1) Funaria is a terrestrial moss that grows in dense green patches in moist, shady areas like damp soil, tree trunks, and walls.
2) It has both underground protonemal filaments and above-ground leafy gametophores that produce rhizoids, a stem, and spirally arranged leaves.
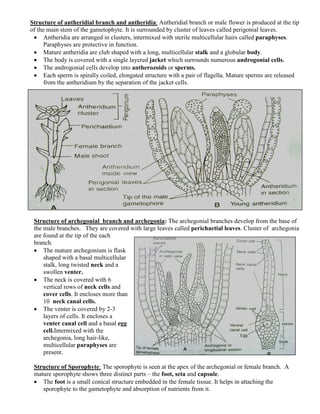
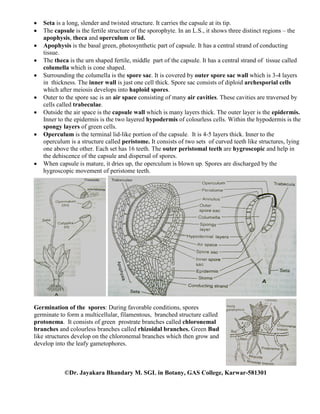
3) Sexual reproduction involves the production of antheridia and archegonia on separate male and female branches that lead to fertilization and the growth of a sporophyte with foot, seta, and capsule containing spores.