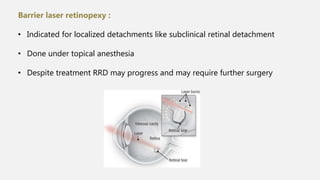
The document summarizes rhegmatogenous retinal detachment (RRD), which occurs when the retina separates from the retinal pigment epithelium due to a break or tear, allowing fluid from the vitreous cavity to enter the subretinal space. It describes the anatomy of the retina, risk factors for RRD like vitreous liquefaction and posterior vitreous detachment, signs and symptoms, examination techniques, and management options like laser retinopexy, pneumatic retinopexy, scleral buckling, and vitrectomy. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is the most common type of retinal detachment and can lead to vision loss if not treated.