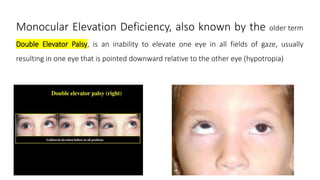
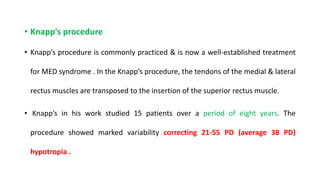
1. Monocular elevation deficiency (MED), also known as double elevator palsy, is characterized by an inability to elevate one eye in all fields of gaze, resulting in hypotropia of the affected eye.
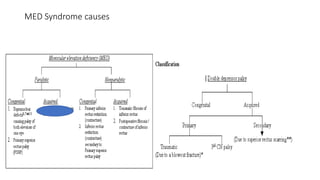
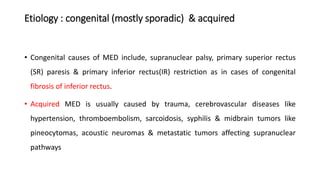
2. The condition can be congenital or acquired, with causes including superior rectus palsy, inferior rectus restriction, and supranuclear lesions.
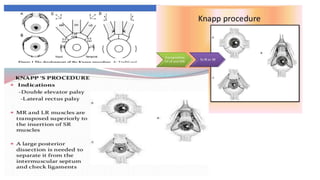
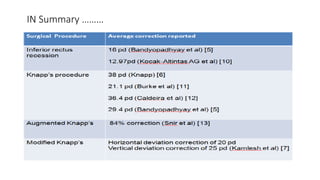
3. Surgical management of MED depends on forced duction test results and may include inferior rectus recession, superior rectus resection, or Knapp's procedure to transpose the horizontal rectus muscles. The goal is to improve eye position and increase binocular vision.