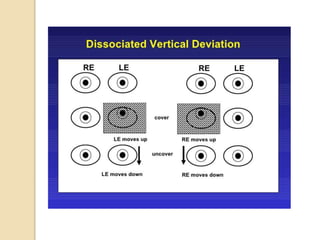
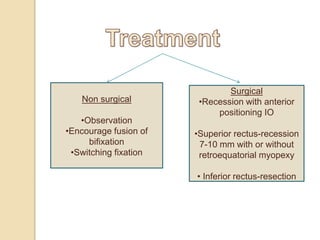
Dissociated vertical deviation (DVD) is a condition where one eye turns upward when the other eye fixes. It typically presents between ages 2-5 years and is often associated with infantile esotropia. DVD violates the rules of ocular motility as the deviating eye does not make a rapid movement to refixate. Measurement and tests like Bielschowsky's phenomenon and red glass testing help differentiate DVD from other vertical deviations. Treatment involves observation, encouraging bifixation, or surgery like superior rectus recession if the deviation is increasing. It is important to differentiate DVD from inferior oblique overaction.