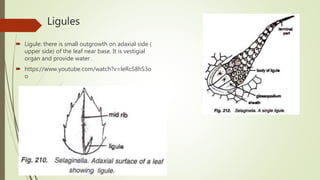
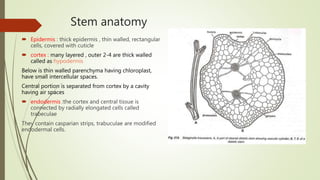
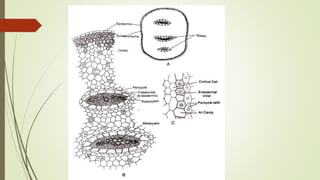
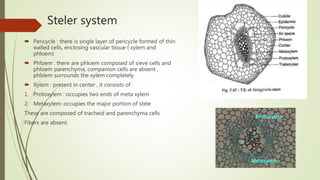
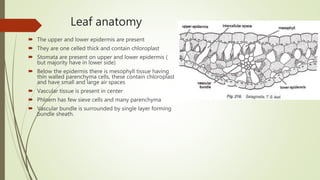
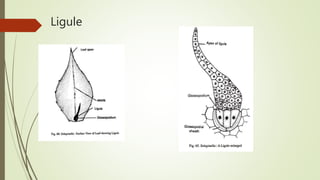
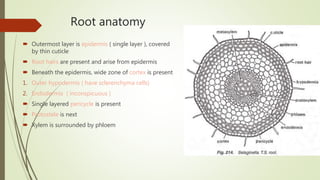
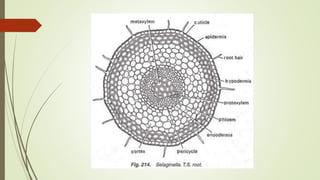
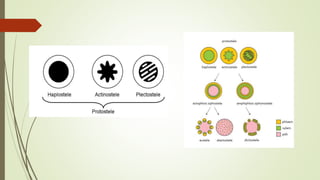
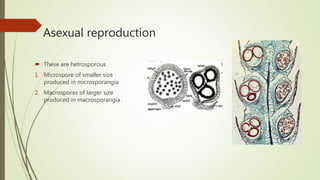
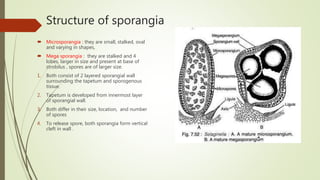
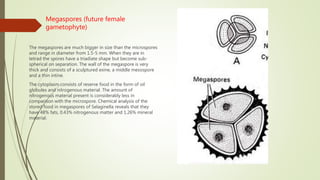
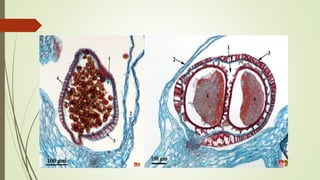
Selaginella, commonly known as club moss or spike moss, is a genus of vascular plants that has worldwide distribution, especially in tropical regions. It reproduces both sexually and asexually. The plant body is differentiated into roots, stems, microphyllous leaves, and ligules. The stems are green and branched. Microspores and megaspores are produced in sporangia and develop into male and female gametophytes, respectively, through precocious germination. Fertilization occurs when sperm from the male gametophyte fuses with eggs in the female gametophyte, forming a diploid sporophyte.