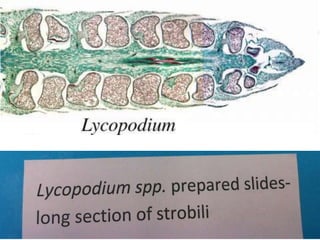
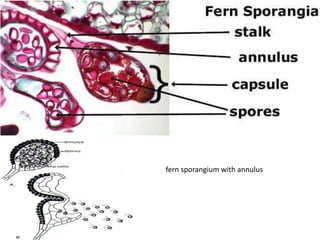
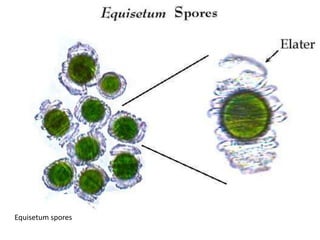
The document describes the characteristics of different plant divisions, including their life cycles, reproductive structures, and distinguishing features. It covers bryophytes like mosses, liverworts, and hornworts as well as seedless vascular plants like club mosses, whisk ferns, horsetails, and true ferns. For each group, it highlights aspects of their sporophyte and gametophyte phases, spores, gametangia, and other structures.