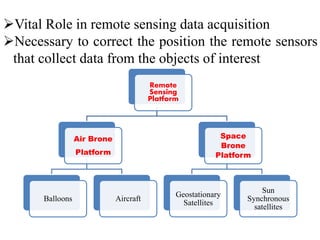
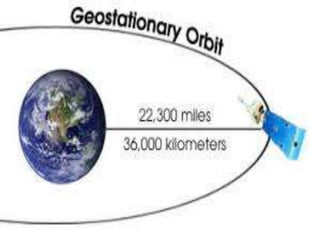
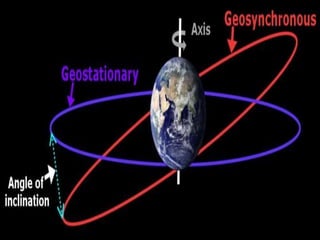
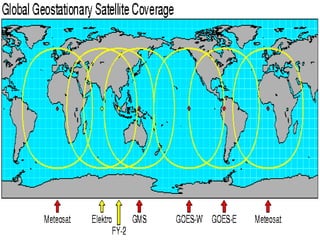
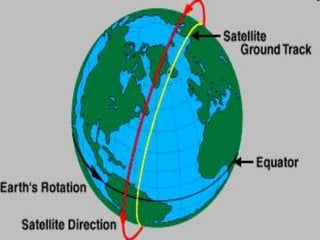
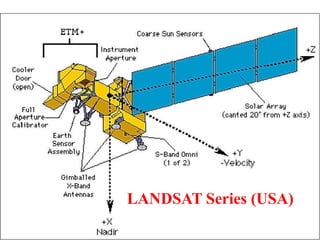
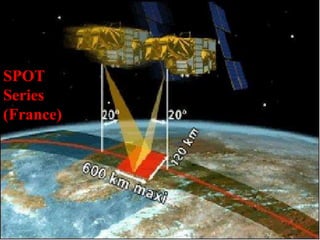
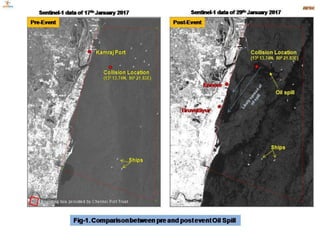
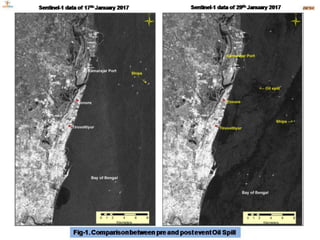
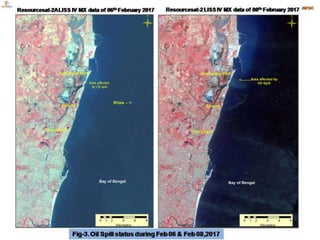
The document discusses various remote sensing platforms including air-based and space-based systems, highlighting their importance in data acquisition for applications like meteorology and resource mapping. It categorizes air-based platforms into free and tethered balloons, aircraft, helicopters, drones, and sailplanes, while detailing their operational parameters. Space-based platforms are classified into geostationary and sun-synchronous satellites, with descriptions of their orbits, purposes, and resolution capabilities.