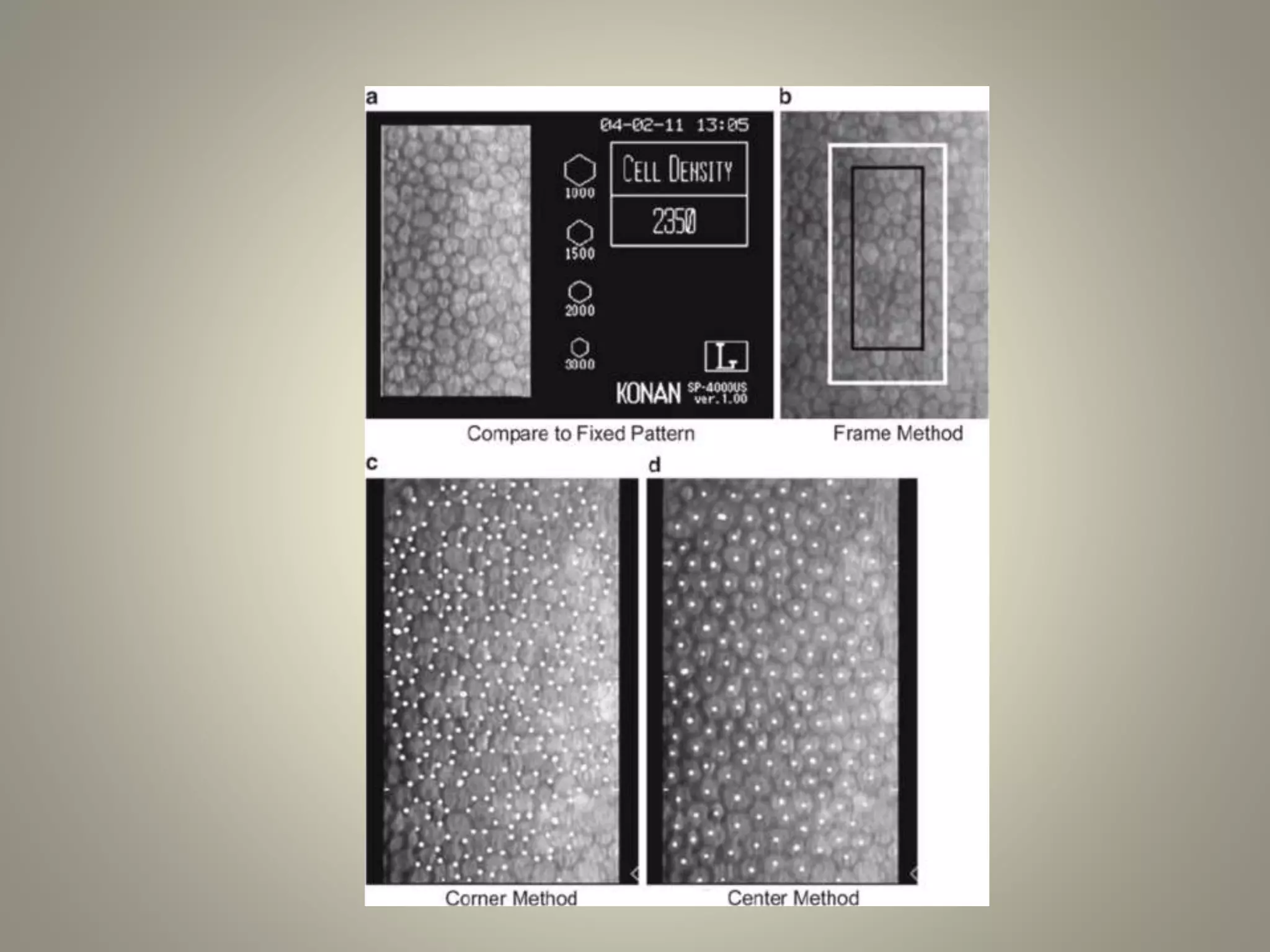
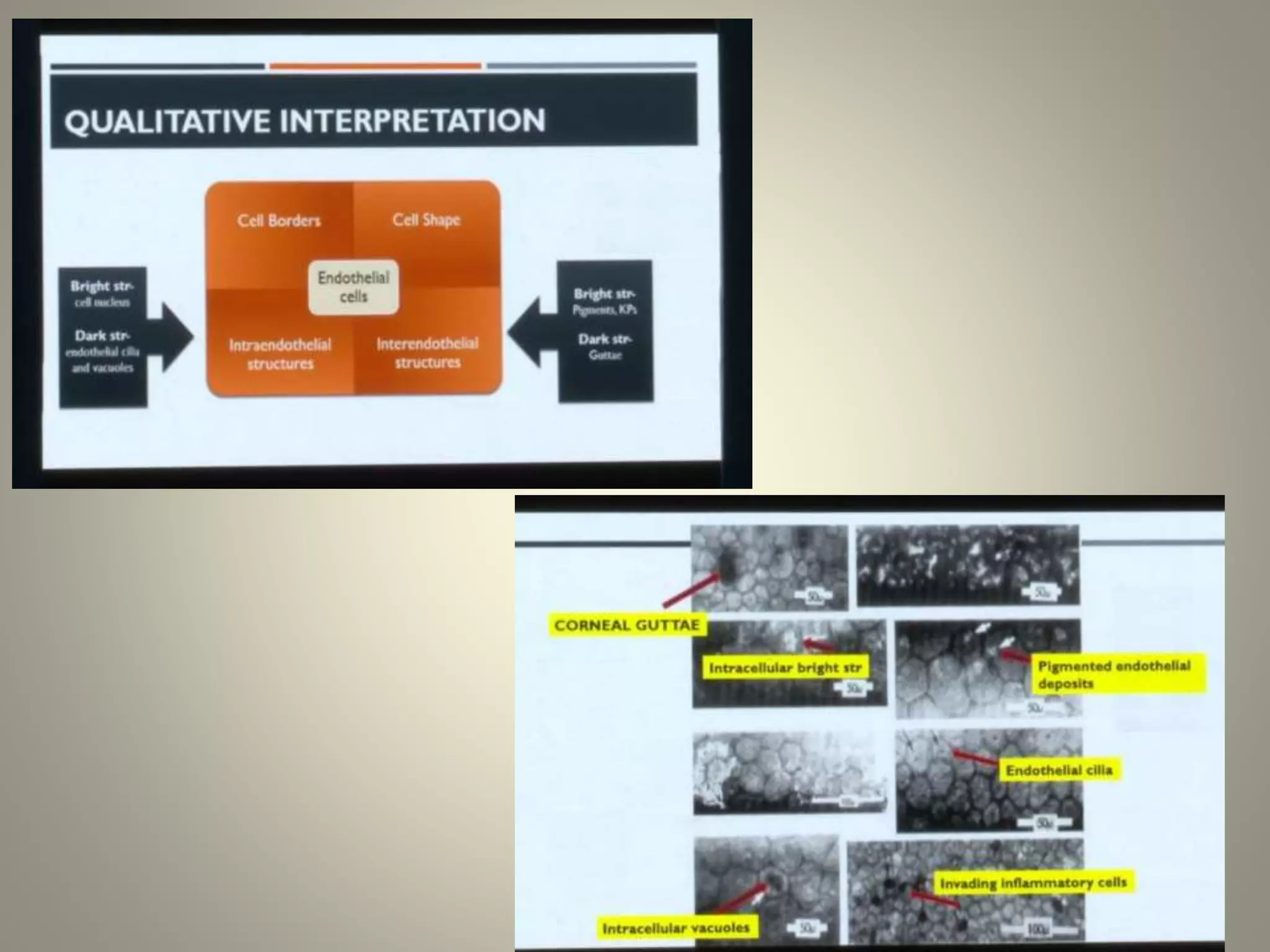
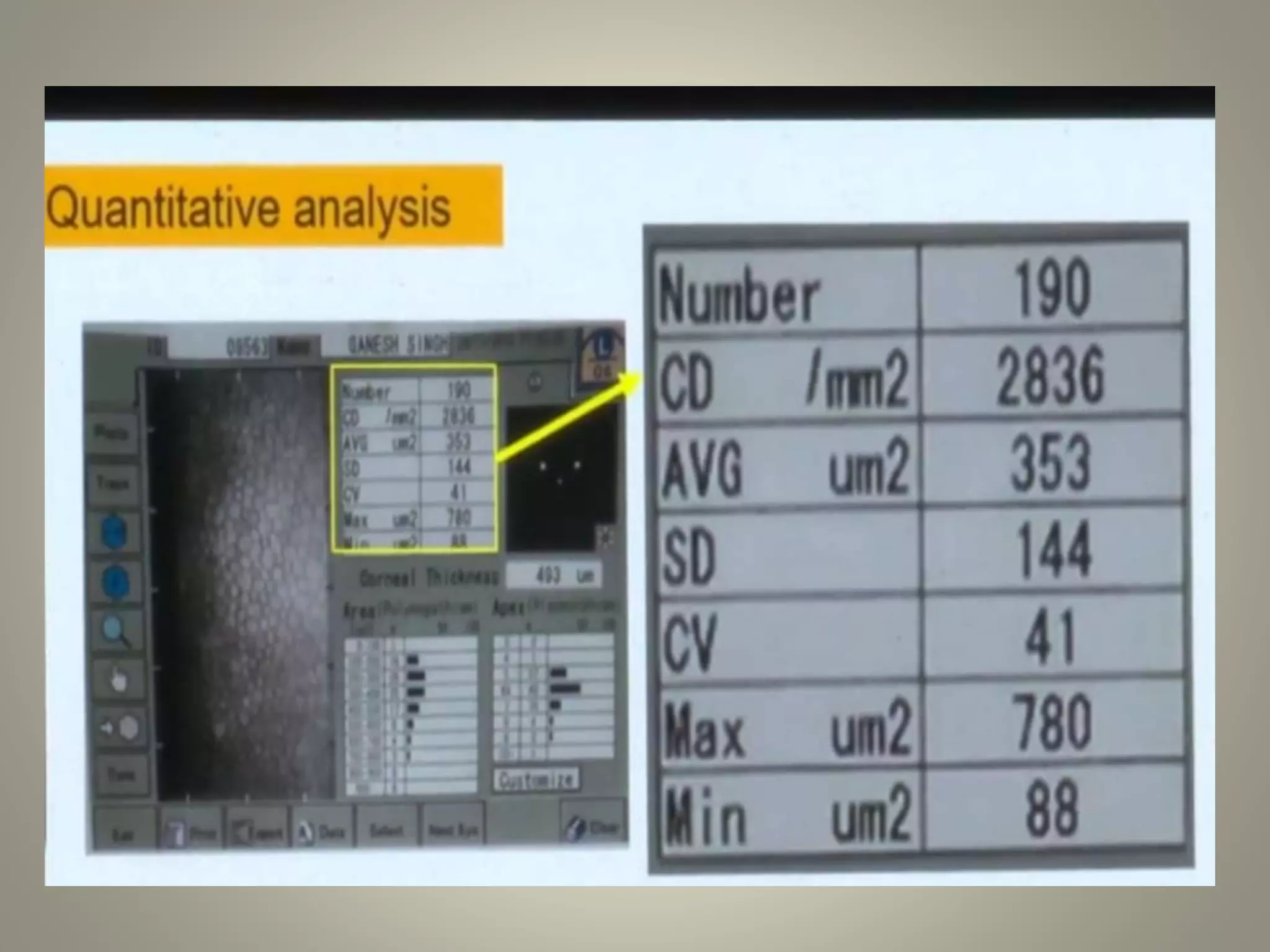
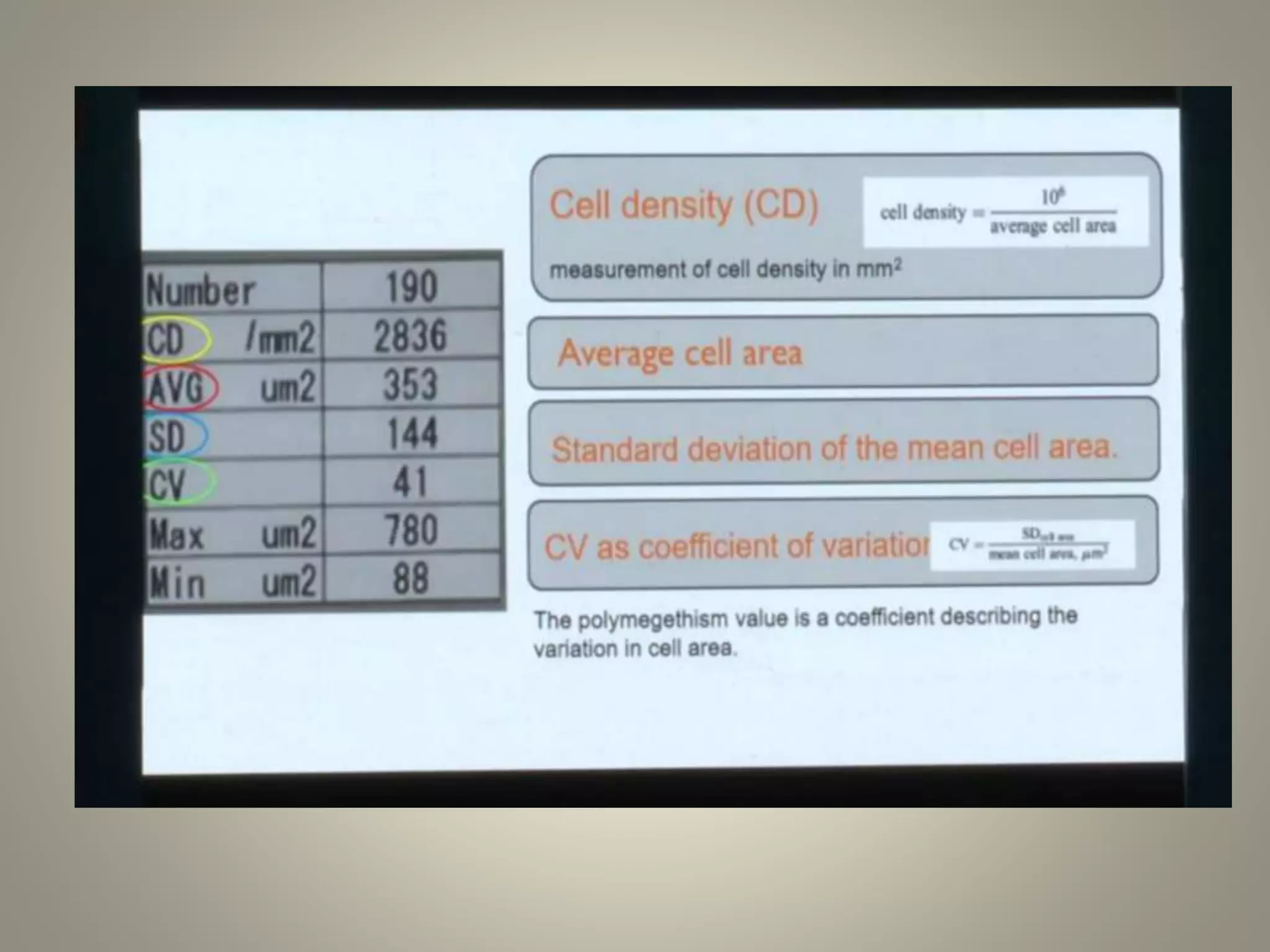
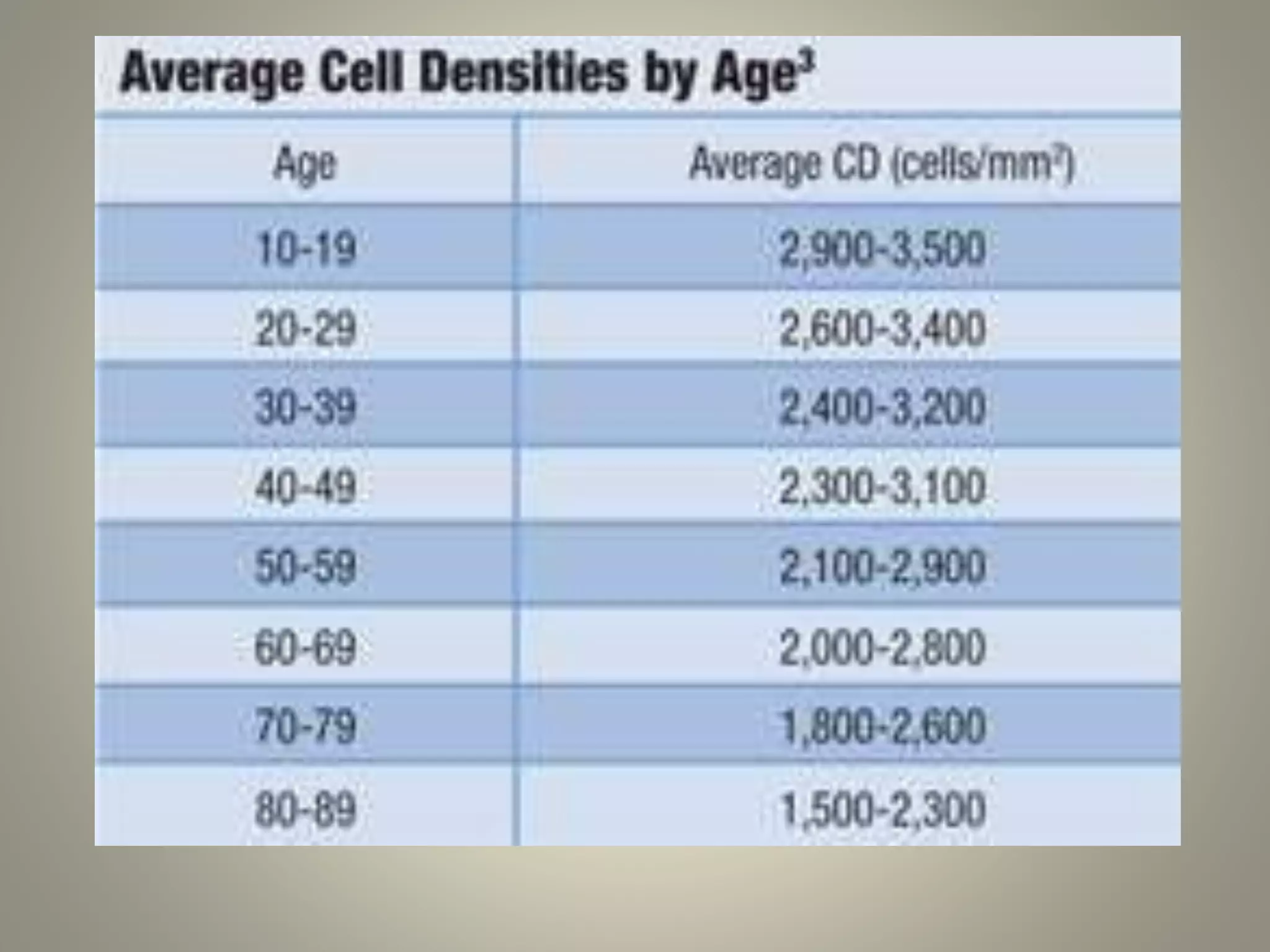
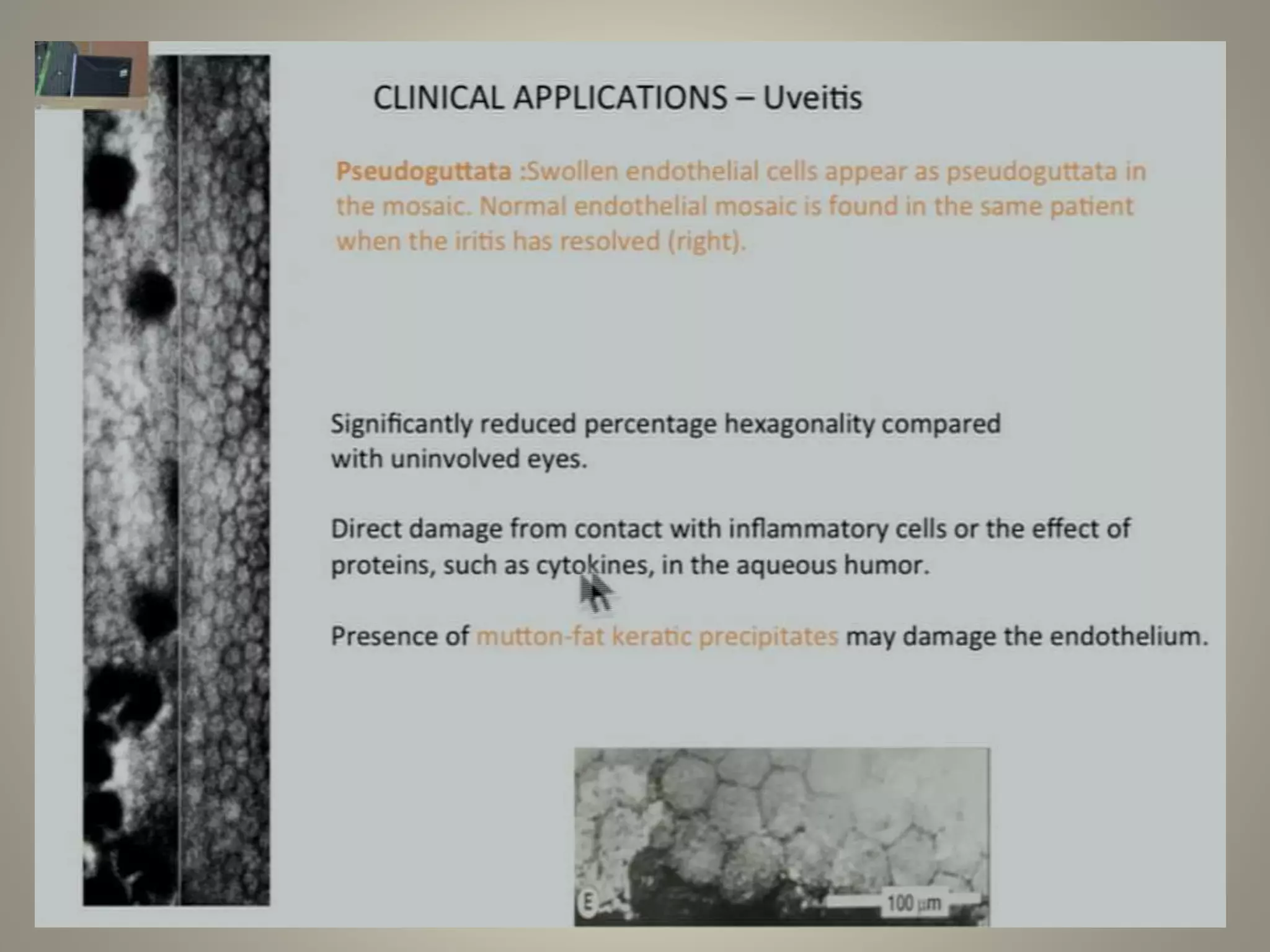
Specular microscopy is used to examine the corneal endothelium and analyze pathological changes. There are contact and non-contact types, with contact providing higher resolution but potential discomfort. The procedure involves placing the patient comfortably and using fixation to keep the eye still while obtaining images. Images are then analyzed to study normal endothelium morphology, diagnose corneal endothelial diseases, and monitor conditions like aging, diabetes, surgery, trauma, and compare surgical techniques. Specular microscopy can detect disorders like Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy and help with decisions like eye banking and surgery.