Embed presentation
Downloaded 313 times


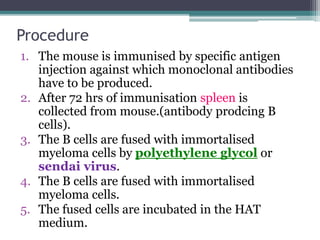

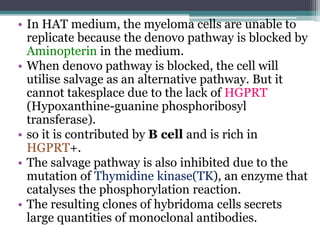
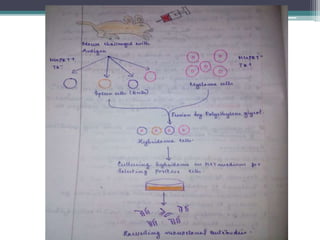

Hybridoma technology is a method for producing monoclonal antibodies by fusing B-lymphocytes with myeloma cells, discovered by G. Kohler and C. Milstein in 1975. The process involves immunizing a mouse, fusing its antibody-producing cells with immortalized cells, and selecting the resulting hybrid cells using HAT medium. This technology has applications in pregnancy detection, cancer diagnosis and treatment, and the development of immunotoxins.






