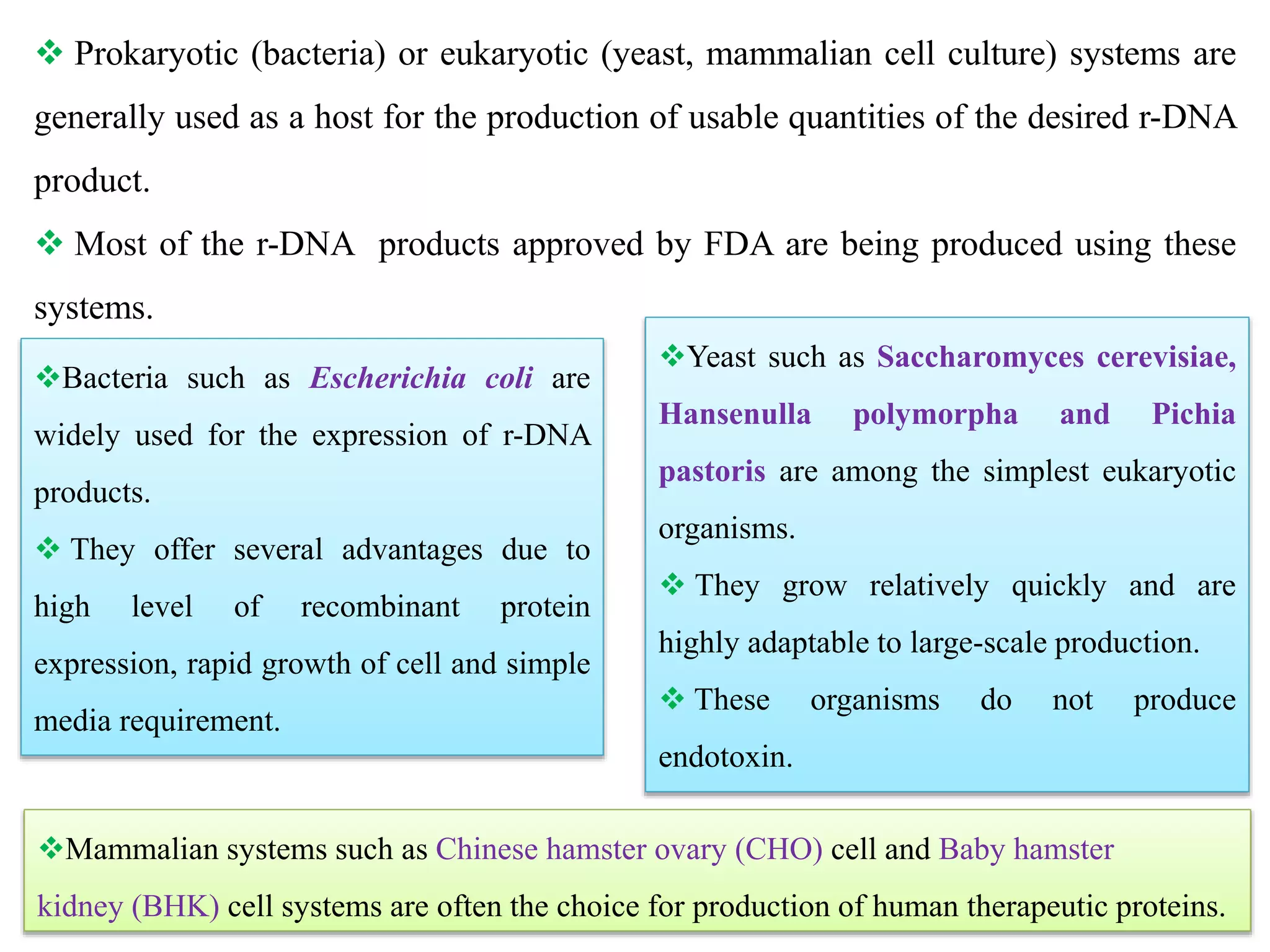
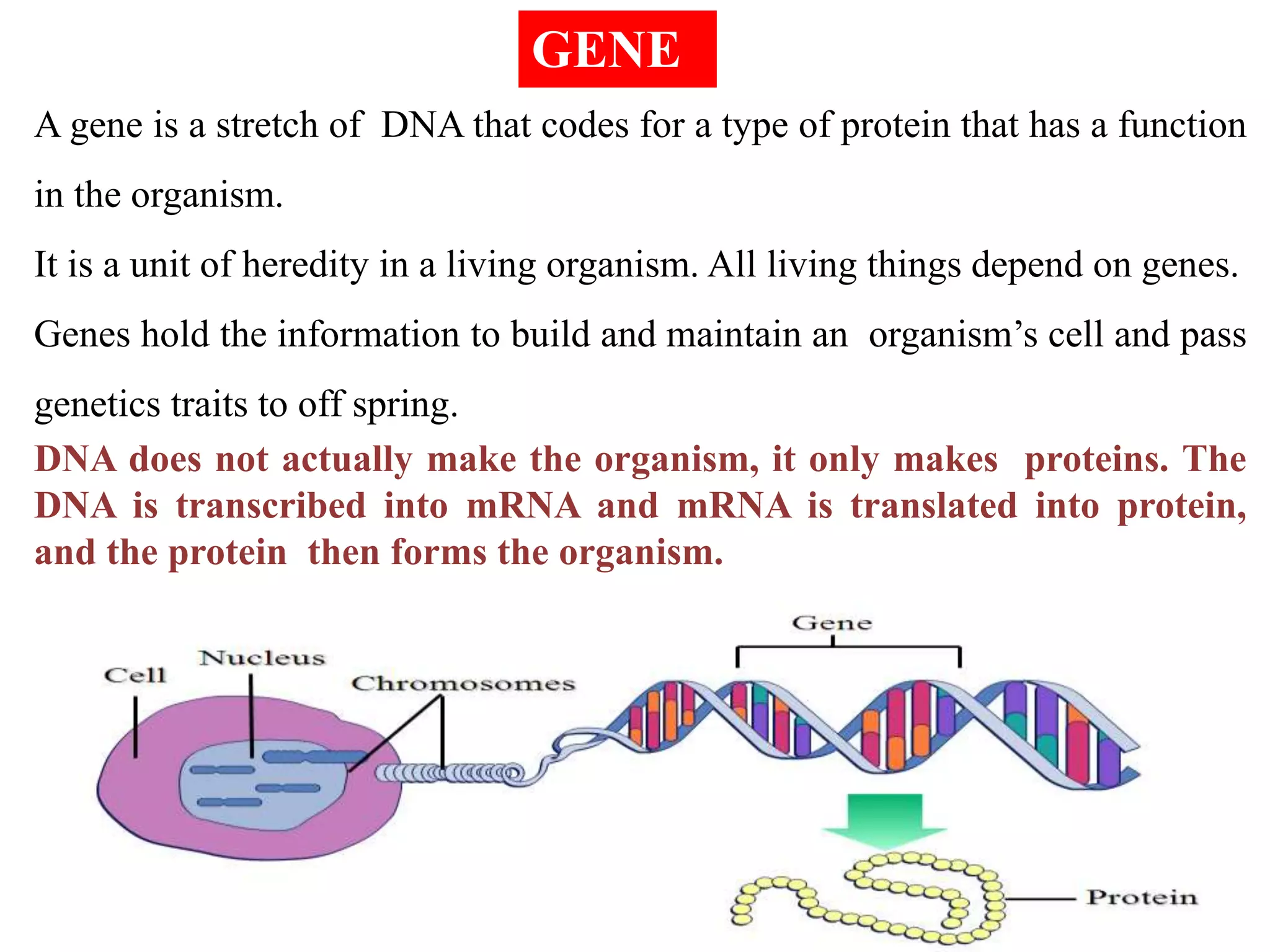
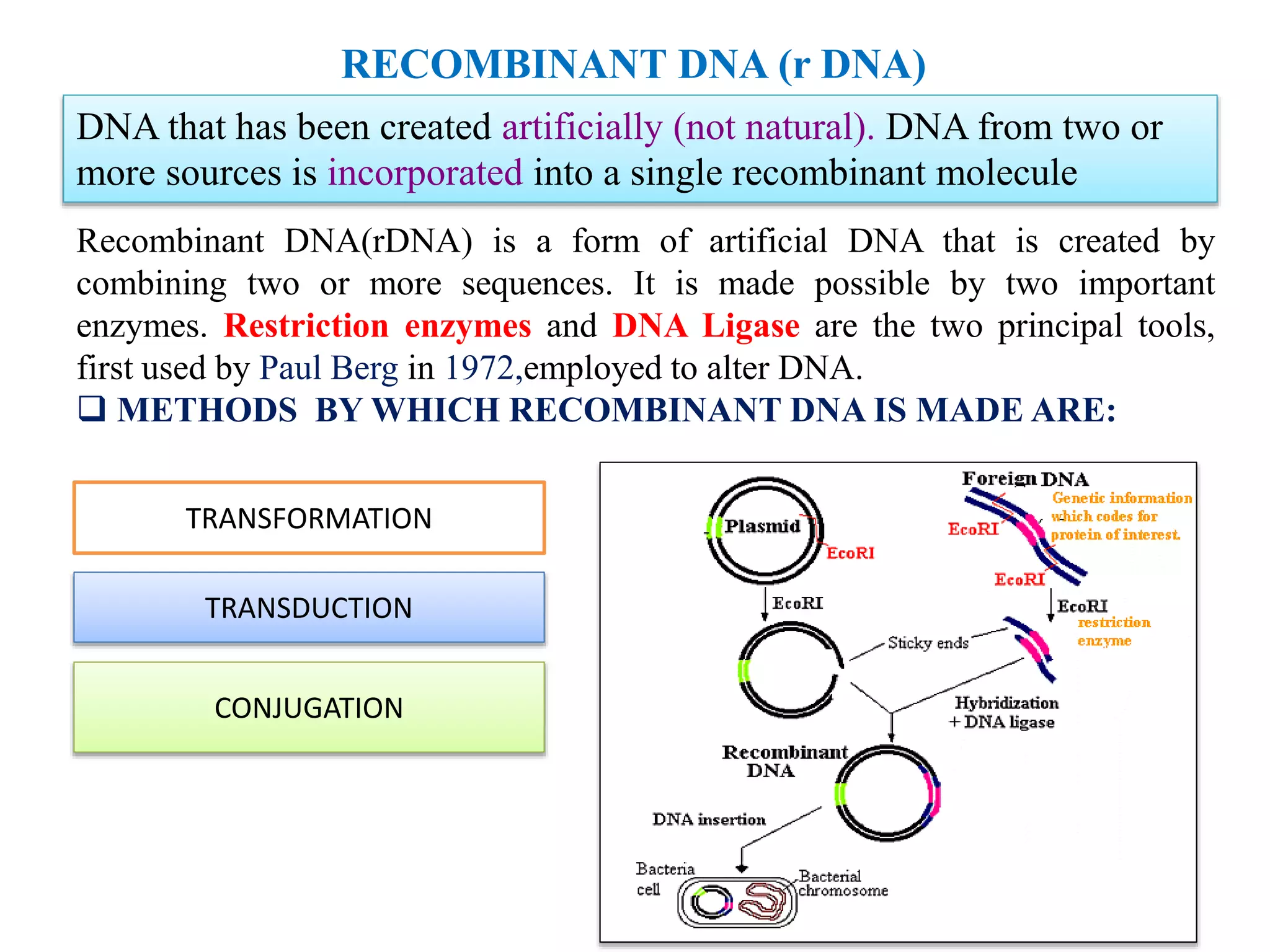
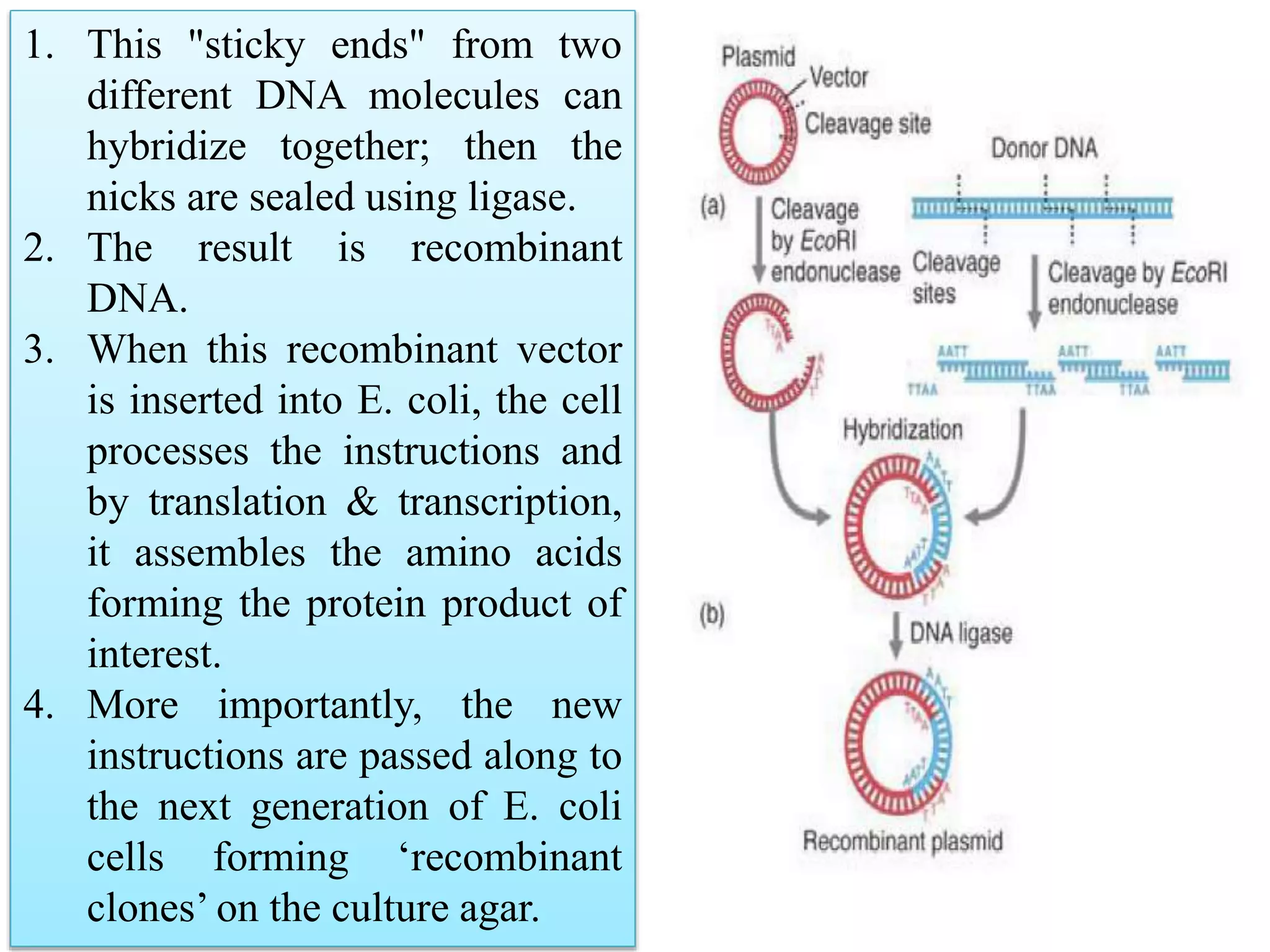
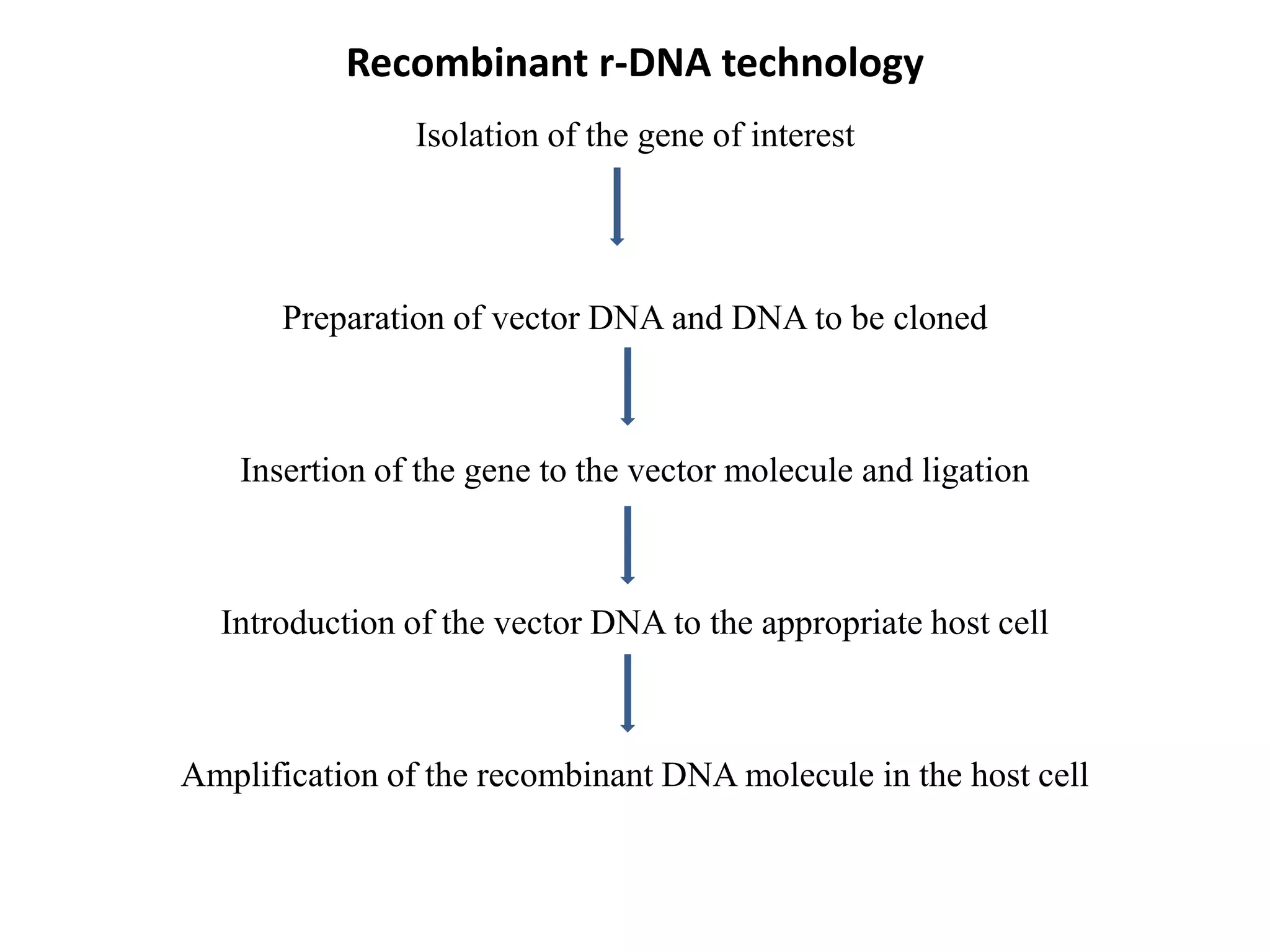
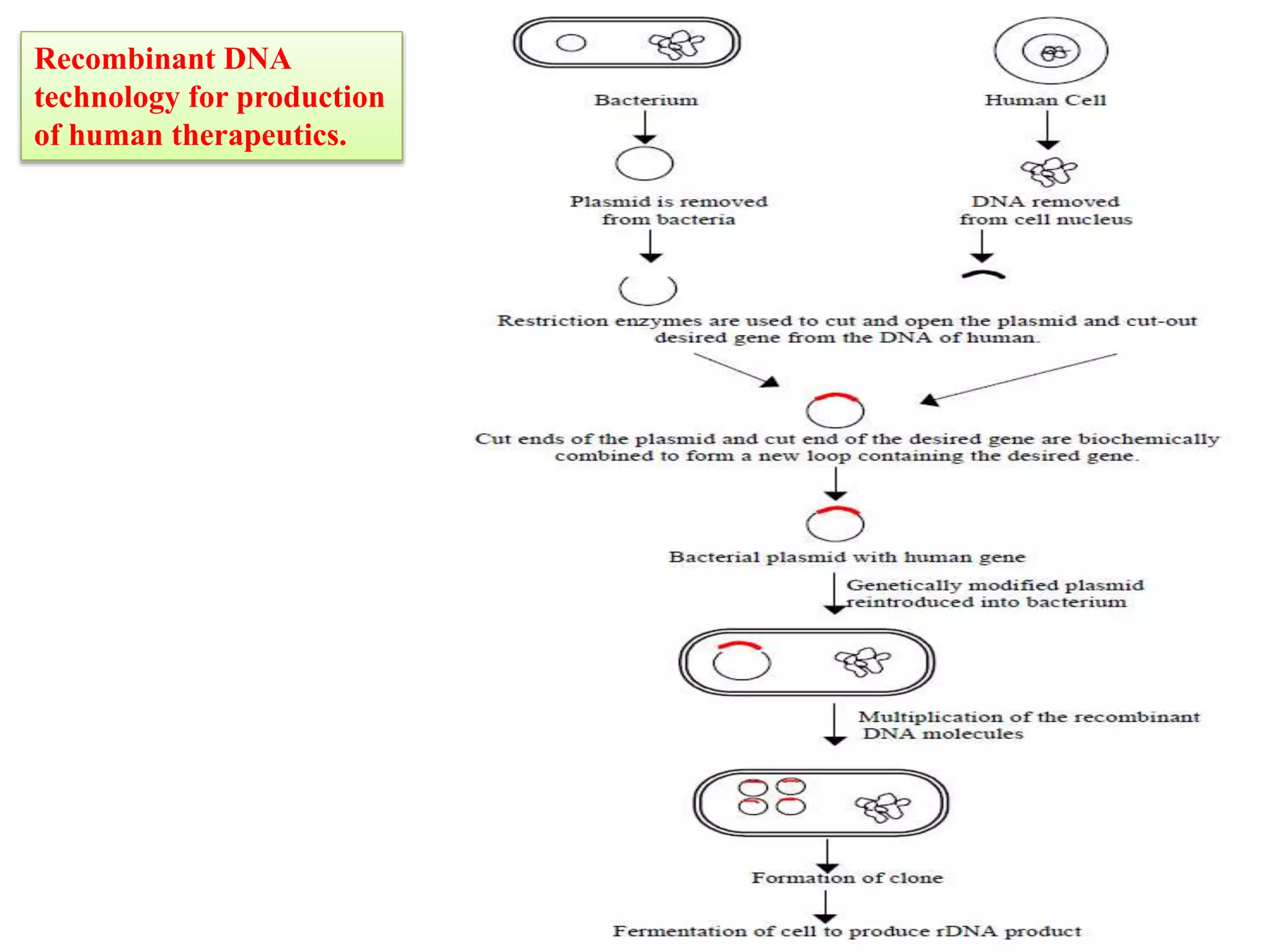
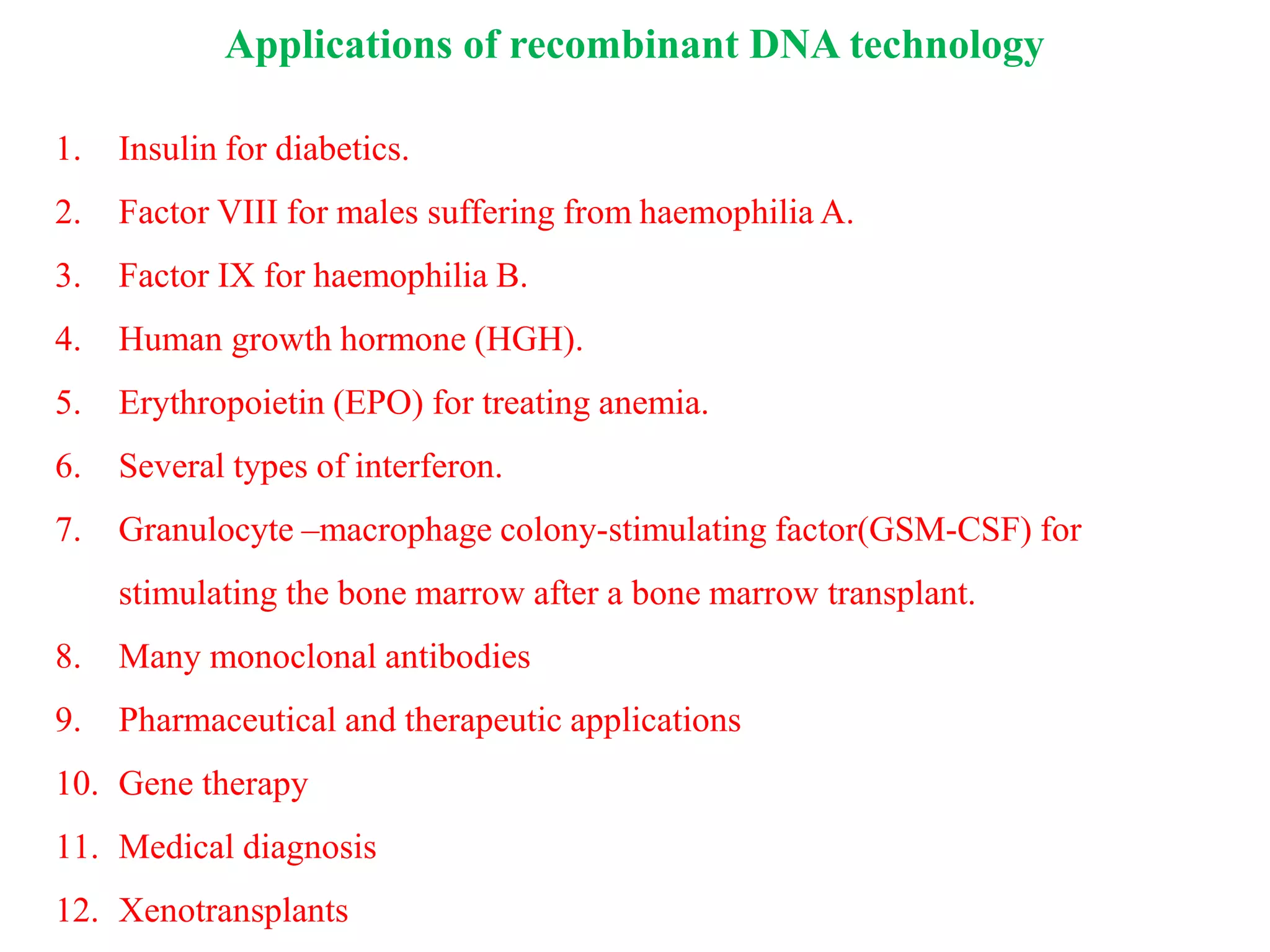
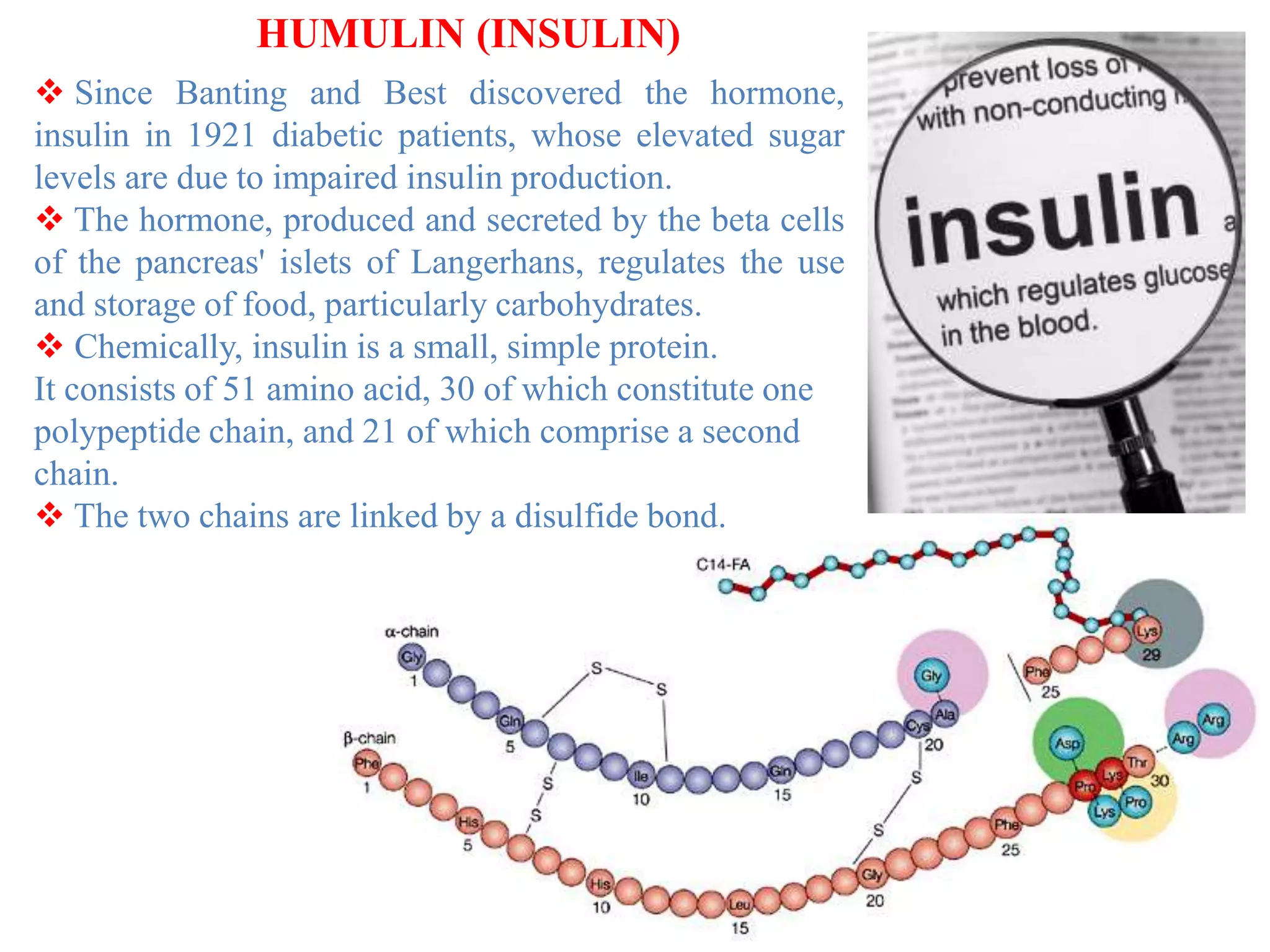
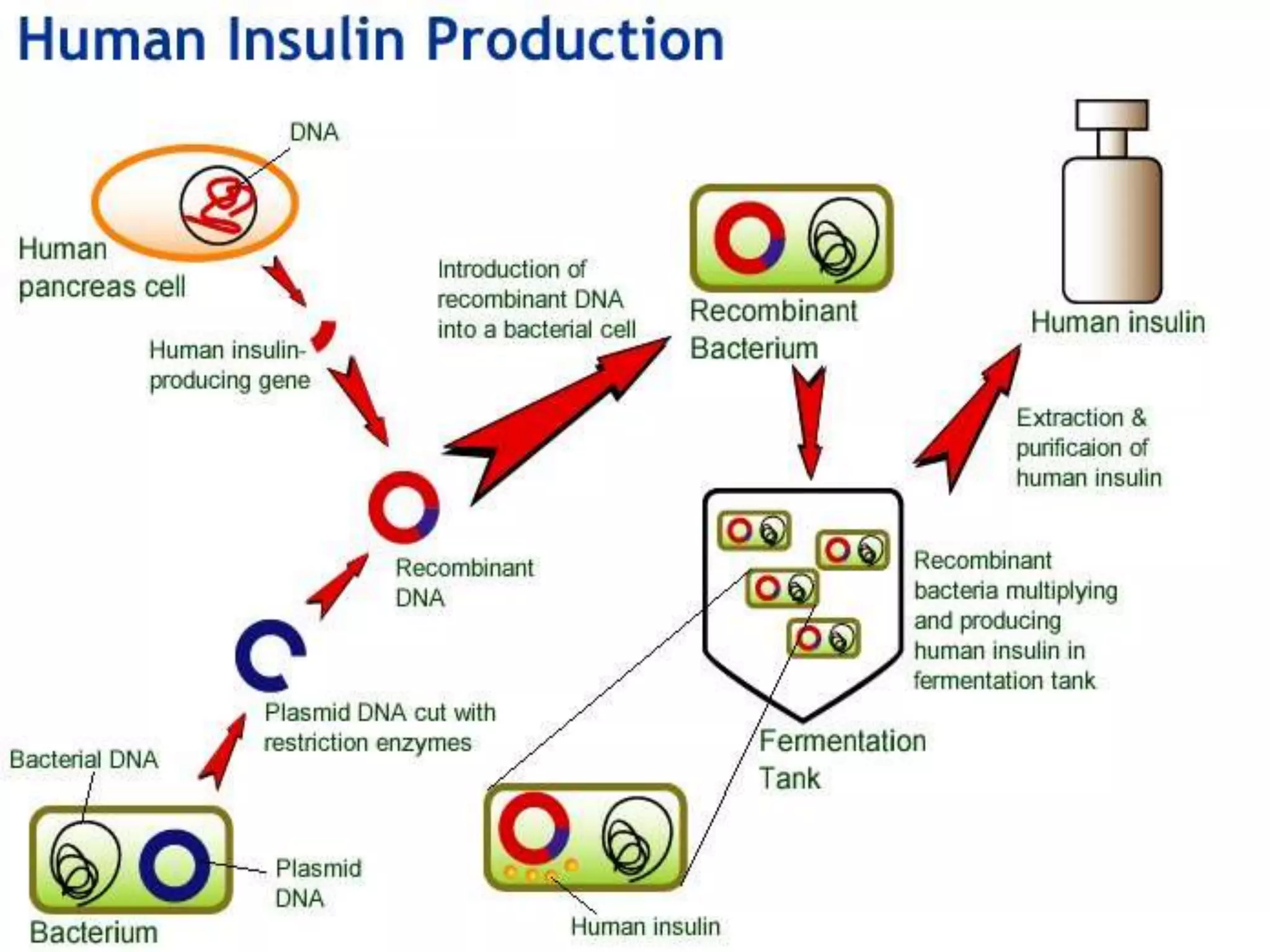
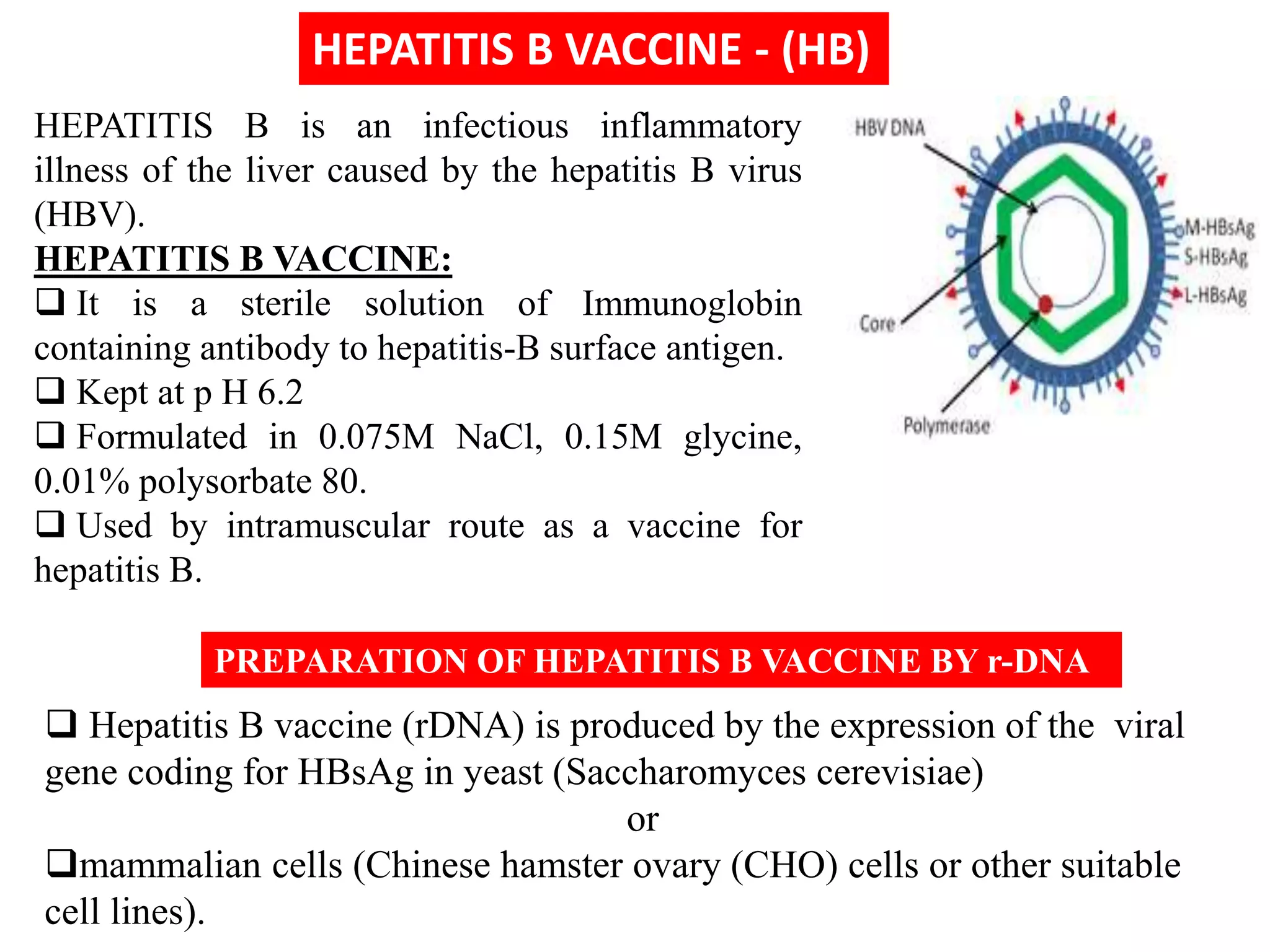
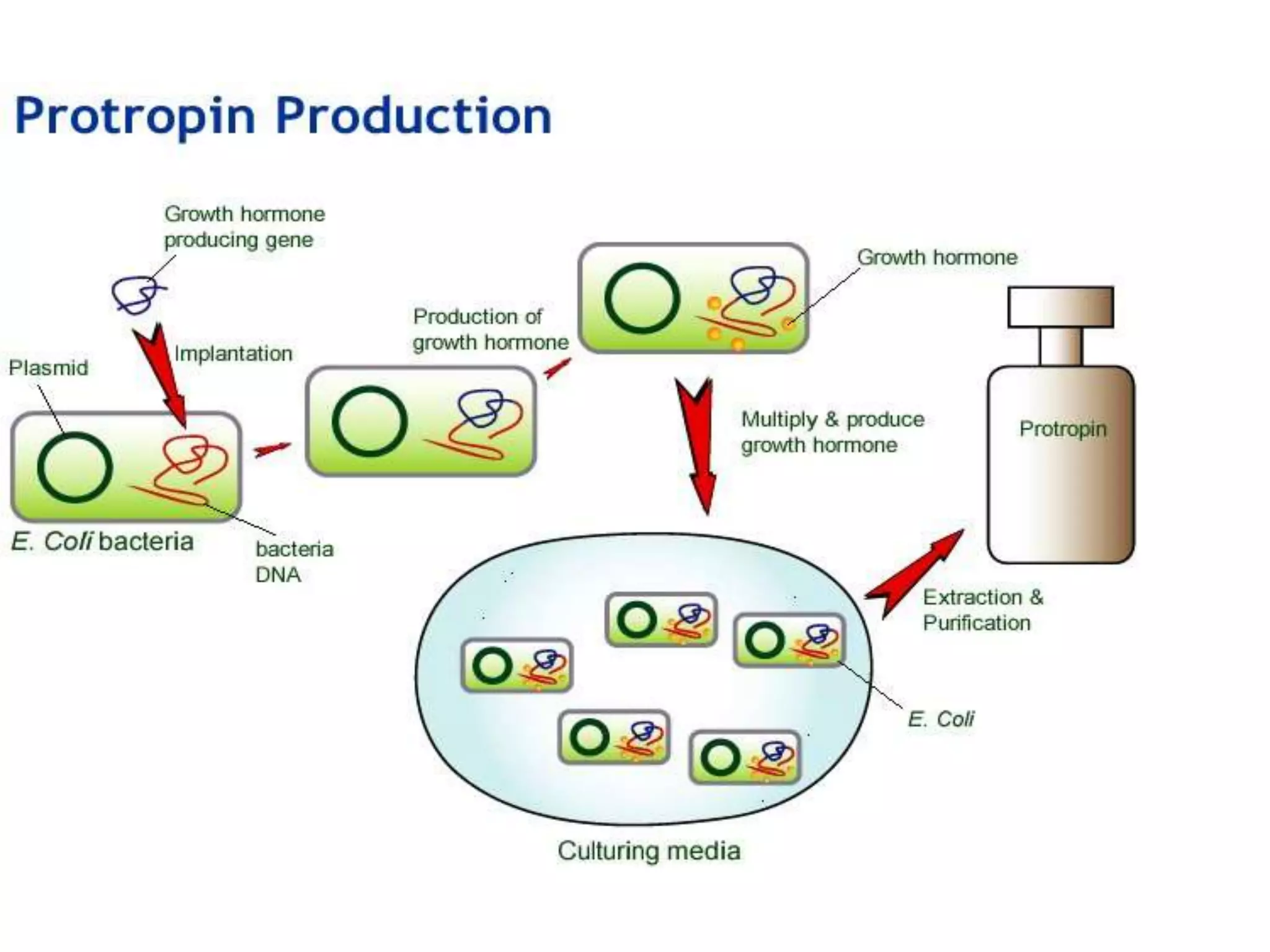
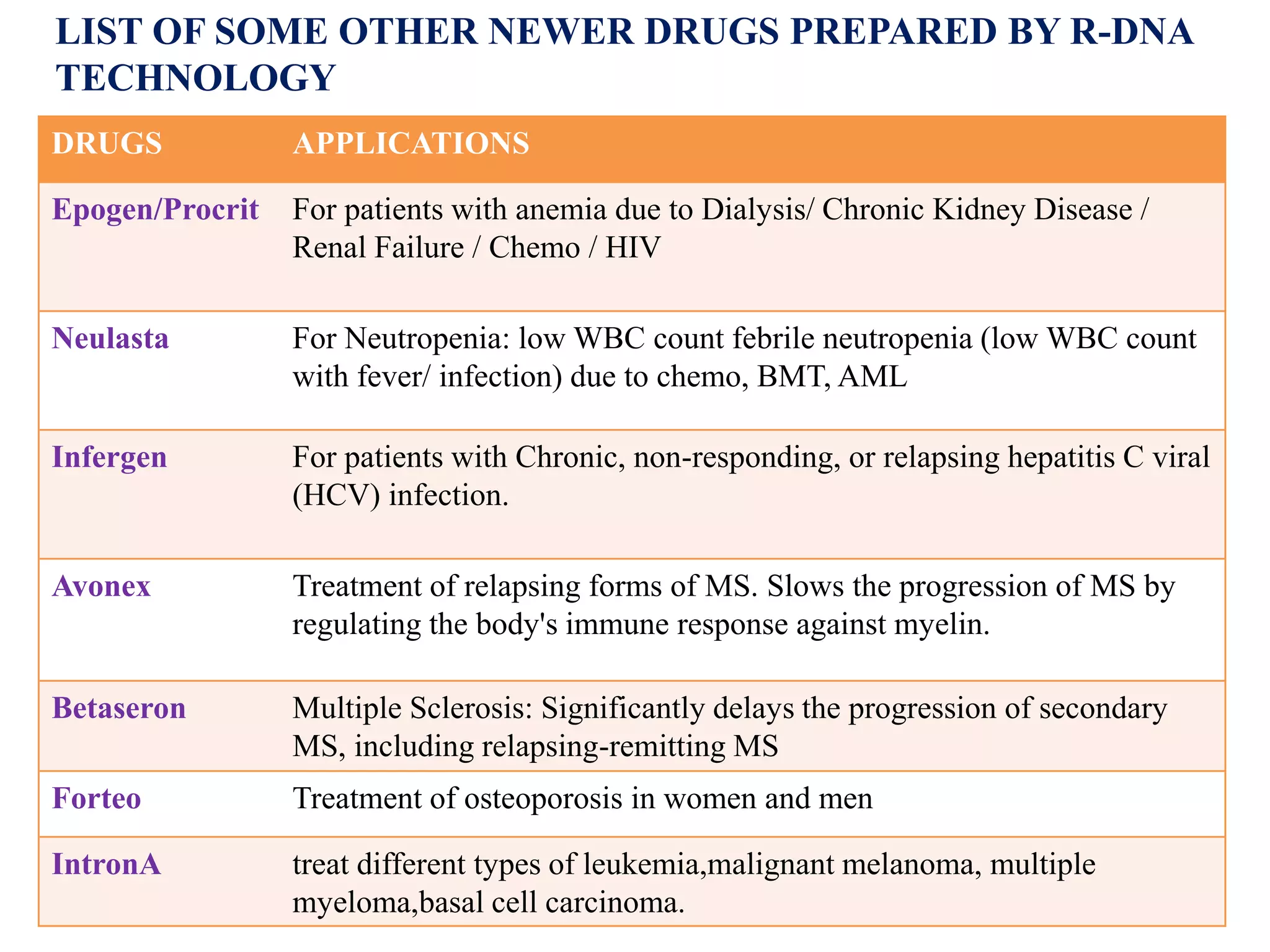
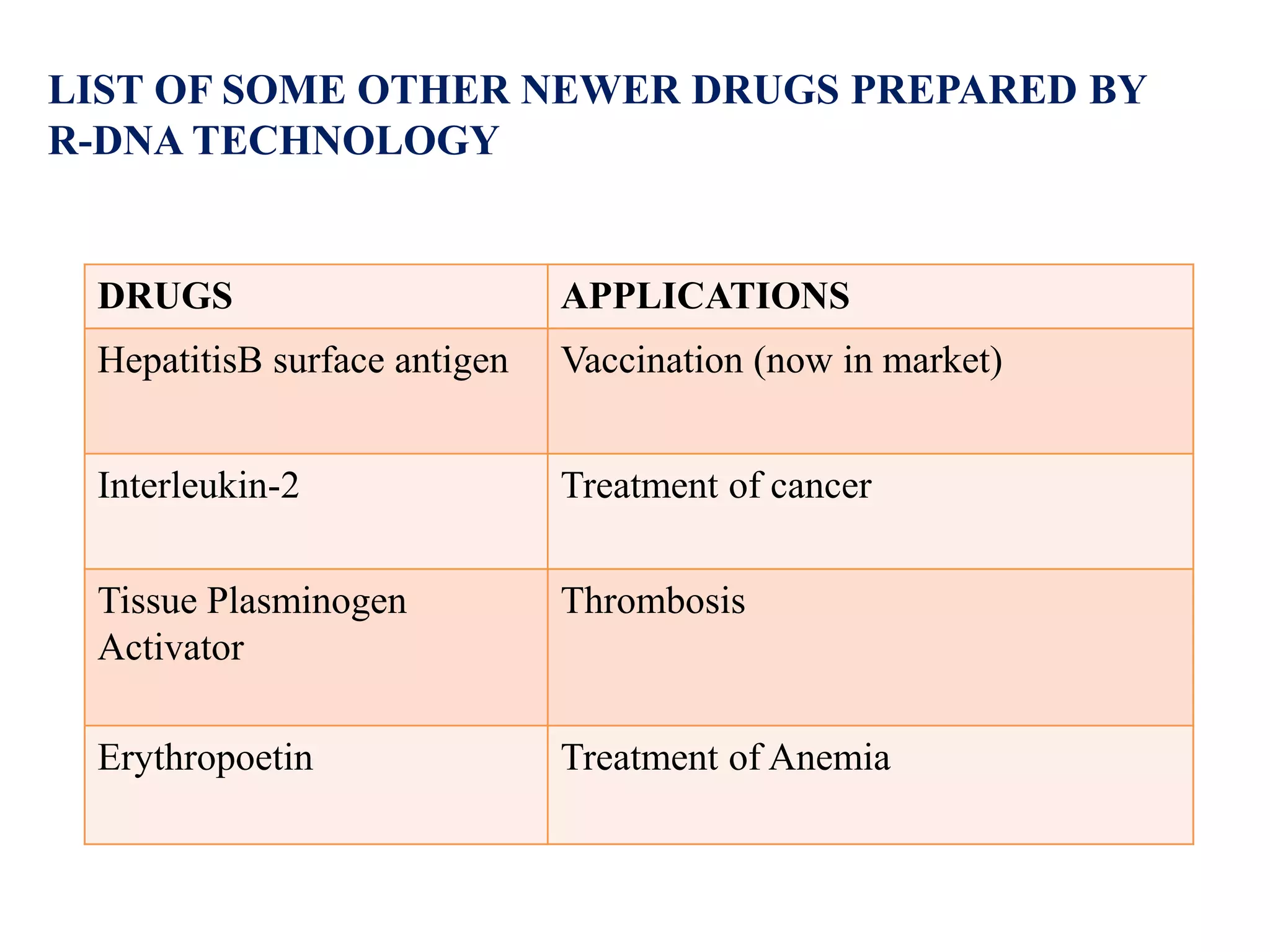
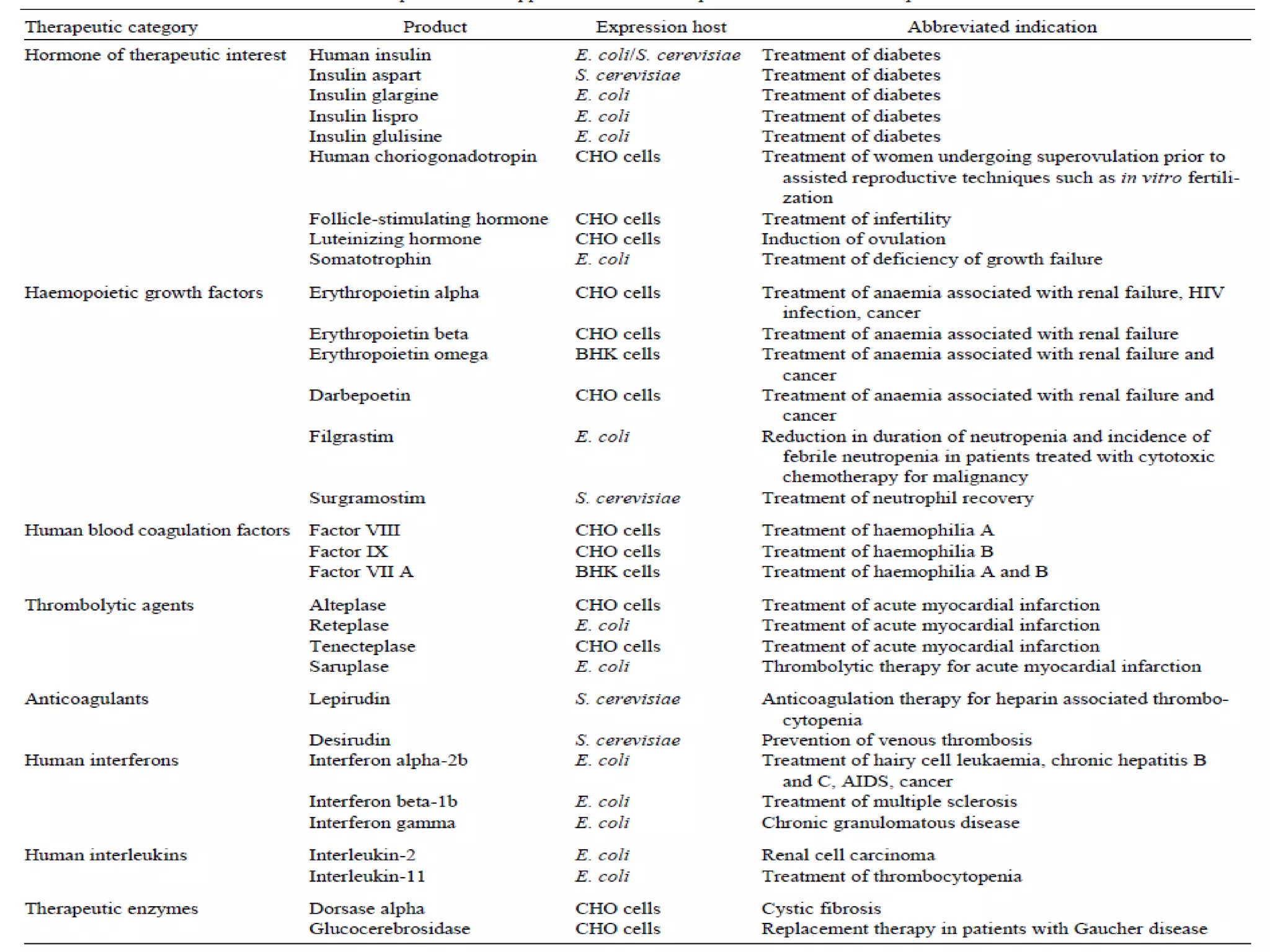
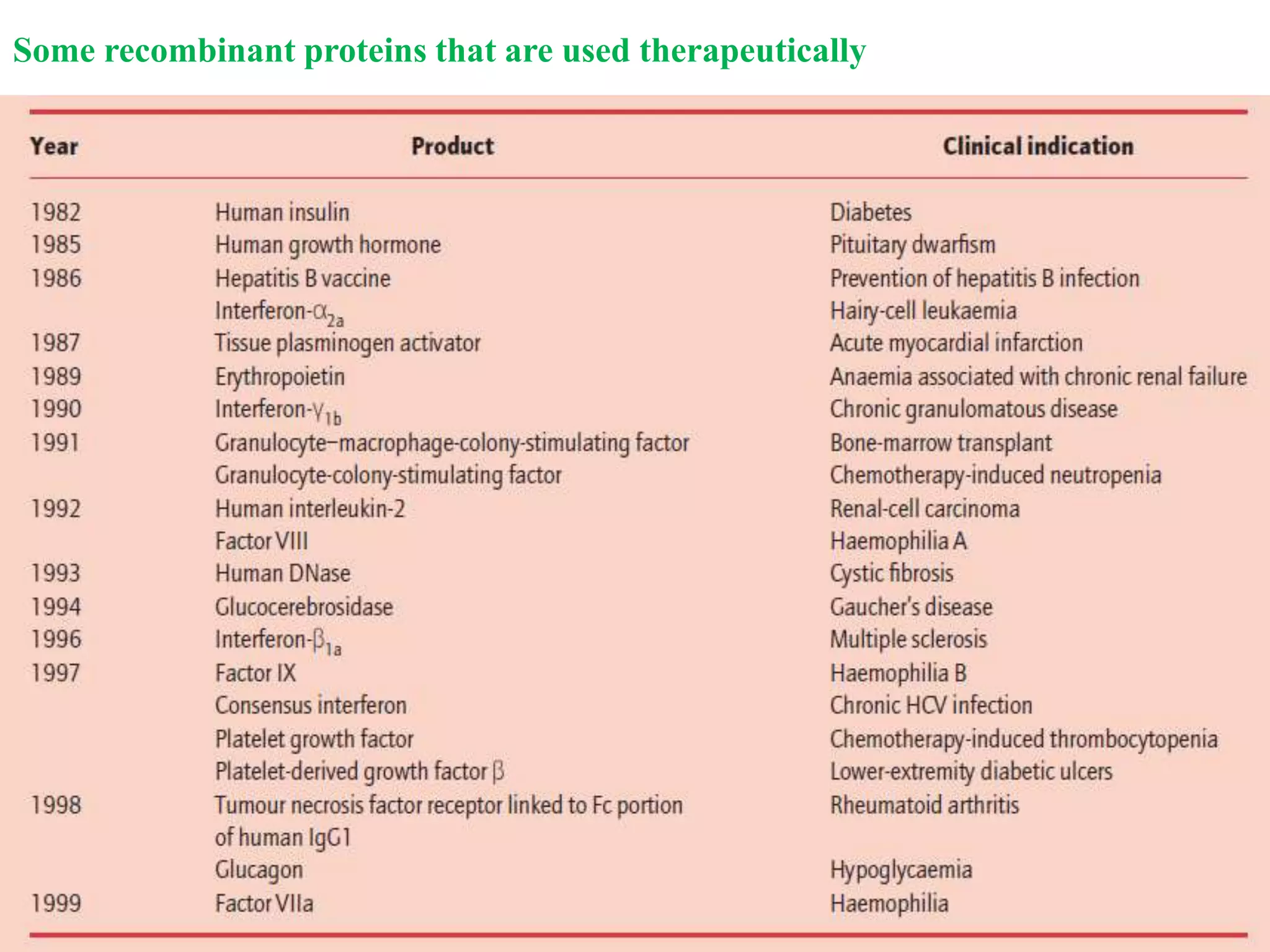
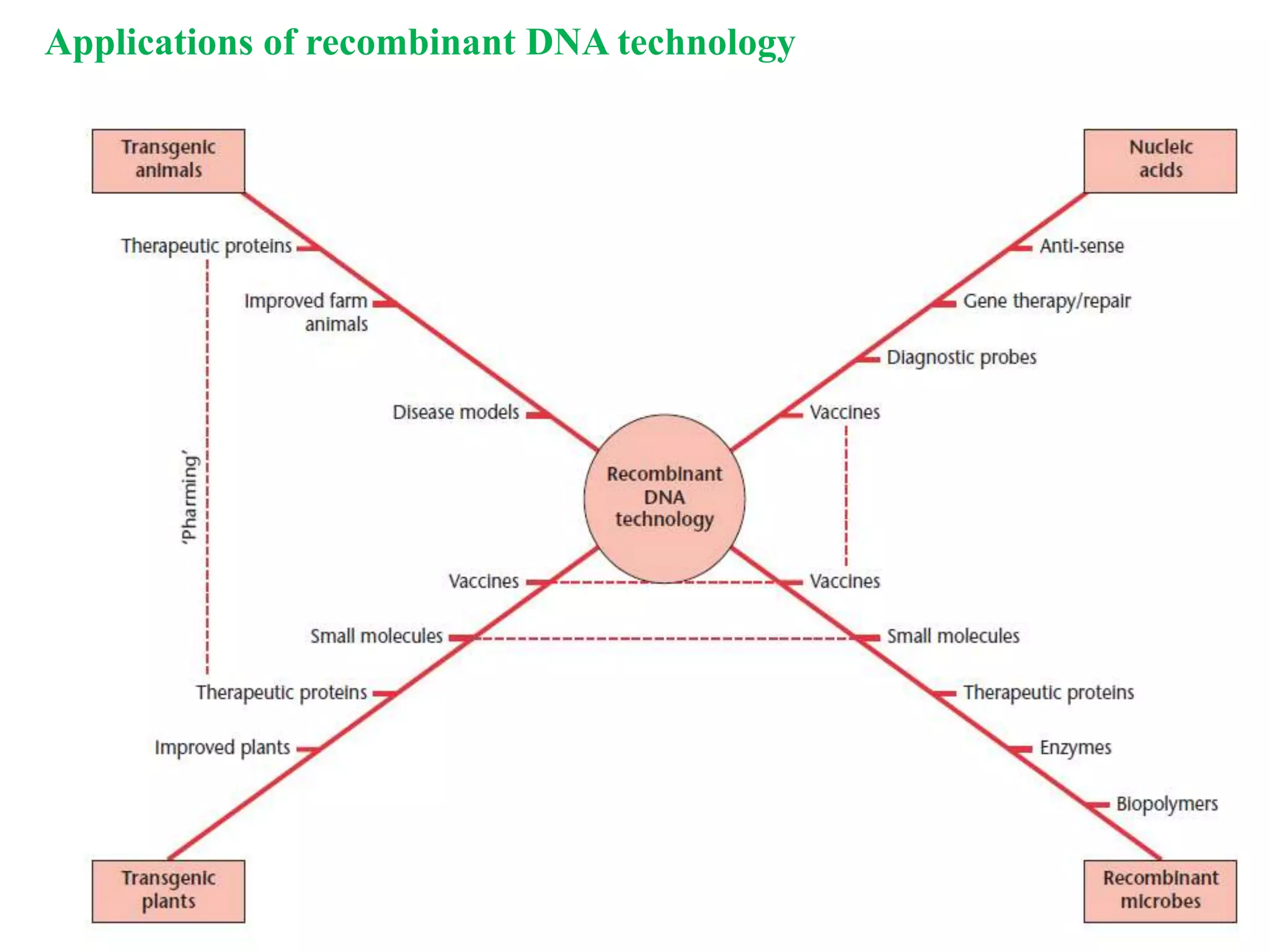
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) technology involves combining DNA molecules from different sources into a single recombinant DNA molecule. This is done using restriction enzymes to cut the DNA at specific sites and DNA ligase to join the fragments. The resulting recombinant DNA can be inserted into a host cell that will replicate it, allowing mass production of useful proteins like insulin, growth hormone, and monoclonal antibodies for therapeutic use. While rDNA technology has generated many medical advances, it also raises safety and ethical concerns that must be carefully considered and addressed.