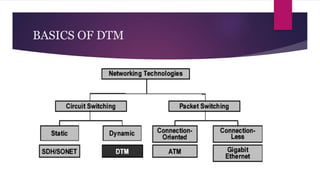
DTM (Dynamic Synchronous Transfer Mode) is a broadband network architecture based on circuit switching and time division multiplexing. It employs simplex channels and allows for dynamic reallocation of time slots. DTM aims to efficiently use bandwidth on fiber optic networks and provide quality of service for real-time multimedia traffic like video streaming. It has applications in enterprise networks and transmitting integrated audio/video data.