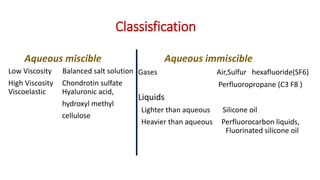
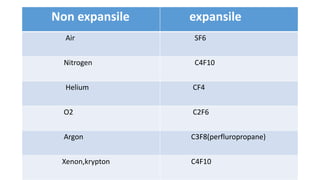
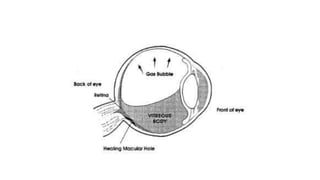
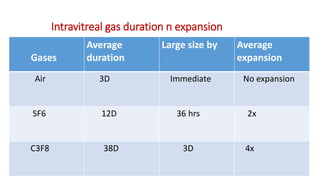
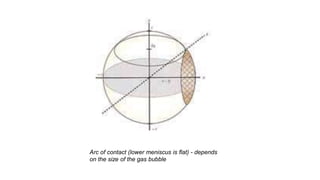
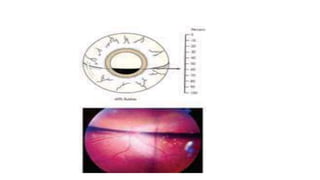
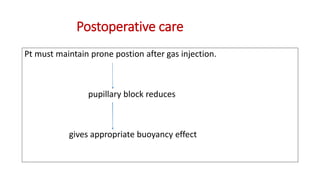
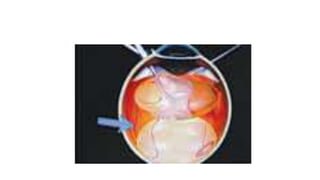
Vitreous substitutes are substances used during vitreoretinal surgery to re-establish intraocular volume, assist with separating membranes from the retina, and manipulate and flatten detached retina. They are also used postoperatively as long-term tamponading agents to maintain the retina in apposition. Common vitreous substitutes used include balanced salt solution, air, viscoelastic fluids, silicone liquid, and perfluorocarbon liquids. Gases such as air, SF6, and C3F8 are employed during retinal detachment surgery to provide internal tamponade and are chosen based on their duration, expansion properties, and buoyancy effects. Complications can include increased intraocular pressure, lens opac