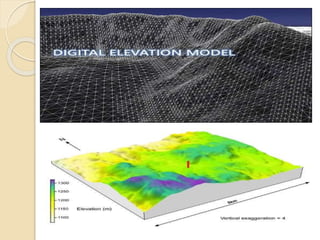
This document summarizes applications of remote sensing for digital elevation models. It discusses how remote sensing uses electromagnetic rays to acquire data without physical contact. Digital elevation models are created using remote sensing techniques to represent terrain and are built systematically or randomly. Methods for creating DEMs include interpolation of contours or using radar data from two passes of a satellite or a single pass with two antennas. The quality depends on factors like terrain roughness and pixel size. Common software used includes TacitView, Socet GXP, and IDRISI.