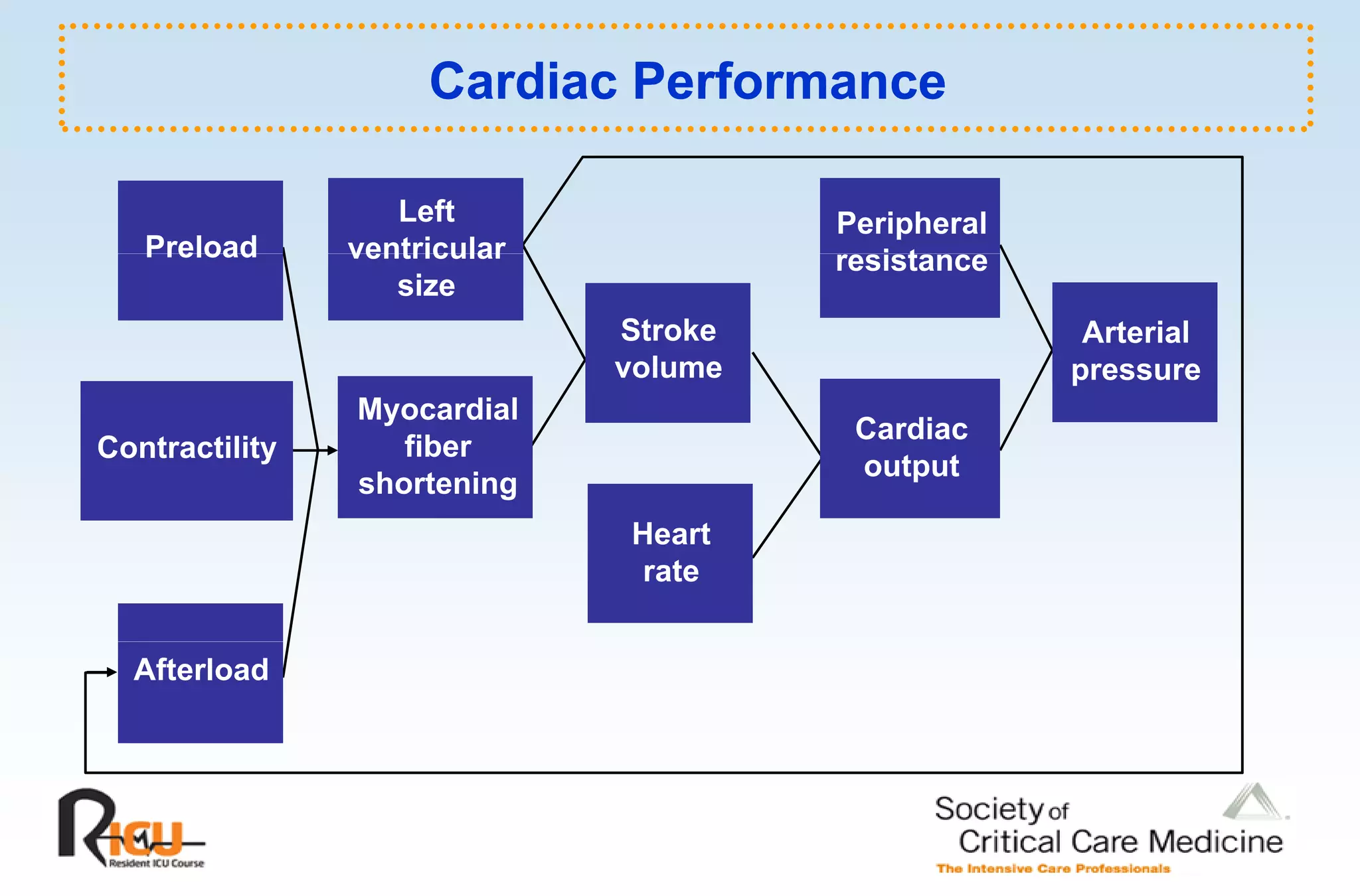
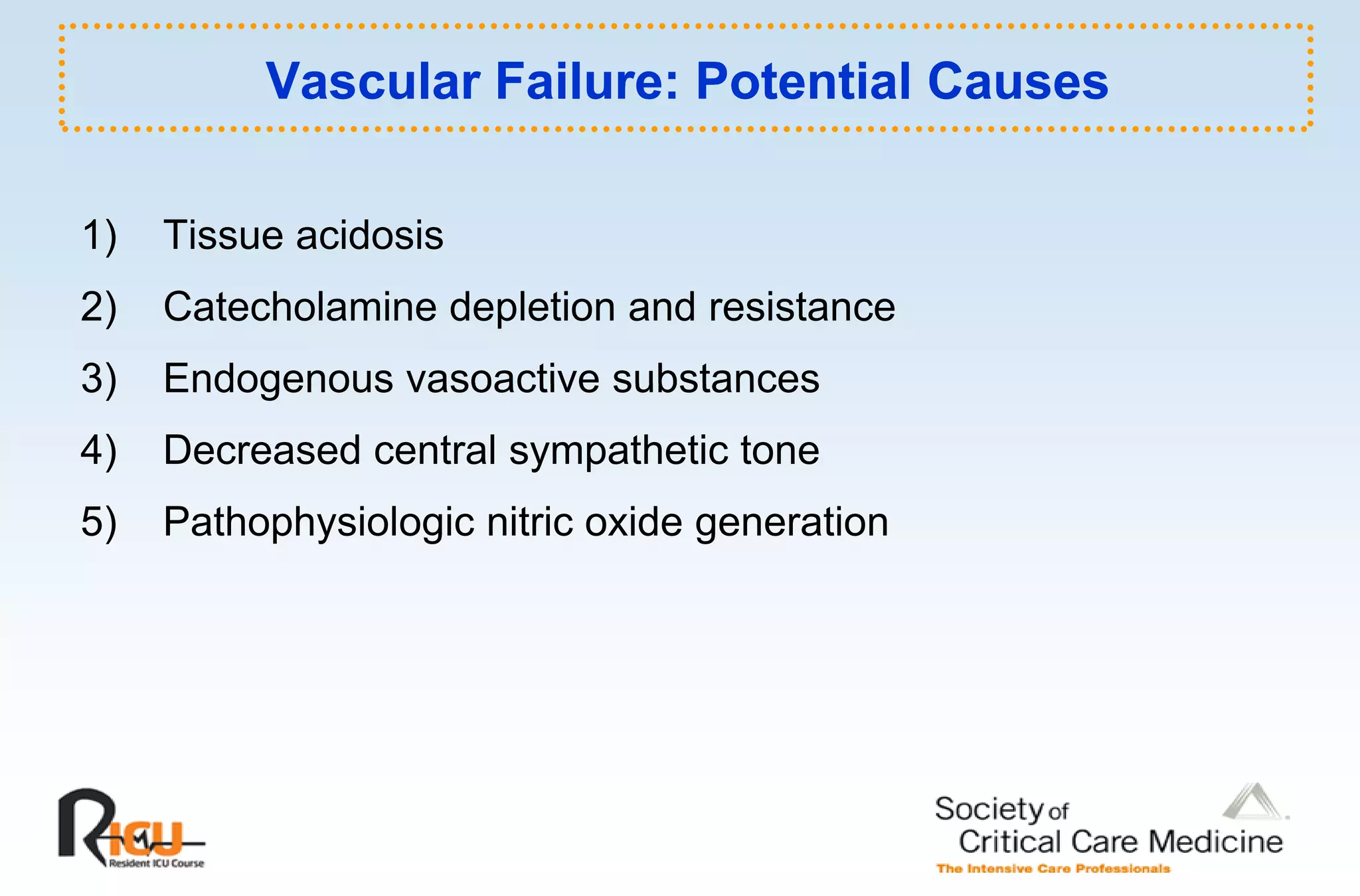
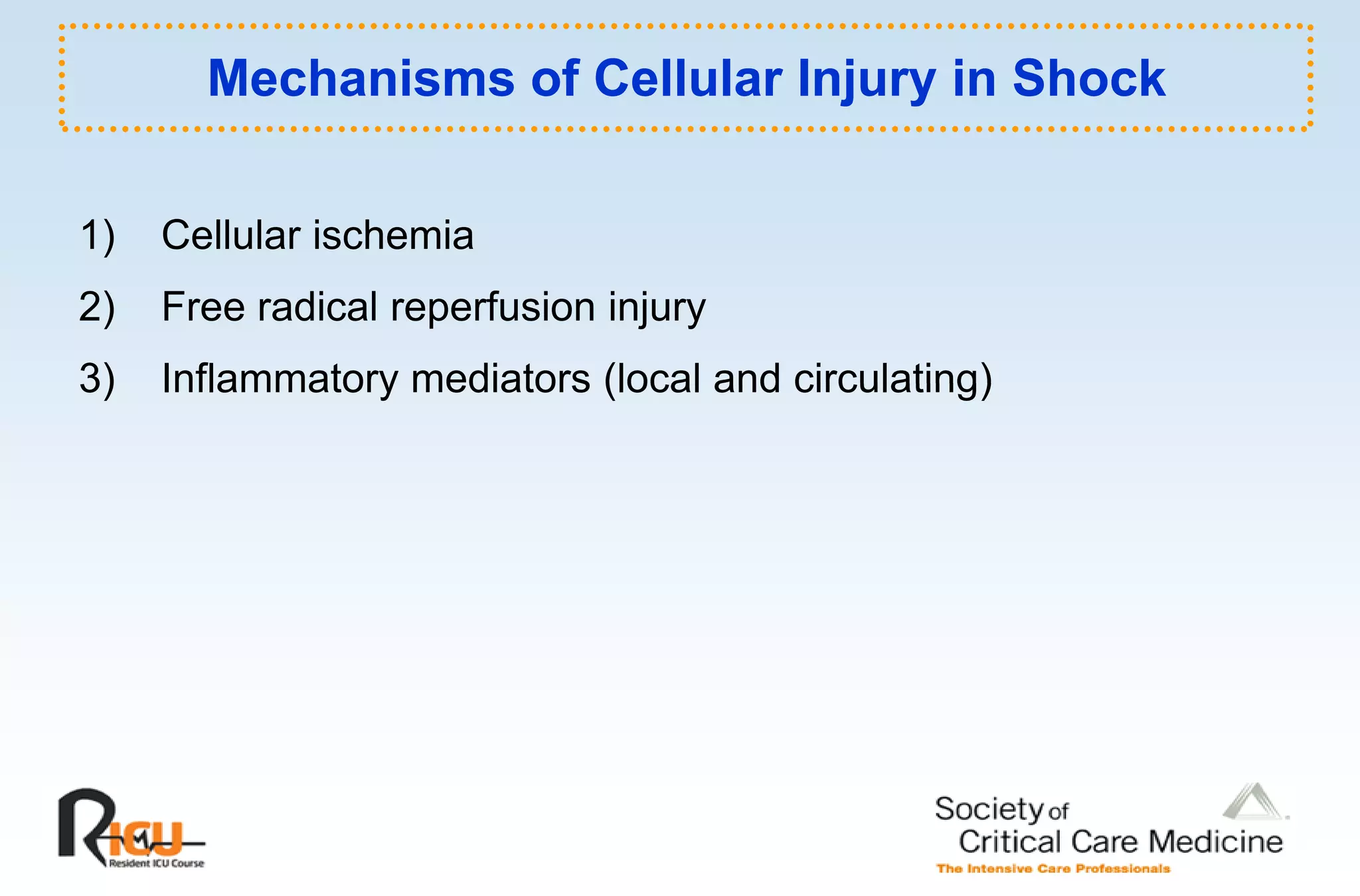
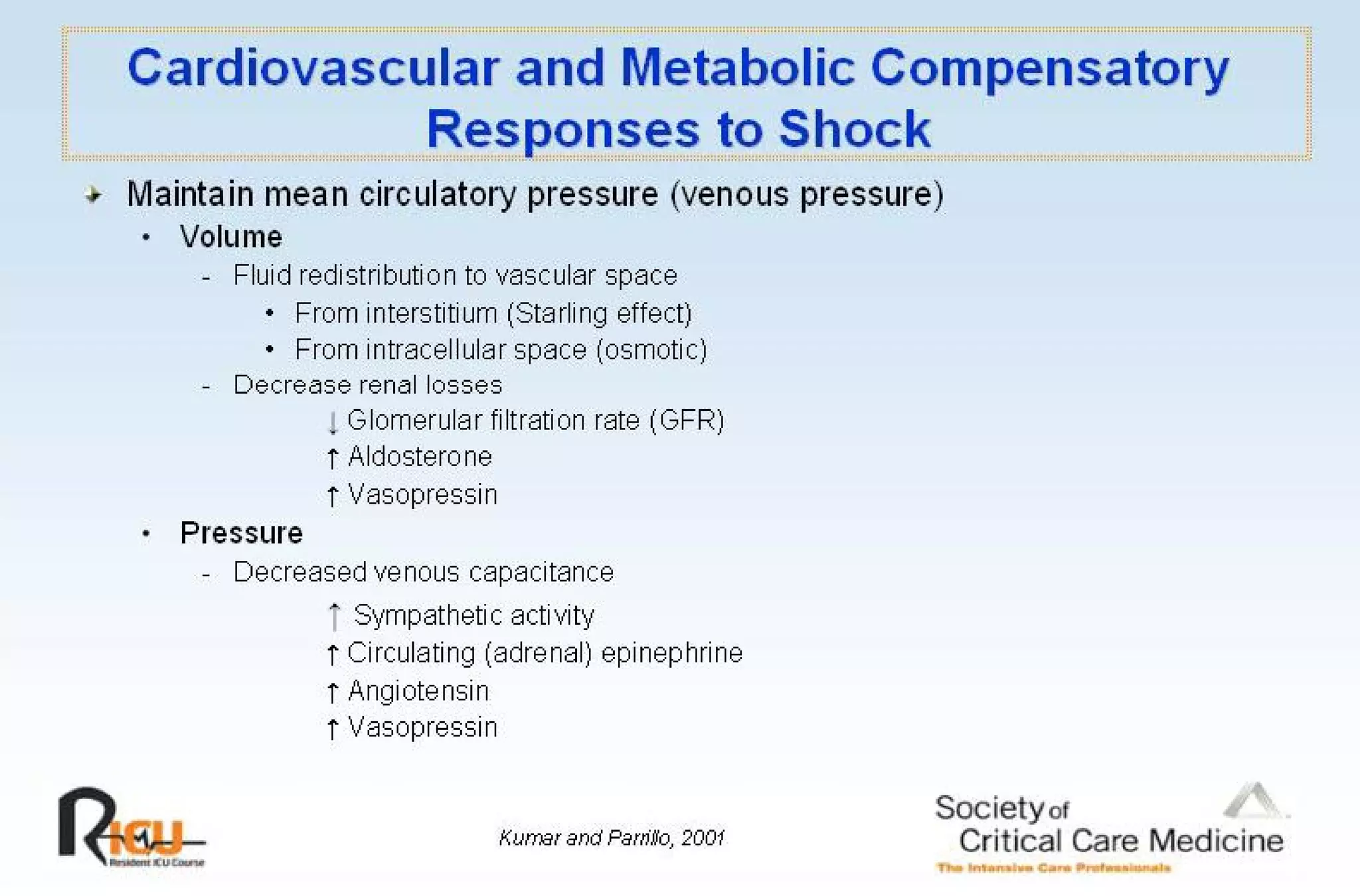
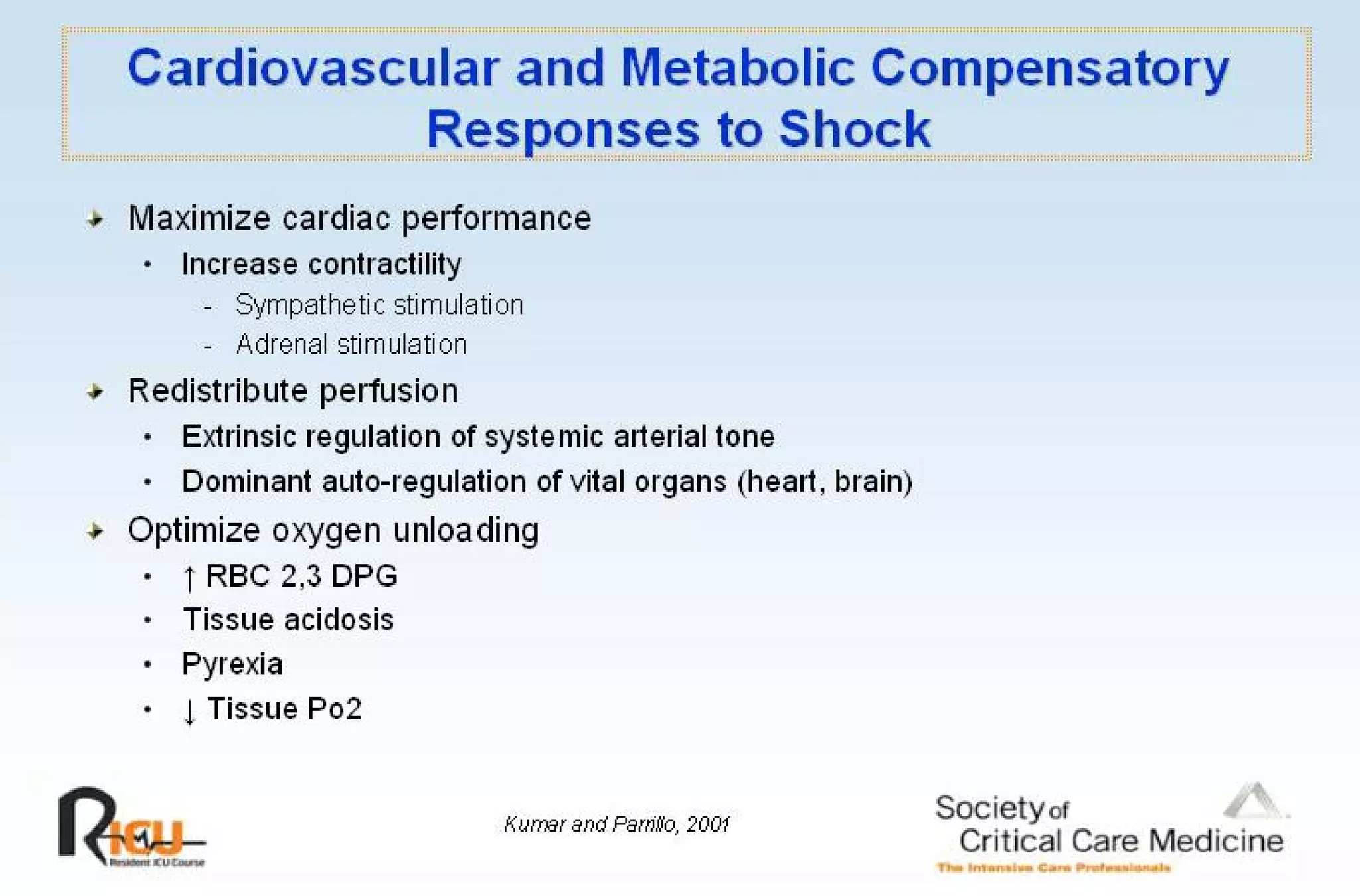
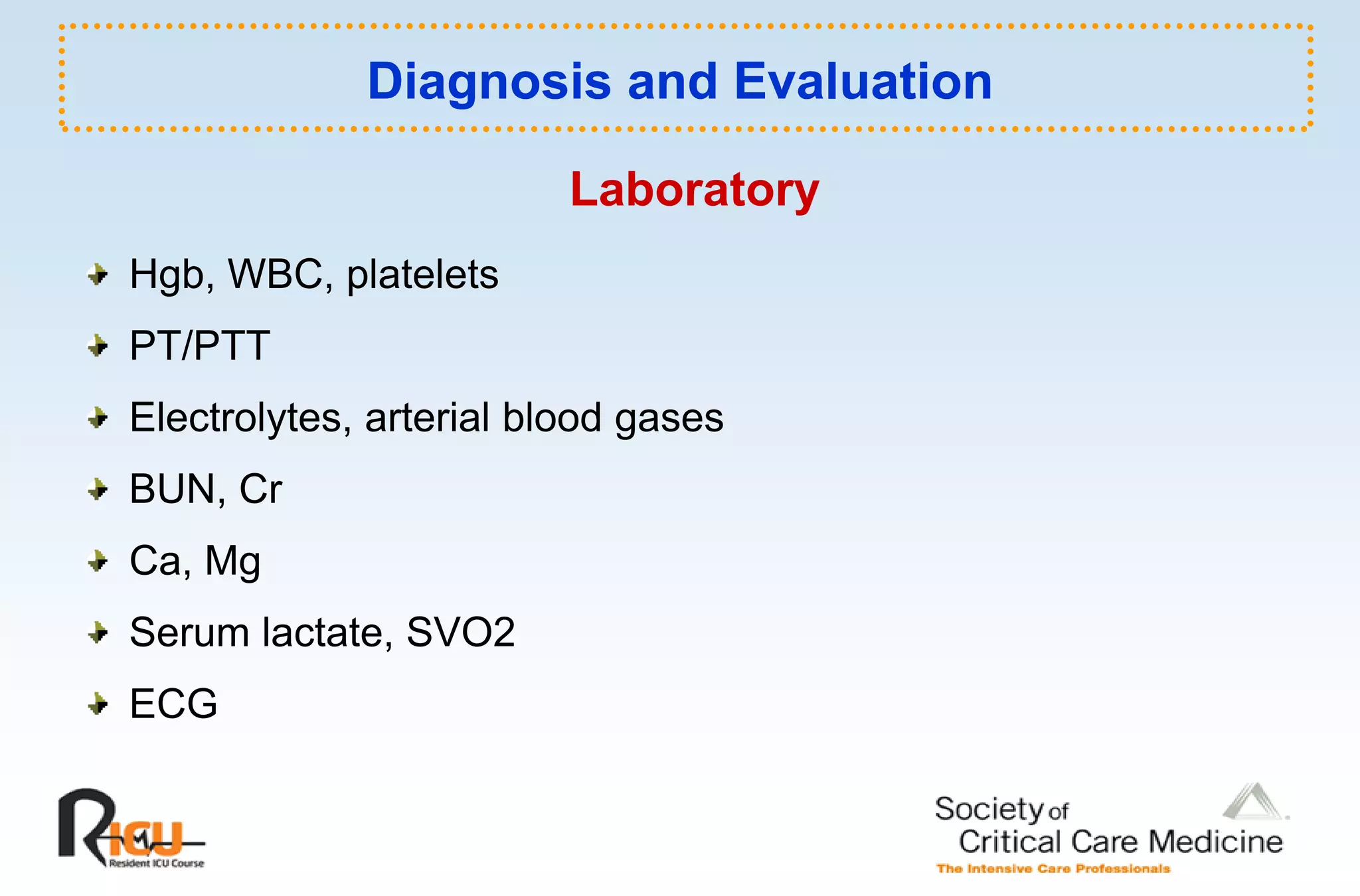
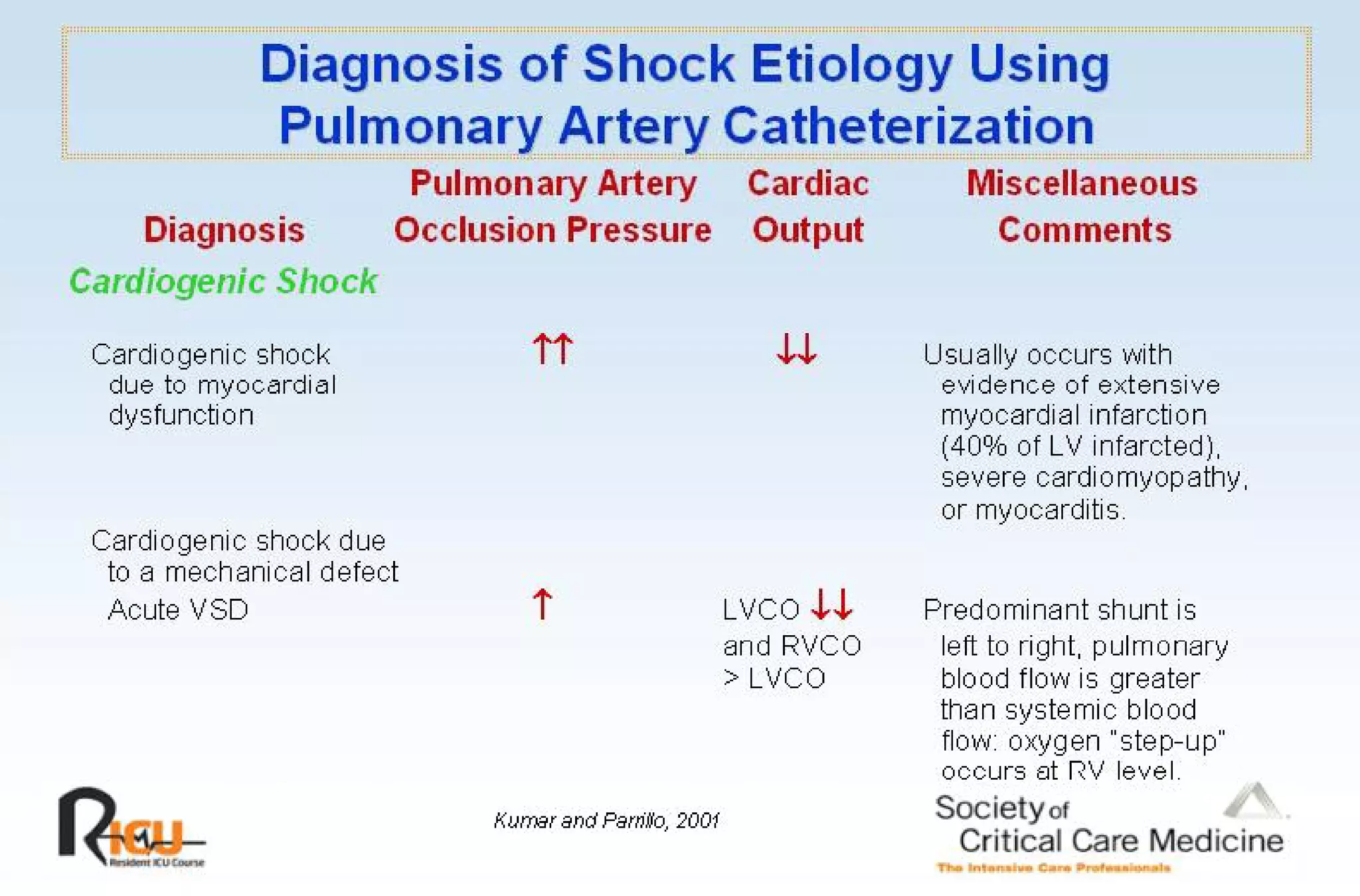
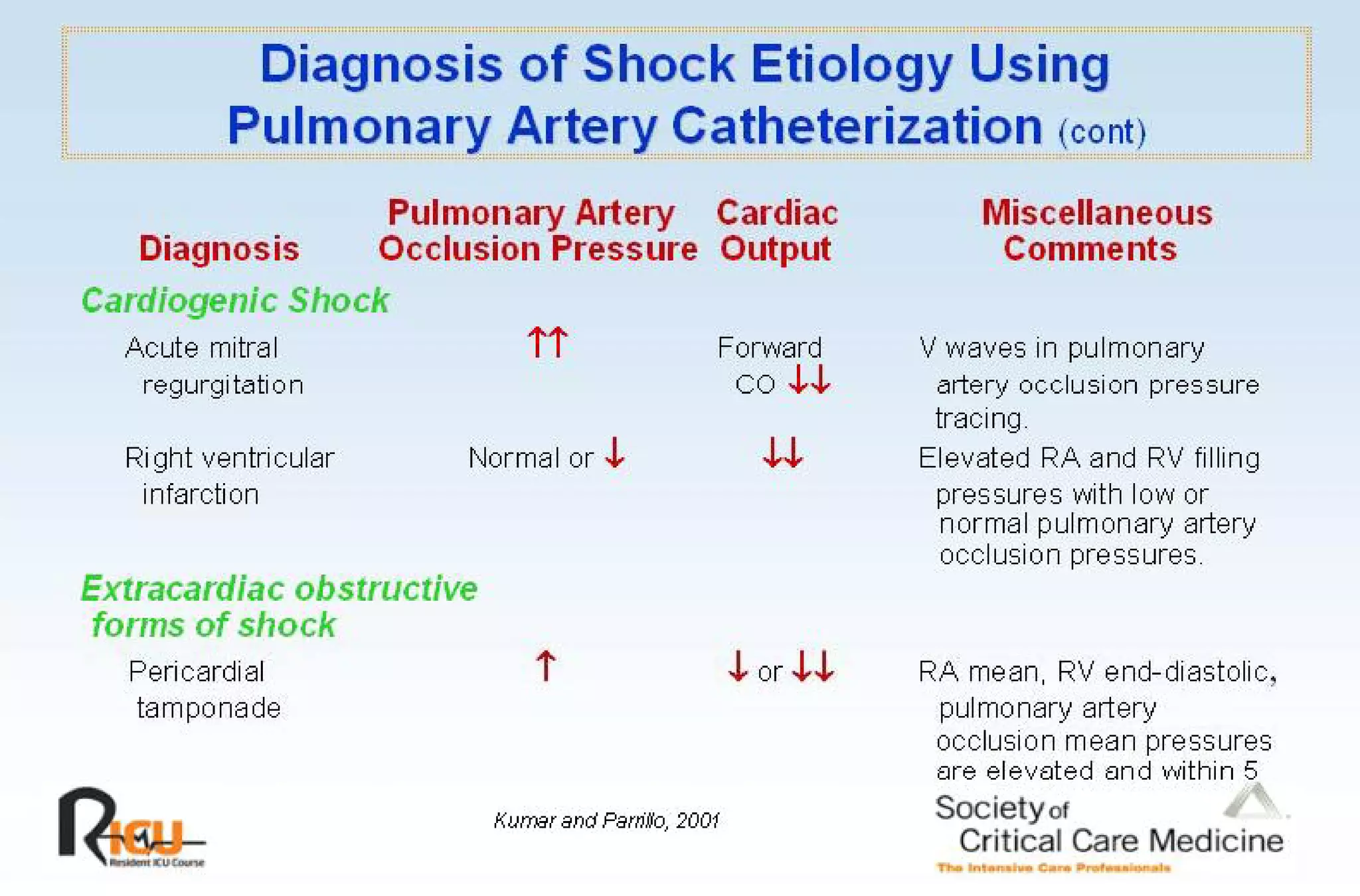
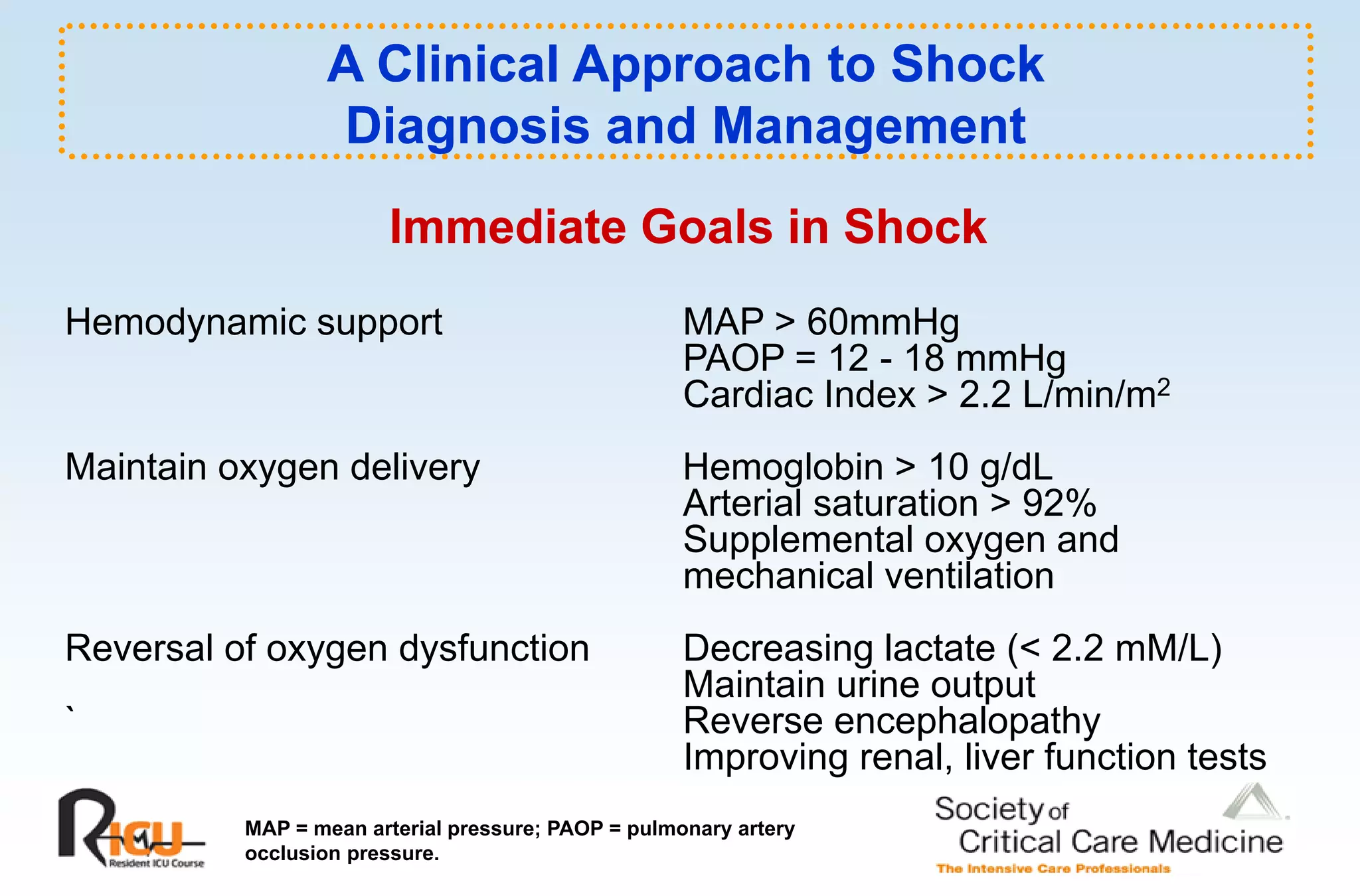
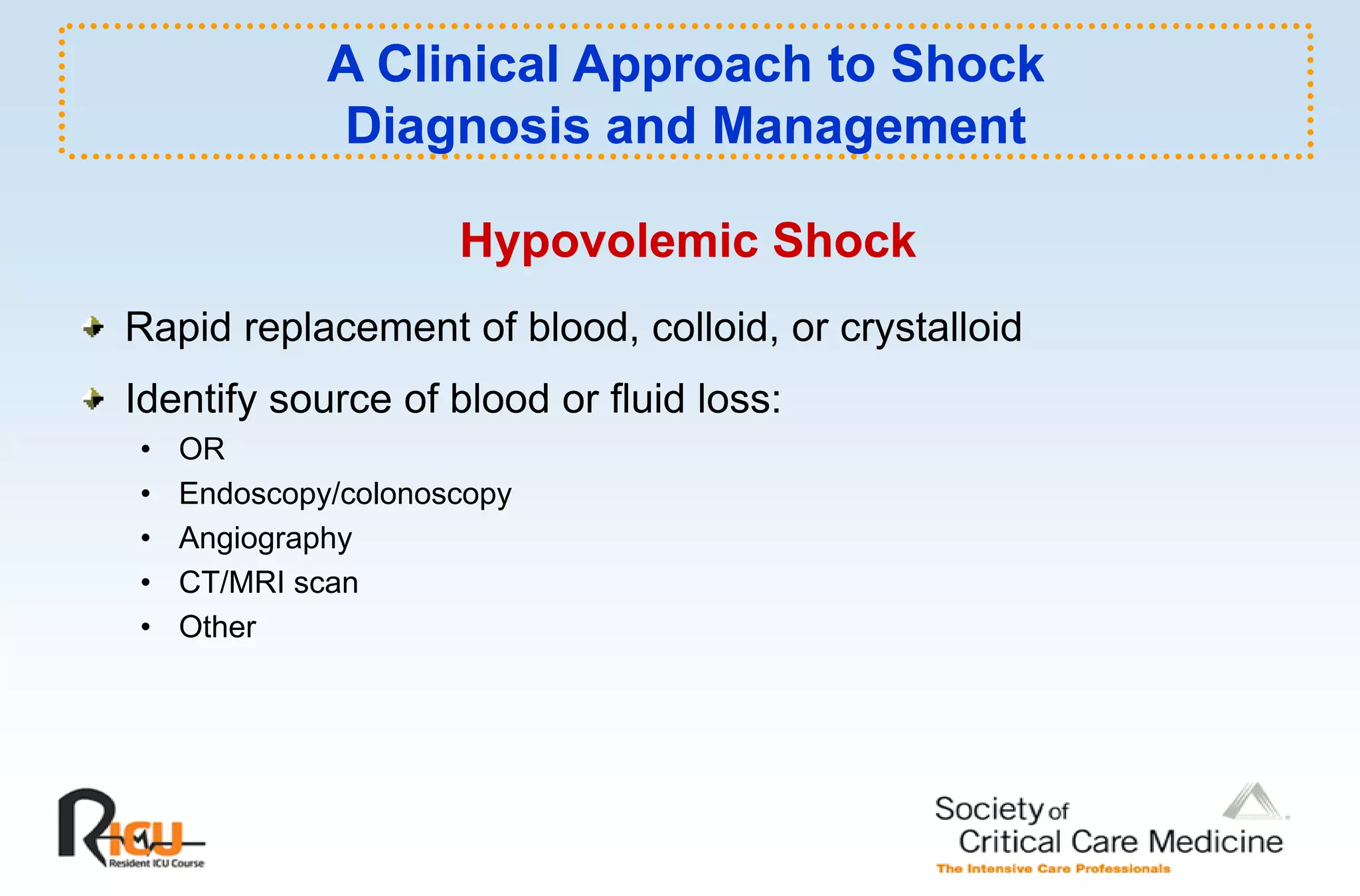
This document discusses the pathophysiology, classification, and management of shock. It defines shock and classifies it into four main categories: hypovolemic, cardiogenic, obstructive, and distributive shock. For each type, the document discusses causes, characteristics, hemodynamics, and clinical correlates. Key points include that distributive shock is most commonly septic shock, and hypovolemic shock is a major cause of early trauma mortality. The document also reviews the diagnosis and evaluation of shock, including clinical signs, laboratory tests, and invasive monitoring techniques. It outlines initial diagnostic and therapeutic steps for managing a patient in shock.